Abstract
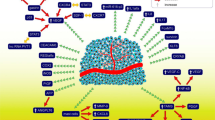
Esophageal cancer has an aggressive behavior with rapid tumor mass growth and frequently poor prognosis; it is known as one of the most fatal types of cancer worldwide. The identification of potential molecular markers that can predict the response to treatment and the prognosis of this cancer has been subject of a vast investigation in the recent years. Among several molecules, various angiogenic factors that are linked to the tumor development, growth, and invasion, such as VEGF, HGF, angiopoietin-2, IL-6, and TGF-B1, were investigated. In this paper, the authors sought to review the role of these angiogenic factors in prognosis and hypothesize how they can be used as a treatment target.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pennathur A, Gibson MK, Jobe BA, et al. Oesophageal carcinoma. Lancet. 2013;381:400–12.
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al. Cancer statistics 2009. CA Cancer Clin. 2009;59:225–49.
Coussens LM, Werb Z. Inflammation and cancer. Nature. 2002;420:860–7.
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–74.
Guo Y, Xu F, Lu T, et al. Interleukin-6 signaling pathway in targeted therapy for cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 2012;38:904–10.
Kishimoto T. Interleukin-6: from basic science to medicine 40 years in immunology. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:1–21.
Oshima Y, Yajima S, Yamazaki K, et al. Angiogenesis-related factors are molecular targets for diagnosis and treatment of patients with esophageal carcinoma. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2010;16:389–93.
Xu Z, Wang S, Wu M, et al. TGF beta1 and HGF protein secretion by esophageal squamous epithelial cells and stromal fibroblasts in oesophageal carcinogenesis. Oncol Lett. 2013;6:401–6.
Sugiura K, Ozawa S, Kitagawa Y, et al. Co-expression of aFGF and FGFR-1 is predictive of a poor prognosis in patients with esophageal cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2005;11:2188–92.
Folkman J. How is blood vessel growth regulated in normal and neoplastic tissue? Cancer Res. 1986;11:467–73.
Leo C, Giaccia AJ, Denko NC. The hypoxic tumor microenvironment and gene expression. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2004;14:207–14.
Kimura S, Kitadai Y, Tanaka S, et al. Expression of hypoxia inducible factor (HIF)-1α is associated with vascular endothelial growth factor expression and tumour angiogenesis in human oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Eur J Cancer. 2004;40:1904–12.
Birchmeier C, Birchmeier W, Gherardi E, et al. Metastasis, motility and more. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003;4:915–25.
Bottaro DP, Rubin JS, Faletto DL, et al. Identification of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor as the c-met proto-oncogene product. Science. 1991;251:802–4.
Ren Yi, Cao Brian, Law Simon, et al. Hepatocyte growth factor promotes cancer cell migration and angiogenic factors expression: a prognostic marker of human esophageal squamous cell carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;3:6190–7.
Saeki H, Oda S, Kawaguchi H, et al. Concurrent overexpression of Ets-1 and c-Met correlates with a phenotype of high cellular motility in human esophageal cancer. Int J Cancer. 2002;98:8–13.
Zhou YZ, Fang XQ, Li H, et al. Role of serum angiopoietin-2 level in screening for esophageal squamous cell cancer and its precursors. Chin Med J (Engl). 2007;120:1216–9.
Dreikhausen L, Blank S, Sisic L, et al. Association of angiogenic factors with prognosis in esophageal cancer. BMC Cancer. 2015;15:121–7.
Bromberg J. Stat proteins and oncogenesis. J Clin Invest. 2002;109:1139–42.
Zhao Z-F, Li J-X, Ye Rui, et al. Interleukin-6 as a potential molecular target in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 2016;11:925–32.
Schindler C, Levy DE, Decker T. JAK-STAT signaling, from interferons to cytokines. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:20059–63.
Michiels C, Minet E, Mottet D, et al. Regulation of gene expression by oxygen: NF-kappaB and HIF-1, two extremes. Free Radic Biol Med. 2002;1:1231–42.
Wang GL, Jiang BH, Rue EA, et al. Hypoxia inducible factor 1 is a basic helix-loop-helix–PAS heterodimer regulated by cellular O2 tension. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995;1:5510–4.
Carmeliet P, Dor Y, Herbert JM, et al. Role of HIF-1α in hypoxia-mediated apoptosis, cell proliferation and tumor angiogenesis. Nature. 1998;394:485–90.
Veikkola T, Alitalo K. VEGFs, receptors and angiogenesis. Semin Cancer Biol. 1999;9:211–20.
Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ. Regulation of angiogenesis by hypoxia: role of the HIF system. Nat Med. 2003;9:677–84.
Dibbens JA, Miller DL, Damert A, et al. Hypoxic regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor mRNA stability requires the cooperation of multiple RNA elements. Mol Biol Cell. 1999;10:907–19.
Ellis LM, Liu W, Fan F, et al. Role of angiogenesis inhibitors in cancer treatment. Oncology (Williston Park). 2001;15:39–46.
Amioka T, Kitadai Y, Tanaka S, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor- C expression predicts lymph node metastasis of human gastric carcinoma invading the submucosa. Eur J Cancer. 2002;15:1413–9.
Zhong H, De Marzo AM, Laughner E, et al. Over-expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α in common human cancers and their metastases. Cancer Res. 1999;59:5830–5.
Aebersold DM, Burri P, Beer KT, et al. Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha: a novel predictive and prognostic parameter in the radiotherapy of oropharyngeal cancer. Cancer Res. 2001;12:2911–6.
Tzao C, Lee S-C, Tung H-J, et al. Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-D as outcome predictors in resected esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Dis Markers. 2008;25:141–8.
Olenyuk BZ, Zhang GJ, Klco JM, et al. Inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor with a sequence-specific hypoxia response element antagonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:16768–73.
Tan C, de Noronha RG, Roecker AJ, et al. Identification of a novel small-molecule inhibitor of the hypoxia-inducible factor 1 pathway. Cancer Res. 2005;65:605–12.
Sandler A. Bevacizumab in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;355:4613–6.
Samson P, Lockhart AC. Biologic therapy in esophageal and gastric malignancies: current therapies and future directions. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2017;8(3):418–29.
Massagué J. TGF-β signal transduction. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998;67:753–91.
Lahm H, Odartchenko N. Role of transforming growth factor β in colorectal cancer. Growth Factors. 1993;9:1–9.
S.-W I, Volpert OV, Bouck NP, et al. Smad4/DPC4-mediated tumor suppression through suppression of angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000;7:9624–9.
Shirai Y, Kawata S, Tamura S, et al. Plasma transforming growth factor-β 1 in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma comparison with chronic liver diseases. Cancer (Phila). 1994;73:2275–9.
Junker U, Knoefel B, Nuske K, et al. Transforming growth factor-β 1 is significantly elevated in plasma of patients suffering from renal cell carcinoma. Cytokine. 1996;8:794–8.
Tsushima H, Kawata S, Tamura S, et al. High levels of transforming growth factor-β 1 in patients with colorectal cancer: association with disease progression. Gastroenterology. 1996;110:375–82.
Saito H, Tsujitani S, Oka S, et al. The expression of transforming growth factor-β1 is significantly correlated with the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and poor prognosis of patients with advanced gastric carcinoma. Cancer (Phila). 1999;86:1455–62.
Shariat SF, Kim JH, Andrews B, et al. Preoperative plasma levels of transforming growth factor-β 1 strongly predict clinical outcome in patients with bladder carcinoma. Cancer (Phila). 2001;92:2985–92.
Narai S, Watanabe M, Hasegawa H, et al. Significance of transforming growth factor-β1 as a new tumor marker for colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 2002;97:508–11.
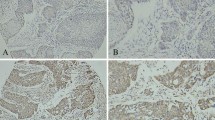
Natsugoe S, Xiangming C, Matsumoto M, et al. Smad4 and transforming growth factor-β1 expression in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Clin Cancer Res. 2002;8:1838–42.
Chevallier JM, Vitte E, Derosier C, et al. The thoracic esophagus: sectional anatomy and radiosurgical applications. Surg Radiol Anat. 1991;13:313–21.
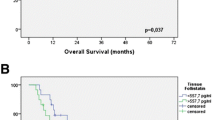
Fukuchi M, Miyazaki T, Fukai Y, et al. Plasma level of transforming growth factor-β1 measured from the azygos vein predicts prognosis in patients with esophageal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:2738–41.
Nakamura T, Ozawa S, Kitagawa Y, et al. Expression of basic fibroblast growth factor is associated with a good outcome in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Oncol Rep. 2005;14:617–23.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical statement
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any author(s).
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest and received no financial support for this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ladeira, K., Macedo, F., Longatto-Filho, A. et al. Angiogenic factors: role in esophageal cancer, a brief review. Esophagus 15, 53–58 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10388-017-0597-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10388-017-0597-1