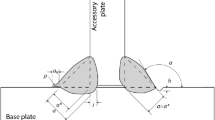
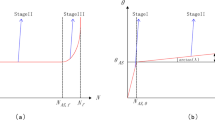
Abstract
Fatigue assessment of welded joint is still far from being completely solved now, since many influencing factors coexist and some important ones should be considered in the developed life prediction models reasonably. Thus, such influencing factors of welded joint fatigue are firstly summarized in this work; and then, the existing life prediction models are reviewed from two aspects, i.e., uniaxial and multiaxial ones; finally, significant conclusions of existing experimental and theoretical researches and some suggestions on improving the fatigue assessment of welded joints, especially for the low-cycle fatigue with the occurrence of ratchetting, are provided.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fricke, W.: IIW Recommendations for the Fatigue Assessment of Welded Structures by Notch Tress Analysis: IIW-2006-09 (2012)
Hobbacher, A.: Recommendations for Fatigue Design of Welded Joints and Components. Springer, Berlin (2015)
Niemi, E., Fricke, W., Maddox, S.J.: Fatigue Analysis of Welded Components: Designer’s Guide to the Structural Hot-Spot Stress Approach. Woodhead Publishing, Sawston (2006)
Casavola, C., Pappalettere, C.: Discussion on local approaches for the fatigue design of welded joints. Int. J. Fatigue 31, 41–49 (2009)
Fricke, W.: Recent developments and future challenges in fatigue strength assessment of welded joints. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C 229, 1224–1239 (2015)
Fricke, W.: Fatigue analysis of welded joints: state of development. Mar. Struct. 16, 185–200 (2003)
Radaj, D.: Design and Analysis of Fatigue Resistant Welded Structures. Elsevier, Amsterdam (1990)
Radaj, D.: Review of fatigue strength assessment of nonwelded and welded structures based on local parameters. Int. J. Fatigue 18, 153–170 (1996)
Radaj, D., Sonsino, C.M., Fricke, W.: Fatigue Assessment of Welded Joints by Local Approaches. Woodhead Publishing, Sawston (2006)
Radaj, D., Sonsino, C.M., Fricke, W.: Recent developments in local concepts of fatigue assessment of welded joints. Int. J. Fatigue 31, 2–11 (2009)
Radaj, D.: State-of-the-art review on the local strain energy density concept and its relation to the J-integral and peak stress method. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 38, 2–28 (2015)
Taylor, D., Barrett, N., Lucano, G.: Some new methods for predicting fatigue in welded joints. Int. J. Fatigue 24, 509–518 (2002)
Maddox, S.: Review of fatigue assessment procedures for welded aluminium structures. Int. J. Fatigue 25, 1359–1378 (2003)
Hobbacher, A.: The new IIW recommendations for fatigue assessment of welded joints and components—a comprehensive code recently updated. Int. J. Fatigue 31, 50–58 (2009)
Susmel, L.: The theory of critical distances: a review of its applications in fatigue. Eng. Fract. Mech. 75, 1706–1724 (2008)
Berto, F., Lazzarin, P.: A review of the volume-based strain energy density approach applied to V-notches and welded structures. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 52, 183–194 (2009)
Fischer, C., Fricke, W., Rizzo, C.M.: Review of the fatigue strength of welded joints based on the notch stress intensity factor and SED approaches. Int. J. Fatigue 84, 59–66 (2016)
Baumgartner, J.: Review and considerations on the fatigue assessment of welded joints using reference radii. Int. J. Fatigue 101, 459–468 (2017)
Bäckström, M., Marquis, G.: A review of multiaxial fatigue of weldments: experimental results, design code and critical plane approaches. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 24, 279–291 (2001)
Sonsino, C.: Multiaxial fatigue assessment of welded joints—recommendations for design codes. Int. J. Fatigue 31, 173–187 (2009)
Pedersen, M.M.: Multiaxial fatigue assessment of welded joints using the notch stress approach. Int. J. Fatigue 83, 269–279 (2016)
Nykanen, T., Marquis, G., Bjork, T.: A simplified fatigue assessment method for high quality welded cruciform joints. Int. J. Fatigue 31, 79–87 (2009)
Benoit, A., Rémy, L., Köster, A., et al.: Experimental investigation of the behavior and the low cycle fatigue life of a welded structure. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 595, 64–76 (2014)
Teng, T.L., Fung, C.P., Chang, P.H.: Effect of weld geometry and residual stresses on fatigue in butt-welded joints. Int. J. Press. Vessels Piping 79, 467–482 (2002)
Lee, C.H., Chang, K.H., Jang, G.C., et al.: Effect of weld geometry on the fatigue life of non-load-carrying fillet welded cruciform joints. Eng. Fail. Anal. 16, 849–855 (2009)
Ye, N., Moan, T.: Improving fatigue life for aluminium cruciform joints by weld toe grinding. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 31, 152–163 (2008)
Shiozaki, T., Yamaguchi, N., Tamai, Y., et al.: Effect of weld toe geometry on fatigue life of lap fillet welded ultra-high strength steel joints. Int. J. Fatigue 116, 409–420 (2018)
Yıldırım, H.C.: Review of fatigue data for welds improved by tungsten inert gas dressing. Int. J. Fatigue 79, 36–45 (2015)
Qiao, J.N., Lu, J.X., Wu, S.K.: Fatigue cracking characteristics of fiber Laser-VPTIG hybrid butt welded 7N01P-T4 aluminum alloy. Int. J. Fatigue 98, 32–40 (2017)
