Abstract
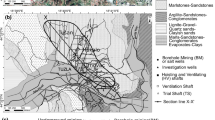
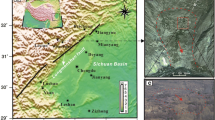
The Pubugou dam is located on the Dadu River in China, with a height of 186 m. The fracturing body at 780 m upstream of its right bank poses a major threat to the downstream reservoir area’s safety as well as the operation of the dam. In this study, a multi-source three-dimensional monitoring mode of space-ground-body is built using synthetic aperture radar, surface sensing, and rock mass stress monitoring. This makes it possible to keep an eye on the entire fracturing body in real time. This study proposes a GCPs selection method that combines the high coherence, small deformation reference points obtained by PS-InSAR inversion and stable deformation points, and realizes the high-precision bank slope deformation time series data acquisition method. It addresses the issue of strong subjectivity in the selection of ground control points (GCPs) in the SBAS-InSAR solution process in mountainous areas. The change in multiple scattering wave velocity and the evolution of the rock mass state inside the slope are both extracted using the seismic background noise cross-correlation technique. Through time series analysis and comparison of various monitoring data, the three-dimensional deformation characteristics, instability mechanism, and significant influence of rainfall on the deformation development of the fracturing body are summarized. Additionally, the adaptability, advantages, and disadvantages of various monitoring modes are evaluated. For the crucial slope of the project, a more trustworthy monitoring method will be available thanks to the mutual integration of the space-ground-body monitoring mode and data.























Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Sentinel-1 data were derived from the following resources available in the public domain: https://search.asf.alaska.edu. Other data cannot be shared publicly, because the data belongs to China Energy Dadu River Hydropower Development Co., Ltd., and the dam monitoring data in China is confidential.
References
Berardino P, Fornaro G, Lanari R, Sansosti E (2002) A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 40(11):2375–2383. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2002.803792
Dai KR, Li ZH, Xu Q, Burgmann R, Milledge DG, Tomas R, Fan XM, Zhao CY, Liu XJ, Peng JB, Zhang Q, Wang Z, Qu TT, He CY, Li DR, Liu JN (2020) Entering the era of earth observation-based landslide warning systems: a novel and exciting framework. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Mag 8(1):136–153. https://doi.org/10.1109/MGRS.2019.2954395
Dai KR, Li ZY, Xu Q, Tomas R, Li T, Jiang LM, Zhang JY, Yin T, Wang H (2023) Identification and evaluation of the high mountain upper slope potential landslide based on multi-source remote sensing: the Aniangzhai landslide case study. Landslides. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-023-02044-4
Dong XJ, Yin T, Dai KR, Pirasteh S, Zhuo GC, Li ZY, Yu B, Xu Q (2022) Identifying Potential Landslides on giant Niexia slope (China) based on integrated multi-remote sensing technologies. Remote Sens. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14246328
Ferretti A, Prati C, Rocca F (2000) Nonlinear subsidence rate estimation using permanent scatterers in differential SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 38(5):2202–2212. https://doi.org/10.1109/36.868878
Fuhrmann T, Garthwaite MC (2019) Resolving three-dimensional surface motion with InSAR: constraints from multi-geometry data fusion. Remote Sens. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11030241
Gou YT, Zhang L, Chen Y, Zhou H, Zhu Q, Liu XT, Lin JH (2023) Monitoring seasonal movement characteristics of the landslide based on time-series InSAR technology: the Cheyiping landslide case study. Remote sensing, China. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15010051
Gudmundsson S, Sigmundsson F, Carstensen JM (2002) Three-dimensional surface motion maps estimated from combined interferometric synthetic aperture radar and GPS data. J Geophys Res Solid Earth. https://doi.org/10.1029/2001JB000283
Guzzetti F, Gariano SL, Peruccacci S, Brunetti MT, Marchesini I, Rossi M, Melillo M (2020) Geographical landslide early warning systems. Earth Sci Rev. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.102973
Hamza V, Stopar B, Sterle O, Pavlovcic-Preseren P (2023) A cost-effective GNSS solution for continuous monitoring of landslides. Remote Sens. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15092287
Huang HB, Dai SG, Xie F (2021) Monitoring in-situ seismic response on rock slopes using ambient noise interferometry: application to the 2019 Changning (Mw 5.7) earthquake. Frontiers in earth science, China. https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2020.610181
Intrieri E, Gigli G, Mugnai F, Fanti R, Casagli N (2012) Design and implementation of a landslide early warning system. Eng Geol 147:124–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2012.07.017
Intrieri E, Gigli G, Casagli N, Nadim F (2013) Brief communication ‘Landslide early warning system: toolbox and general concepts.’ Nat Hazard 13(1):85–90. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-13-85-2013
Intrieri E, Raspini F, Fumagalli A, Lu P, Del Conte S, Farina P, Allievi J, Ferretti A, Casagli N (2018) The Maoxian landslide as seen from space: detecting precursors of failure with Sentinel-1 data. Landslides 15(1):123–133. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-017-0915-7
