Abstract
Aims
We estimated the rates and compared the risk factors for pregnancy and abortion between sexually active female and male adolescents with pregnant partner(s).
Subject and methods
This nationally representative, anonymous, cross-sectional study analyzed the Taiwan Global School-Based Student Health Survey (GSHS), 2006–2016, for grade 7–12 students from junior and senior high schools, comprehensive schools, vocational high schools, and night schools. We examined the association between covariates (i.e., demographics, sexual behaviors, substance use) and outcomes (i.e., pregnancy and abortion).
Results
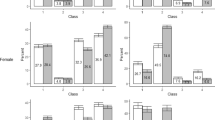
The rates of sexually active female and male adolescents involved in pregnancy were 17.63% (95% CI = 15.44–19.83%) and 15.91% (14.01–17.82%), respectively. The abortion rates among female and male adolescents involved in pregnancy were 78.79% (73.09–84.48%) and 66.19% (59.79–72.59%), respectively. Female and male adolescents involved in pregnancy were associated with similar risk factors (i.e., night schools, multiple sexual partner(s), early sexual debut, emergency contraceptive pills, and current cigarette smokers). However, males were further associated with contraception non-use. Among those involved in pregnancy, abortion was associated with multiple sexual partners and current cigarette smokers, but males involved in abortion were associated with the sexual debut at ≥ 14 years old and emergency contraception use.
Conclusions
Most pregnant Taiwanese adolescents prefer abortion, unlike many Western countries. This study highlights the importance of involving male and female adolescents in preventing adolescent pregnancy and abortion.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability (data transparency)
No data is available due to government restrictions.
Code availability (software application or custom code)
Not applicable.
References
Algur E, Wang E, Friedman HS, Deperthes B (2019) A systematic global review of condom availability programs in high schools. J Adolesc Health 64(3):292–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2018.11.013
Brown LD, Cai TT, DasGupta A (2001) Interval Estimation for a Binomial Proportion. Stat Sci 16(2):101–133
Cavazos-Rehg PA, Krauss MJ, Spitznagel EL, Schootman M, Cottler LB, Bierut LJ (2011a) Number of sexual partners and associations with initiation and intensity of substance use. AIDS Behav 15(4):869–874. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-010-9669-0
Cavazos-Rehg PA, Krauss MJ, Spitznagel EL, Schootman M, Cottler LB, Bierut LJ (2011b) Substance use and the risk for sexual intercourse with and without a history of teenage pregnancy among adolescent females. J Stud Alcohol Drugs 72(2):194–198. https://doi.org/10.15288/jsad.2011.72.194
Chen PC, Chang LC, Hsu C, Lee YC (2019) Dual use of e-cigarettes and traditional cigarettes among adolescents in Taiwan, 2014–2016. Nicotine Tob Res 21(1):48–54. https://doi.org/10.1093/ntr/nty003
Connor S, Edvardsson K, Spelten E (2018) Male adolescents’ role in pregnancy prevention and unintended pregnancy in rural Victoria: health care Professional’s and educators’ perspectives. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 18(1):245. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-018-1886-y
Corliss HL, Rosario M, Birkett MA, Newcomb ME, Buchting FO, Matthews AK (2014) Sexual orientation disparities in adolescent cigarette smoking: intersections with race/ethnicity, gender, and age. Am J Public Health 104(6):1137–1147. https://doi.org/10.2105/AJPH.2013.301819
Demissie Z, Everett Jones S, Clayton HB, King BA (2017) Adolescent risk behaviors and use of electronic vapor products and cigarettes. Pediatrics 139(2). https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2016-2921
Epstein M, Madeline F, Kosterman R, Bailey JA, King KM, Vasilenko SA, Steeger CM, Hill KG (2018) Adolescent age of sexual initiation and subsequent adult health outcomes. Am J Public Health 108(6):822–828. https://doi.org/10.2105/AJPH.2018.304372
Genetic Health Act (2009) https://law.moj.gov.tw/ENG/LawClass/LawAll.aspx?pcode=L0070001. Accessed 9 May 2022
Global School-based Student Health Survey (GSHS) - Taiwan. (2016). https://www.cdc.gov/gshs/countries/westpacific/taiwan.htm. Accessed May 20 2022
Greenland S, Mansournia MA, Altman DG (2016) Sparse data bias: a problem hiding in plain sight. BMJ 352:i1981. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.i1981
Grubb LK, Powers M, Adolescence CO (2020) Emerging issues in male adolescent sexual and reproductive health care. Pediatrics 145(5). https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2020-0627
Health Promotion Administration Annual Report (2021). vol 2022. Health Promotion Administration, Ministry of Health and Welfare
Kelly Y (2022) Adolescent Health and Wellbeing in the UK. In: Heinen A, Samuel R, Vögele C, Willems H (eds) Wohlbefinden und Gesundheit im Jugendalter: Theoretische Perspektiven, empirische Befunde und Praxisansätze. Springer Fachmedien Wiesbaden, Wiesbaden, pp 647–664. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-658-35744-3_29
Kutner MH, Nachtsheim CJ, Neter J (2004) Applied Linear Regression Models 4th edn. McGraw-Hill Irwin
Lee T-Y, Chou C-C, Chen C-M, Weng M-H, Liu Y-C (2014) The lived experience of teen girls’ abortion in Taiwan. SAGE Open 4(3):2158244014543788. https://doi.org/10.1177/2158244014543788
Leung H, Shek DTL, Leung E, Shek EYW (2019) Development of Contextually-relevant Sexuality Education: Lessons from a Comprehensive Review of Adolescent Sexuality Education Across Cultures. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16(4). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16040621