Barsoum, Z., Barsoum, I.: Residual stress effects on fatigue life of welded structures using LEFM. Eng. Fail. Anal. 16, 449–467 (2009)
Do, V.N.V., Lee, C.H., Chang, K.H.: High cycle fatigue analysis in presence of residual stresses by using a continuum damage mechanics model. Int. J. Fatigue 70, 51–62 (2015)
Zhan, Z., Hu, W., Shen, F., et al.: Fatigue life calculation for a specimen with an impact pit considering impact damage, residual stress relaxation and elastic-plastic fatigue damage. Int. J. Fatigue 96, 208–223 (2017)
Wang, X., Meng, Q., Hu, W.: Fatigue life prediction for butt-welded joints considering weld-induced residual stresses and initial damage, relaxation of residual stress, and elasto-plastic fatigue damage. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 42, 1373–1386 (2019)
Liu, Z.C., Jiang, C., Li, B.C., et al.: A residual stress dependent multiaxial fatigue life model of welded structures. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 41, 300–313 (2018)
Harati, E., Karlsson, L., Svensson, L.E., et al.: The relative effects of residual stresses and weld toe geometry on fatigue life of weldments. Int. J. Fatigue 77, 160–165 (2015)
Cheng, X.: Residual stress modification by post-weld treatment and its beneficial effect on fatigue strength of welded structures. Int. J. Fatigue 25, 1259–1269 (2003)
Sidhom, N., Laamouri, A., Fathallah, R., et al.: Fatigue strength improvement of 5083 H11 Al-alloy T-welded joints by shot peening: experimental characterization and predictive approach. Int. J. Fatigue 27, 729–745 (2005)
Pavan, M., Furfari, D., Ahmad, B., et al.: Fatigue crack growth in a laser shock peened residual stress field. Int. J. Fatigue 123, 157–167 (2019)
Yildirim, H.C., Marquis, G.B.: Fatigue strength improvement factors for high strength steel welded joints treated by high frequency mechanical impact. Int. J. Fatigue 44, 168–176 (2012)
Sonsino, C.M.: Effect of residual stresses on the fatigue behaviour of welded joints depending on loading conditions and weld geometry. Int. J. Fatigue 31, 88–101 (2009)
Kang, H.T., Lee, Y.L., Sun, X.J.: Effects of residual stress and heat treatment on fatigue strength of weldments. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 497, 37–43 (2008)
Wang, D., Zhang, H., Gong, B., et al.: Residual stress effects on fatigue behaviour of welded T-joint: a finite fracture mechanics approach. Mater. Des. 91, 211–217 (2016)
Kainuma, S., Mori, T.: A study on fatigue crack initiation point of load-carrying fillet welded cruciform joints. Int. J. Fatigue 30, 1669–1677 (2008)
Gu, C., Lian, J., Bao, Y., et al.: Microstructure-based fatigue modelling with residual stresses: prediction of the microcrack initiation around inclusions. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 751, 133–141 (2019)
Cui, C., Zhang, Q., Bao, Y., et al.: Fatigue life evaluation of welded joints in steel bridge considering residual stress. J. Constr. Steel Res. 153, 509–518 (2019)
McClung, R.C.: A literature survey on the stability and significance of residual stresses during fatigue. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 30, 173–205 (2007)
Xie, X., Jiang, W., Luo, Y., et al.: A model to predict the relaxation of weld residual stress by cyclic load: experimental and finite element modeling. Int. J. Fatigue 95, 293–301 (2017)
Liljedahl, C.D.M., Brouard, J., Zanellato, O., et al.: Weld residual stress effects on fatigue crack growth behaviour of aluminium alloy 2024-T351. Int. J. Fatigue 31, 1081–1088 (2009)
Elber, W.: The significance of fatigue crack closure. In: Damage Tolerance in Aircraft Structures, ASTM STP 486. American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia, pp 230–242 (1971)
Servetti, G., Zhang, X.: Predicting fatigue crack growth rate in a welded butt joint: the role of effective R ratio in accounting for residual stress effect. Eng. Fract. Mech. 76, 1589–1602 (2009)
Ceschini, L., Boromei, I., Minak, G., et al.: Microstructure, tensile and fatigue properties of AA6061/20vol.%Al2O3p friction stir welded joints. Compos. A 38, 1200–1210 (2007)
Kchaou, Y., Haddar, N., Hénaff, G., et al.: Microstructural, compositional and mechanical investigation of Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW) welded superaustenitic UNS N08028 (Alloy 28) stainless steel. Mater. Des. 63, 278–285 (2014)
Besel, Y., Besel, M., Alfaro Mercado, U., et al.: Influence of local fatigue damage evolution on crack initiation behavior in a friction stir welded Al–Mg–Sc alloy. Int. J. Fatigue 99, 151–162 (2017)
Cortés, R., Rodríguez, N.K., Ambriz, R.R., et al.: Fatigue and crack growth behavior of Inconel 718-AL6XN dissimilar welds. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 745, 20–30 (2019)
Velu, M., Bhat, S.: Experimental investigations of fracture and fatigue crack growth of copper-steel joints arc welded using nickel-base filler. Mater. Des. 67, 244–260 (2015)
Wang, X., Shao, C., Liu, X., et al.: Transition and fracture shift behavior in LCF test of dissimilar welded joint at elevated temperature. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 34, 720–731 (2018)