Lindberg L, Santelli J, Desai S (2016) Understanding the Decline in Adolescent Fertility in the United States, 2007–2012. J Adolesc Health 59(5):577–583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2016.06.024
Maharaj P, Rogan M (2011) Missing opportunities for preventing unwanted pregnancy: a qualitative study of emergency contraception. J Fam Plann Reprod Health Care 37(2):89–96. https://doi.org/10.1136/jfprhc.2011.0055
Maravilla JC, Betts KS, Couto ECC, Alati R (2017) Factors influencing repeated teenage pregnancy: a review and meta-analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol 217(5):527–545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2017.04.021 (e531)
Marcell AV, Waks AB, Rutkow L, McKenna R, Rompalo A, Hogan MT (2012) What do we know about males and emergency contraception? A synthesis of the literature. Perspect Sex Reprod Health 44(3):184–193. https://doi.org/10.1363/4418412
Marcell AV, Gibbs SE, Pilgrim NA, Page KR, Arrington-Sanders R, Jennings JM, Loosier PS, Dittus PJ (2018) Sexual and reproductive health care receipt among young males aged 15–24. J Adolesc Health 62(4):382–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2017.08.016
Martin JA, Hamilton BE, Osterman MJK, Driscoll AK (2021) Births: Final data for 2019. Natl Vital Stat Rep 70(2):1–51
Pinzon JL, Jones VF, Adolescence CO, Childhood COE (2012) Care of adolescent parents and their children. Pediatrics 130(6):e1743-1756. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2012-2879
Powers ME, Takagishi J, COMMITTEE ON ADOLESCENCE COEC, Alderman EM, Chung RJ, Grubb LK, Lee J, Upadhya KK, Wallace SB, Alderman SL, Sells JM, Glusman M, Guevara JP, Hashikawa AN, Miller-Fitzwater A, Navsaria D, Nelson BB, Shriver AE, Vanderbilt DL (2021) Care of adolescent parents and their children. Pediatrics 147(5). https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2021-050919
Secura GM, Madden T, McNicholas C, Mullersman J, Buckel CM, Zhao Q, Peipert JF (2014) Provision of no-cost, long-acting contraception and teenage pregnancy. N Engl J Med 371(14):1316–1323. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1400506
Sedgh G, Finer LB, Bankole A, Eilers MA, Singh S (2015) Adolescent pregnancy, birth, and abortion rates across countries: levels and recent trends. J Adolesc Health 56(2):223–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2014.09.007
Selvin S (1995) Practical biostatistical methods. Brooks/Cole.
Siu WHS, Li PR, See LC (2021) Rate of condom use among sexually active adolescents: a nationwide cross-sectional study in Taiwan from 2012 to 2016. BMJ Open 11(8):e047727. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2020-047727
Sully EA, Biddlecom A, Darroch JE, Riley T, Ashford LS, Lince-Deroche N, Firestein L, Murro R (2020) Adding it up: investing in sexual and reproductive health 2019. Guttmacher Institute, New York. https://doi.org/10.1363/2020.31593
Taiwan Global School-Based Student Health Survey (GSHS). (2015). https://www.hpa.gov.tw/Pages/Detail.aspx?nodeid=1077&pid=6205. Accessed May 3, 2022 2022
Towns S, DiFranza JR, Jayasuriya G, Marshall T, Shah S (2017) Smoking cessation in adolescents: targeted approaches that work. Paediatr Respir Rev 22:11-22.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prrv.2015.06.001
Tuddenham S, Hamill MM, Ghanem KG (2022) Diagnosis and treatment of sexually transmitted infections: a review. JAMA 327(2):161–172. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2021.23487
Upadhya KK, ADOLESCENCE CO, Breuner CC, Alderman EM, Grubb LK, Hornberger LL, Powers ME, Wallace SB (2019) Emergency contraception. Pediatrics 144(6). https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2019-3149
Vargas G, Borus J, Charlton BM (2017) Teenage pregnancy prevention: the role of young men. Curr Opin Pediatr 29(4):393–398. https://doi.org/10.1097/MOP.0000000000000510
Vashishtha R, Pennay A, Dietze PM, Livingston M (2021) Trends in adolescent alcohol and other risky health- and school-related behaviours and outcomes in Australia. Drug Alcohol Rev 40(6):1071–1082. https://doi.org/10.1111/dar.13269
Vasilenko SA, Lanza ST (2014) Predictors of multiple sexual partners from adolescence through young adulthood. J Adolesc Health 55(4):491–497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2013.12.025
Wang T, Lurie M, Govindasamy D, Mathews C (2018) The effects of school-based condom availability programs (CAPs) on condom acquisition, use and sexual behavior: A systematic review. AIDS Behav 22(1):308–320. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-017-1787-5
Yang H-C (2014) Teaching sexual matters in Taiwan: the analytical framework for popular culture and youth sexuality education. Asia Pacific Journal of Education 34(1):49–64. https://doi.org/10.1080/02188791.2013.822790
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the study participants, staff of participating schools and the Health Promotion Administration, Ministry of Health and Welfare of Taiwan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WHS Siu designed the study, conducted data analysis, interpreted the data, and wrote the manuscript. LH Tsai revised the manuscript. PR Li and LC See obtained the Taiwan GSHS dataset, interpreted the data, and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and Consent to participate
The Institutional Review Board (IRB) of the Chang Gung Medical Foundation approved this study and waived the requirement for informed consent for this anonymous survey (IRB number: 202001534B0).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Siu, W.H.S., Tsai, LH., Li, PR. et al. Prevalence and risk factors for female and male adolescents involved in pregnancy and abortion: a population-based cross-sectional study in Taiwan, 2006–2016. J Public Health (Berl.) 31, 1999–2010 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10389-022-01772-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10389-022-01772-6