Kermanidis, A.T., Tzamtzis, A.: An experimental approach for estimating the effect of heat affected zone (HAZ) microstructural gradient on fatigue crack growth rate in aluminum alloy FSW. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 691, 110–120 (2017)
Chen, R., Jiang, P., Shao, X., et al.: Analysis of crack tip transformation zone in austenitic stainless steel laser-MIG hybrid welded joint. Mater. Charact. 132, 260–268 (2017)
Liu, Z., Guo, X., Cui, H., et al.: Role of misorientation in fatigue crack growth behavior for NG-TIG welded joint of Ni-based alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 710, 151–163 (2018)
Oh, J., Kim, N.J., Lee, S., et al.: Correlation of fatigue properties and microstructure in investment cast Ti-6Al-4V welds. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 340, 232–242 (2003)
Balasubramanian, T.S., Balasubramanian, V., Muthu Manickam, M.A.: Fatigue crack growth behaviour of gas tungsten arc, electron beam and laser beam welded Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Mater. Des. 32, 4509–4520 (2011)
Hu, Y.N., Wu, S.C., Song, Z., et al.: Effect of microstructural features on the failure behavior of hybrid laser welded AA7020. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 41, 2010–2023 (2018)
Yuan, H., Zhang, W., Castelluccio, G.M., et al.: Microstructure-sensitive estimation of small fatigue crack growth in bridge steel welds. Int. J. Fatigue 112, 183–197 (2018)
Suresh, S., Ritchie, R.O.: Propagation of short fatigue cracks. Int. Met. Rev. 29, 445–475 (1984)
Zerbst, U., Ainsworth, R.A., Beier, H.T., et al.: Review on fracture and crack propagation in weldments—a fracture mechanics perspective. Eng. Fract. Mech. 132, 200–276 (2014)
Shao, C., Cui, H., Lu, F., et al.: Quantitative relationship between weld defect characteristic and fatigue crack initiation life for high-cycle fatigue property. Int. J. Fatigue 123, 238–247 (2019)
Lin, S., Deng, Y.L., Tang, J.G., et al.: Microstructures and fatigue behavior of metal-inert-gas-welded joints for extruded Al–Mg–Si alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 745, 63–73 (2019)
Ohta, A., Sasaki, E., Nihei, M., et al.: Fatigue crack propagation rates and threshold stress intensity factors for welded joints of HT80 steel at several stress ratios. Int. J. Fatigue 4, 233–237 (1982)
Nykänen, T., Björk, T.: Assessment of fatigue strength of steel butt-welded joints in as-welded condition—alternative approaches for curve fitting and mean stress effect analysis. Mar. Struct. 44, 288–310 (2015)
Karakas, Ö.: Consideration of mean-stress effects on fatigue life of welded magnesium joints by the application of the Smith–Watson–Topper and reference radius concepts. Int. J. Fatigue 49, 1–17 (2013)
Skriko, T., Ghafouri, M., Björk, T.: Fatigue strength of TIG-dressed ultra-high-strength steel fillet weld joints at high stress ratio. Int. J. Fatigue 94, 110–120 (2017)
Gaur, V., Enoki, M., Okada, T., et al.: A study on fatigue behavior of MIG-welded Al–Mg alloy with different filler-wire materials under mean stress. Int. J. Fatigue 107, 119–129 (2018)
Shao, C., Lu, F., Cui, H., et al.: Characterization of high-gradient welded microstructure and its failure mode in fatigue test. Int. J. Fatigue 113, 1–10 (2018)
Baumgartner, J.: Enhancement of the fatigue strength assessment of welded components by consideration of mean and residual stresses in the crack initiation and propagation phases. Weld. World 60, 547–558 (2016)
Mikkola, E., Murakami, Y., Marquis, G.: Equivalent crack approach for fatigue life assessment of welded joints. Eng. Fract. Mech. 149, 144–155 (2015)
Sonsino, C.M., Fricke, W., Bruyne, F.D., et al.: Notch stress concepts for the fatigue assessment of welded joints—background and applications. Int. J. Fatigue 34, 2–16 (2012)
Frank, D., Remes, H., Romanoff, J.: On the slope of the fatigue resistance curve for laser stake-welded T-joints. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 36, 1336–1351 (2013)
Wiebesiek, J., Störzel, K., Bruder, T., et al.: Multiaxial fatigue behaviour of laserbeam-welded thin steel and aluminium sheets under proportional and non-proportional combined loading. Int. J. Fatigue 33, 992–1005 (2011)
Sonsino, C.M.: Influence of material’s ductility and local deformation mode on multiaxial fatigue response. Int. J. Fatigue 33, 930–947 (2011)
Frendo, F., Bertini, L.: Fatigue resistance of pipe-to-plate welded joint under in-phase and out-of-phase combined bending and torsion. Int. J. Fatigue 79, 46–53 (2015)
Kueppers, M., Sonsino, C.M.: Critical plane approach for the assessment of the fatigue behaviour of welded aluminium under multiaxial loading. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 26, 507–513 (2003)
Proton, V., Alexis, J., Andrieu, E., et al.: Characterisation and understanding of the corrosion behaviour of the nugget in a 2050 aluminium alloy Friction Stir Welding joint. Corros. Sci. 73, 130–142 (2013)
Price, J.W.H., Ziara-Paradowska, A., Joshi, S., et al.: Comparison of experimental and theoretical residual stresses in welds: the issue of gauge volume. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 50, 513–521 (2008)
Yang, S., Yang, H., Liu, G., et al.: Approach for fatigue damage assessment of welded structure considering coupling effect between stress and corrosion. Int. J. Fatigue 88, 88–95 (2016)
Mutombo, K., Toit, M.D.: Corrosion fatigue behaviour of aluminium alloy 6061-T651 welded using fully automatic gas metal arc welding and ER5183 filler alloy. Int. J. Fatigue 33, 1539–1547 (2011)
Tao, J., Hu, S., Ji, L.: Effect of trace solute hydrogen on the fatigue life of electron beam welded Ti-6Al-4V alloy joints. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 684, 542–551 (2017)
Mehmanparast, A., Brennan, F., Tavares, I.: Fatigue crack growth rates for offshore wind monopile weldments in air and seawater: SLIC inter-laboratory test results. Mater. Des. 114, 494–504 (2017)
Wang, L., Hui, L., Zhou, S., et al.: Effect of corrosive environment on fatigue property and crack propagation behavior of Al 2024 friction stir weld. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 26, 2830–2837 (2016)
Fricke, W., Kahl, A.: Comparison of different structural stress approaches for fatigue assessment of welded ship structures. Mar. Struct. 18, 473–488 (2005)
Shen, W., Yan, R., Barltrop, N., et al.: A method of determining structural stress for fatigue strength evaluation of welded joints based on notch stress strength theory. Int. J. Fatigue 90, 87–98 (2016)
Dong, P.: A structural stress definition and numerical implementation for fatigue analysis of welded joints. Int. J. Fatigue 23, 865–876 (2001)
Xiao, Z., Yamada, K.: A method of determining geometric stress for fatigue strength evaluation of steel welded joints. Int. J. Fatigue 26, 1277–1293 (2004)
Remes, H., Fricke, W.: Influencing factors on fatigue strength of welded thin plates based on structural stress assessment. Weld. World 58, 915–923 (2014)
Liu, G., Liu, Y., Huang, Y.: A novel structural stress approach for multiaxial fatigue strength assessment of welded joints. Int. J. Fatigue 63, 171–182 (2014)
Poutiainen, I., Marquis, G.: A fatigue assessment method based on weld stress. Int. J. Fatigue 28, 1037–1046 (2006)
Zhang, G.: Method of effective stress for fatigue: part I—a general theory. Int. J. Fatigue 37, 17–23 (2012)
Neuber, H.: Theory of Notch Stresses: Principles for Exact Calculation of Strength with Reference to Structural Form and Material, p. 292. Springer, Berlin (1958)
Peterson, R.: Notch sensitivity. In: Sines, G., Waisman, J.L. (eds.) Metal Fatigue, pp. 293–306. McGraw Hill, New York (1959)
Taylor, D.: The theory of critical distances. Eng. Fract. Mech. 75, 1696–1705 (2008)
Radaj, D., Lazzarin, P., Berto, F.: Generalised Neuber concept of fictitious notch rounding. Int. J. Fatigue 51, 105–115 (2013)
Zhang, G., Sonsino, C.M., Sundermeier, R.: Method of effective stress for fatigue: part II—applications to V-notches and seam welds. Int. J. Fatigue 37, 24–40 (2012)
Karakaş, Ö.: Application of Neuber’s effective stress method for the evaluation of the fatigue behaviour of magnesium welds. Int. J. Fatigue 101, 115–126 (2017)
Liinalampi, S., Remes, H., Lehto, P., et al.: Fatigue strength analysis of laser-hybrid welds in thin plate considering weld geometry in microscale. Int. J. Fatigue 87, 143–152 (2016)
Berto, F., Lazzarin, P., Radaj, D.: Fictitious notch rounding concept applied to sharp V-notches: evaluation of the microstructural support factor for different failure hypotheses. Eng. Fract. Mech. 76, 1151–1175 (2009)
Pedersen, M.M., Mouritsen, O.Ø., Hansen, M.R., et al.: Re-analysis of fatigue data for welded joints using the notch stress approach. Int. J. Fatigue 32, 1620–1626 (2010)
Tovo, R., Livieri, P.: An implicit gradient application to fatigue of sharp notches and weldments. Eng. Fract. Mech. 74, 515–526 (2007)
Cristofori, A., Livieri, P., Tovo, R.: An application of the implicit gradient method to welded structures under multiaxial fatigue loadings. Int. J. Fatigue 31, 12–19 (2009)
Taylor, D., Hoey, D.: High cycle fatigue of welded joints: the TCD experience. Int. J. Fatigue 31, 20–27 (2009)
Karakaş, Ö., Zhang, G., Sonsino, C.M.: Critical distance approach for the fatigue strength assessment of magnesium welded joints in contrast to Neuber’s effective stress method. Int. J. Fatigue 112, 21–35 (2018)
Santus, C., Taylor, D., Benedetti, M.: Determination of the fatigue critical distance according to the line and the point methods with rounded V-notched specimen. Int. J. Fatigue 106, 208–218 (2018)
Nisitani, H., Teranishi, T.: KI of a circumferential crack emanating from an ellipsoidal cavity obtained by the crack tip stress method in FEM. Eng. Fract. Mech. 71, 579–585 (2004)
Meneghetti, G., Lazzarin, P.: Significance of the elastic peak stress evaluated by FE analyses at the point of singularity of sharp V-notched components. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 30, 95–106 (2007)
Meneghetti, G.: The peak stress method applied to fatigue assessments of steel and aluminium fillet-welded joints subjected to mode I loading. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 31, 346–369 (2008)
Meneghetti, G., Guzzella, C., Atzori, B.: The peak stress method combined with 3D finite element models for fatigue assessment of toe and root cracking in steel welded joints subjected to axial or bending loading. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 37, 722–739 (2014)
Meneghetti, G., Marchi, A.D., Campagnolo, A.: Assessment of root failures in tube-to-flange steel welded joints under torsional loading according to the Peak Stress Method. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 83, 19–30 (2016)
Meneghetti, G., Campagnolo, A., Babini, V., et al.: Multiaxial fatigue assessment of welded steel details according to the peak stress method: industrial case studies. Int. J. Fatigue 125, 362–380 (2019)
Casavola, C., Nobile, R., Pappalettere, C.: A local strain method for the evaluation of welded joints fatigue resistance: the case of thin main-plates thickness. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 28, 759–767 (2005)
Dong, P., Pei, X., Xing, S., et al.: A structural strain method for low-cycle fatigue evaluation of welded components. Int. J. Press. Vessels Pip 119, 39–51 (2014)
Pei, X., Dong, P.: An analytically formulated structural strain method for fatigue evaluation of welded components incorporating nonlinear hardening effects. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 42, 239–255 (2018)
Pei, X., Dong, P., Xing, S.: A structural strain parameter for a unified treatment of fatigue behaviors of welded components. Int. J. Fatigue 124, 444–460 (2019)
Savaidis, G., Malikoutsakis, M.: Advanced notch strain based calculation of S–N curves for welded components. Int. J. Fatigue 83, 84–92 (2016)
Sołtysiak, R., Boroński, D.: Strain analysis at notch root in laser welded samples using material properties of individual weld zones. Int. J. Fatigue 74, 71–80 (2015)
Saiprasertkit, K., Hanji, T., Miki, C.: Fatigue strength assessment of load-carrying cruciform joints with material mismatching in low- and high-cycle fatigue regions based on the effective notch concept. Int. J. Fatigue 40, 120–128 (2012)
Lazzarin, P., Tovo, R.: A notch intensity factor approach to the stress analysis of welds. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 21, 1089–1103 (1998)
Atzori, B., Lazzarin, P., Meneghetti, G.: Fatigue strength assessment of welded joints: from the integration of Paris’ law to a synthesis based on the notch stress intensity factors of the uncracked geometries. Eng. Fract. Mech. 75, 364–378 (2008)
Atzori, B., Lazzarin, P., Tovo, R.: From a local stress approach to fracture mechanics: a comprehensive evaluation of the fatigue strength of welded joints. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 22, 369–381 (1999)
Lazzarin, P., Livieri, P.: Notch stress intensity factors and fatigue strength of aluminium and steel welded joints. Int. J. Fatigue 23, 225–232 (2001)
Radaj, D.: State-of-the-art review on extended stress intensity factor concepts. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 37, 1–28 (2014)
Livieri, P., Lazzarin, P.: Fatigue strength of steel and aluminium welded joints based on generalised stress intensity factors and local strain energy values. Int. J. Fract. 133, 247–276 (2005)
Atzori, B., Lazzarin, P., Tovo, R.: Stress field parameters to predict the fatigue strength of notched components. J. Strain Anal. Eng. Des. 34, 437–453 (1999)
Meneghetti, G., Guzzella, C.: The peak stress method to estimate the mode I notch stress intensity factor in welded joints using three-dimensional finite element models. Eng. Fract. Mech. 115, 154–171 (2014)
Lazzarin, P., Berto, F., Zappalorto, M.: Rapid calculations of notch stress intensity factors based on averaged strain energy density from coarse meshes: theoretical bases and applications. Int. J. Fatigue 32, 1559–1567 (2010)
Lepore, M., Solberg, K., Berto, F.: A comparison between numerical and approximate methods for rapid calculation of NSIFs. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 101, 67–79 (2019)
Lazzarin, P., Lassen, T., Livieri, P.: A notch stress intensity approach applied to fatigue life predictions of welded joints with different local toe geometry. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 26, 49–58 (2003)
Lazzarin, P., Zambardi, R.: A finite-volume-energy based approach to predict the static and fatigue behavior of components with sharp V-shaped notches. Int. J. Fract. 112, 275–298 (2001)
Lazzarin, P., Berto, F.: Some expressions for the strain energy in a finite volume surrounding the root of blunt V-notches. Int. J. Fract. 135, 161–185 (2005)
Lazzarin, P., Livieri, P., Berto, F., et al.: Local strain energy density and fatigue strength of welded joints under uniaxial and multiaxial loading. Eng. Fract. Mech. 75, 1875–1889 (2008)
Berto, F., Vinogradov, A., Filippi, S.: Application of the strain energy density approach in comparing different design solutions for improving the fatigue strength of load carrying shear welded joints. Int. J. Fatigue 101, 371–384 (2017)
Lazzarin, P., Berto, F., Gomez, F.J., et al.: Some advantages derived from the use of the strain energy density over a control volume in fatigue strength assessments of welded joints. Int. J. Fatigue 30, 1345–1357 (2008)
Meneghetti, G., Campagnolo, A., Berto, F., et al.: Averaged strain energy density evaluated rapidly from the singular peak stresses by FEM: cracked components under mixed-mode (I + II) loading. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 79, 113–124 (2015)
Song, W., Liu, X., Razavi, S.M.J.: Fatigue assessment of steel load-carrying cruciform welded joints by means of local approaches. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 41, 2598–2613 (2018)
Fischer, C., Fricke, W., Rizzo, C.M.: Experiences and recommendations for numerical analyses of notch stress intensity factor and averaged strain energy density. Eng. Fract. Mech. 165, 98–113 (2016)
Radaj, D., Berto, F., Lazzarin, P.: Local fatigue strength parameters for welded joints based on strain energy density with inclusion of small-size notches. Eng. Fract. Mech. 76, 1109–1130 (2009)
Varvani-Farahani, A.: A new energy-critical plane parameter for fatigue life assessment of various metallic materials subjected to in-phase and out-of-phase multiaxial fatigue loading conditions. Int. J. Fatigue 22, 295–305 (2000)
Pakandam, F., Varvani-Farahani, A.: Fatigue damage assessment of various welded joints under uniaxial loading based on energy methods. Int. J. Fatigue 33, 519–528 (2011)
Song, W., Liu, X., Berto, F., et al.: Energy-based low cycle fatigue indicator prediction of non-load-carrying cruciform welded joints. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 96, 247–261 (2018)
Feng, L., Qian, X.: A hot-spot energy indicator for welded plate connections under cyclic axial loading and bending. Eng. Struct. 147, 598–612 (2017)
Shen, F., Zhao, B., Li, L., et al.: Fatigue damage evolution and lifetime prediction of welded joints with the consideration of residual stresses and porosity. Int. J. Fatigue 103, 272–279 (2017)
Zhang, W., Jiang, W., Zhao, X., et al.: Fatigue life of a dissimilar welded joint considering the weld residual stress: experimental and finite element simulation. Int. J. Fatigue 109, 182–190 (2018)
Chaboche, J.L., Lesne, P.M.: A non-linear continuous fatigue damage model. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 11, 1–17 (1988)
Jie, Z., Li, Y., Wei, X., et al.: Fatigue life prediction of welded joints with artificial corrosion pits based on continuum damage mechanics. J. Constr. Steel Res. 148, 542–550 (2018)
Xiao, Y.C., Li, S., Gao, Z.: A continuum damage mechanics model for high cycle fatigue. Int. J. Fatigue 20, 503–508 (1998)
Kintzel, O., Khan, S., Mosler, J.: A novel isotropic quasi-brittle damage model applied to LCF analyses of Al2024. Int. J. Fatigue 32, 1948–1959 (2010)
Al-Mukhtar, A.M., Biermann, H., Hübner, P., et al.: Determination of some parameters for fatigue life in welded joints using fracture mechanics method. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 19, 1225–1234 (2010)
Zerbst, U., Madia, M.: Fracture mechanics based assessment of the fatigue strength: approach for the determination of the initial crack size. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 38, 1066–1075 (2015)
Zong, L., Shi, G., Wang, Y.Q., et al.: Fatigue assessment on butt welded splices in plates of different thicknesses. J. Constr. Steel Res. 129, 93–100 (2017)
Hoh, H.J., Pang, J.H.L., Tsang, K.S.: Stress intensity factors for fatigue analysis of weld toe cracks in a girth-welded pipe. Int. J. Fatigue 87, 279–287 (2016)
Zong, L., Shi, G., Wang, Y.Q., et al.: Investigation on fatigue behaviour of load-carrying fillet welded joints based on mix-mode crack propagation analysis. Arch. Civil Mech. Eng. 17, 677–686 (2017)
Gadallah, R., Osawa, N., Tanaka, S., et al.: A novel approach to evaluate mixed-mode SIFs for a through-thickness crack in a welding residual stress field using an effective welding simulation method. Eng. Fract. Mech. 197, 48–65 (2018)
Carpinteri, A.: Fatigue growth of a surface crack in a welded T-joint. Int. J. Fatigue 27, 59–69 (2005)
Pang, J.H.L., Hoh, H.J., Tsang, K.S., et al.: Fatigue crack propagation analysis for multiple weld toe cracks in cut-out fatigue test specimens from a girth welded pipe. Int. J. Fatigue 94, 158–165 (2017)
Lados, D., Apelian, D., Donald, J.: Fracture mechanics analysis for residual stress and crack closure corrections. Int. J. Fatigue 29, 687–694 (2007)
Choi, D.H., Choi, H.Y.: Fatigue life prediction of out-of-plane gusset welded joints using strain energy density factor approach. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 44, 17–27 (2005)
Remes, H.: Strain-based approach to fatigue crack initiation and propagation in welded steel joints with arbitrary notch shape. Int. J. Fatigue 52, 114–123 (2013)
Sun, G., Wang, C., Wei, X., et al.: Study on small fatigue crack initiation and growth for friction stir welded joints. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 739, 71–85 (2019)
Mikulski, Z., Lassen, T.: Fatigue crack initiation and subsequent crack growth in fillet welded steel joints. Int. J. Fatigue 120, 303–318 (2019)
Shiraiwa, T., Briffod, F., Enoki, M.: Development of integrated framework for fatigue life prediction in welded structures. Eng. Fract. Mech. 198, 158–170 (2018)
Lassen, T., Recho, N.: Proposal for a more accurate physically based S–N curve for welded steel joints. Int. J. Fatigue 31, 70–78 (2009)
Josefson, B.L., Ringsberg, J.W.: Assessment of uncertainties in life prediction of fatigue crack initiation and propagation in welded rails. Int. J. Fatigue 31, 1413–1421 (2009)
Zhang, Y.H., Maddox, S.J.: Fatigue life prediction for toe ground welded joints. Int. J. Fatigue 31, 1124–1136 (2009)
da Silva, A.L.L., Correia, J.A.F.O., de Jesus, A.M.P., et al.: Influence of fillet end geometry on fatigue behaviour of welded joints. Int. J. Fatigue 123, 196–212 (2019)
Al Zamzami, I., Susmel, L.: On the accuracy of nominal, structural, and local stress based approaches in designing aluminium welded joints against fatigue. Int. J. Fatigue 101, 137–158 (2017)
Khurshid, M., Barsoum, Z., Däuwel, T., et al.: Root fatigue strength assessment of fillet welded tube-to-plate joints subjected to multi-axial stress state using stress based local methods. Int. J. Fatigue 101, 209–223 (2017)
Bäckström, M., Marquis, G.: Interaction equations for multiaxial fatigue assessment of welded structures. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 27, 991–1003 (2004)
Sonsino, C.M.: Multiaxial fatigue of welded joints under in-phase and out-of-phase local strains and stresses. Int. J. Fatigue 17, 55–70 (1995)
Sonsino, C., Kueppers, M., Eibl, M., et al.: Fatigue strength of laser beam welded thin steel structures under multiaxial loading. Int. J. Fatigue 28, 657–662 (2006)
Fatemi, A., Shamsaei, N.: Multiaxial fatigue: an overview and some approximation models for life estimation. Int. J. Fatigue 33, 948–958 (2011)
Karolczuk, A., Macha, E.: A review of critical plane orientations in multiaxial fatigue failure criteria of metallic materials. Int. J. Fract. 134, 267–304 (2005)
Findley, W.N.: A theory for the effect of mean stress on fatigue of metals under combined torsion and axial load or bending. J. Eng. Ind. 81, 301–305 (1959)
Jen, Y.M., Chang, L.Y., Fang, C.F.: Assessing the fatigue life of butt-welded joints under oblique loading by using local approaches. Int. J. Fatigue 30, 603–613 (2008)
Marquis, G., Bäckström, M., Siljander, A.: Multiaxial fatigue damage parameters for welded joints: design code and critical plane approaches. In: Proc. First North European Engineering and Science Conference (1997)
Lopez-Jauregi, A., Esnaola, J.A., Ulacia, I., et al.: Fatigue analysis of multipass welded joints considering residual stresses. Int. J. Fatigue 79, 75–85 (2015)
Bolchoun, A., Wiebesiek, J., Kaufmann, H., et al.: Application of stress-based multiaxial fatigue criteria for laserbeam-welded thin aluminium joints under proportional and non-proportional variable amplitude loadings. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 73, 9–16 (2014)
Shen, W., Xu, L., He, F., et al.: Notch stress to assess multiaxial fatigue of complex welded structures under non-proportional loading. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 102, 151–161 (2019)
Carpinteri, A., Spagnoli, A., Vantadori, S.: Multiaxial fatigue life estimation in welded joints using the critical plane approach. Int. J. Fatigue 31, 188–196 (2009)
Papadopoulos, I.V., Davoli, P., Gorla, C., et al.: A comparative study of multiaxial high-cycle fatigue criteria for metals. Int. J. Fatigue 19, 219–235 (1997)
Jiang, C., Liu, Z.C., Wang, X.G., et al.: A structural stress-based critical plane method for multiaxial fatigue life estimation in welded joints. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 39, 372–383 (2016)
Carpinteri, A., Boaretto, J., Fortese, G., et al.: Fatigue life estimation of fillet-welded tubular T-joints subjected to multiaxial loading. Int. J. Fatigue 101, 263–270 (2017)
Susmel, L.: A simple and efficient numerical algorithm to determine the orientation of the critical plane in multiaxial fatigue problems. Int. J. Fatigue 32, 1875–1883 (2010)
Araújo, J.A., Dantas, A.P., Castro, F.C., et al.: On the characterization of the critical plane with a simple and fast alternative measure of the shear stress amplitude in multiaxial fatigue. Int. J. Fatigue 33, 1092–1100 (2011)
Mamiya, E.N., Araújo, J.A., Castro, F.C.: Prismatic hull: a new measure of shear stress amplitude in multiaxial high cycle fatigue. Int. J. Fatigue 31, 1144–1153 (2009)
Fatemi, A., Socie, D.F.: A critical plane approach to multiaxial fatigue damage including out-of-phase loading. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 11, 149–165 (1988)
Hemmesi, K., Farajian, M., Fatemi, A.: Application of the critical plane approach to the torsional fatigue assessment of welds considering the effect of residual stresses. Int. J. Fatigue 101, 271–281 (2017)
Rettenmeier, P., Roos, E., Weihe, S.: Fatigue analysis of multiaxially loaded crane runway structures including welding residual stress effects. Int. J. Fatigue 82, 179–187 (2016)
Susmel, L., Lazzarin, P.: A bi-parametric Wöhler curve for high cycle multiaxial fatigue assessment. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 25, 63–78 (2002)
Susmel, L., Tovo, R.: On the use of nominal stresses to predict the fatigue strength of welded joints under biaxial cyclic loading. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 27, 1005–1024 (2004)
Susmel, L., Tovo, R.: Local and structural multiaxial stress states in welded joints under fatigue loading. Int. J. Fatigue 28, 564–575 (2006)
Susmel, L., Sonsino, C.M., Tovo, R.: Accuracy of the modified Wöhler Curve Method applied along with the rref = 1 mm concept in estimating lifetime of welded joints subjected to multiaxial fatigue loading. Int. J. Fatigue 33, 1075–1091 (2011)
Susmel, L., Taylor, D.: The modified Wöhler curve method applied along with the theory of critical distances to estimate finite life of notched components subjected to complex multiaxial loading paths. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 31, 1047–1064 (2008)
Susmel, L., Hattingh, D.G., James, M.N., et al.: Multiaxial fatigue assessment of friction stir welded tubular joints of Al 6082-T6. Int. J. Fatigue 101, 282–296 (2017)
Al Zamzami, I., Susmel, L.: On the use of hot-spot stresses, effective notch stresses and the point method to estimate lifetime of inclined welds subjected to uniaxial fatigue loading. Int. J. Fatigue 117, 432–449 (2018)
Wei, Z., Dong, P.: Multiaxial fatigue life assessment of welded structures. Eng. Fract. Mech. 77, 3011–3021 (2010)
Mei, J., Dong, P.: An equivalent stress parameter for multi-axial fatigue evaluation of welded components including non-proportional loading effects. Int. J. Fatigue 101, 297–311 (2017)
Van Dang, K., Bignonnet, A., Fayard, J., et al.: Assessment of welded structures by a local multiaxial fatigue approach. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 24, 369–376 (2001)
Lazzarin, P., Sonsino, C.M., Zambardi, R.: A notch stress intensity approach to assess the multiaxial fatigue strength of welded tube-to-flange joints subjected to combined loadings. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 27, 127–140 (2004)
Liu, B., Yan, X.: An extension research on the theory of critical distances for multiaxial notch fatigue finite life prediction. Int. J. Fatigue 117, 217–229 (2018)
Meneghetti, G., Campagnolo, A., Rigon, D.: Multiaxial fatigue strength assessment of welded joints using the Peak Stress Method—part I: approach and application to aluminium joints. Int. J. Fatigue 101, 328–342 (2017)
Meneghetti, G., Campagnolo, A., Rigon, D.: Multiaxial fatigue strength assessment of welded joints using the Peak Stress Method—part II: application to structural steel joints. Int. J. Fatigue 101, 343–362 (2017)
Koster, M., Lis, A., Lee, W.J., et al.: Influence of elastic–plastic base material properties on the fatigue and cyclic deformation behavior of brazed steel joints. Int. J. Fatigue 82, 49–59 (2016)
Zeng, Z., Oliveira, J.P., Yang, M., et al.: Functional fatigue behavior of NiTi-Cu dissimilar laser welds. Mater. Des. 114, 282–287 (2017)
Koster, M., Kenel, C., Stutz, A., et al.: Fatigue and cyclic deformation behavior of brazed steel joints. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 581, 90–97 (2013)
Li, M., Barrett, R.A., Scully, S., et al.: Cyclic plasticity of welded P91 material for simple and complex power plant connections. Int. J. Fatigue 87, 391–404 (2016)
Guo, S.J., Wang, R.Z., Chen, H., et al.: A comparative study on the cyclic plasticity and fatigue failure behavior of different subzones in CrNiMoV steel welded joint. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 150, 66–78 (2019)
Wang, H., Jing, H., Zhao, L., et al.: Uniaxial ratcheting behaviour of 304L stainless steel and ER308L weld joints. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 708, 21–42 (2017)
Wang, H., Jing, H., Zhao, L., et al.: Dislocation structure evolution in 304L stainless steel and weld joint during cyclic plastic deformation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 690, 16–31 (2017)
Tang, J., Zhang, Z., Lu, H., et al.: Ratcheting behavior of weld joints under uniaxial cyclic loading using miniature specimen. Trans. Tianjin Univ. 25, 85–94 (2019)
Luo, H., Kang, G., Kan, Q., et al.: Experimental investigation on the heterogeneous ratchetting of SUS301L stainless steel butt weld joint during uniaxial cyclic loading. Int. J. Fatigue 105, 169–179 (2017)
Besel, Y., Besel, M., Dietrich, E., et al.: Heterogeneous local straining behavior under monotonic and cyclic loadings in a friction stir welded aluminum alloy. Int. J. Fatigue 125, 138–148 (2019)
Kang, G., Liu, Y., Li, Z.: Experimental study on ratchetting-fatigue interaction of SS304 stainless steel in uniaxial cyclic stressing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 435–436, 396–404 (2006)
He, C., Huang, C., Liu, Y., et al.: Effects of mechanical heterogeneity on the tensile and fatigue behaviours in a laser-arc hybrid welded aluminium alloy joint. Mater. Des. 65, 289–296 (2015)
Luo, H., Kang, G., Kan, Q., et al.: Experimental study on the whole-life heterogeneous ratchetting and ratchetting-fatigue interaction of SUS301L stainless steel butt-welded joint. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 43, 36–50 (2020)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant 11532010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, G., Luo, H. Review on fatigue life prediction models of welded joint. Acta Mech. Sin. 36, 701–726 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-020-00957-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-020-00957-0