Jia HY, Wang YJ, Ge DQ, Deng YK, Wang R (2022) InSAR study of landslides: early detection, three-dimensional, and long-term surface displacement estimation-a case of Xiaojiang river basin. Remote sensing, China. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14071759
Kao H, Kan CW, Chen RY, Chang CH, Rosenberger A, Shin TC, Leu PL, Kuo KW, Liang WT (2012) Locating, monitoring, and characterizing typhoon-linduced landslides with real-time seismic signals. Landslides 9(4):557–563. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-012-0322-z
Larose E, Carriere S, Voisin C, Bottelin P, Baillet L, Gueguen P, Walter F, Jongmans D, Guillier B, Garambois S, Gimbert F, Massey C (2015) Environmental seismology: what can we learn on earth surface processes with ambient noise? J Appl Geophys 116:62–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappgeo.2015.02.001
Lecocq T, Caudroni C, Brenguier F (2014) MSNoise, a Python package for monitoring seismic velocity changes using ambient seismic noise. Seismol Res Lett 85(3):715–726. https://doi.org/10.1785/0220130073
Li YS, Jiao QS, Hu XH, Li ZL, Li BQ, Zhang JF, Jiang WL, Luo Y, Li Q, Ba RJ (2020) Detecting the slope movement after the 2018 Baige Landslides based on ground-based and space-borne radar observations. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2019.101949
Li WG, Kacmarik M, Pospisil P (2022) Multi-GNSS positioning for landslide monitoring: a case study at the Recica landslide. Acta geodynamica et geomaterialia 19(3):255–270. https://doi.org/10.13168/AGG.2022.0011
Liu ZJ, Qiu HJ, Zhu YR, Liu Y, Yang DD, Ma SY, Zhang JJ, Wang YY, Wang LY, Tang BZ (2022) Efficient identification and monitoring of landslides by time-series InSAR combining single- and multi-look phases. Remote Sens. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14041026
Maghsoudi Y, van der Meer F, Hecker C, Perissin D, Saepuloh A (2018) Using PS-InSAR to detect surface deformation in geothermal areas of West Java in Indonesia. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 64:386–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2017.04.001
Mainsant G, Larose E, Bronnimann C, Jongmans D, Michoud C, Jaboyedoff M (2012) Ambient seismic noise monitoring of a clay landslide: toward failure prediction. J Geophys Res Earth Surf. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011JF002159
Manconi A, Giordan D (2016) Landslide failure forecast in near-real-time. Geomat Nat Haz Risk 7(2):639–648. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2014.942388
Minh D, Hanssen R, Rocca F (2020) Radar interferometry: 20 years of development in time series techniques and future perspectives. Remote Sens. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12091364
Moreira A, Prats-Iraola P, Younis M, Krieger G, Hajnsek I, Papathanassiou KP (2013) A tutorial on synthetic aperture radar. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Mag 1(1):6–43. https://doi.org/10.1109/MGRS.2013.2248301
Niu FL, Silver PG, Daley TM, Cheng X, Majer EL (2008) Preseismic velocity changes observed from active source monitoring at the Parkfield SAFOD drill site. Nature 454(7201):204–244. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07111
Peternel T, Janza M, Segina E, Bezak N, Macek M (2022) Recognition of landslide triggering mechanisms and dynamics using GNSS, UAV photogrammetry and in situ monitoring data. Remote Sens. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14143277
Segina E, Peternel T, Urbancic T, Realini E, Zupan M, Jez J, Caldera S, Gatti A, Tagliaferro G, Consoli A, Gonzalez JR, Auflic MJ (2020) Monitoring surface displacement of a deep-seated landslide by a low-cost and near real-time GNSS System. Remote Sens. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12203375
Snieder R (2004) Extracting the Green’s function from the correlation of coda waves: a derivation based on stationary phase. Phys Rev E. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.69.046610
Snieder R (2006) The theory of coda wave interferometry. Pure Appl Geophys 163(2–3):455–473. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-005-0026-6
van Natijne AL, Bogaard TA, van Leijen FJ, Hanssen RF, Lindenbergh RC (2022) World-wide InSAR sensitivity index for landslide deformation tracking. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2022.102829
Wasowski J, Keefer DK, Lee CT (2011) Toward the next generation of research on earthquake-induced landslides: current issues and future challenges. Eng Geol 122(1–2):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2011.06.001
Whiteley JS, Chambers JE, Uhlemann S, Wilkinson PB, Kendall JM (2019) Geophysical monitoring of moisture-induced landslides: a review. Rev Geophys 57(1):106–145. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018RG000603
Xiao RY, Jiang M, Li ZH, He XF (2022) New insights into the 2020 Sardoba dam failure in Uzbekistan from Earth observation. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2022.102705
Xie F, Ren YQ, Zhou YS, Larose E, Baillet L (2018) Monitoring local changes in granite rock under biaxial test: a spatiotemporal imaging application with diffuse waves. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 123(3):2214–2227. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017JB014940
Xie F, Larose E, Wang QY, Zhang YX (2023) In-situ monitoring of rock slope destabilization with ambient seismic noise interferometry in southwest China. Eng Geol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2022.106922
Yang X et al (2013) Characteristics and analysis of deformation of tension-displaced rock mass on right bank at head area of pubugou hydropower station. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 32:549–552. in Chinese, with English summary
Yao JM, Yao X, Liu XH (2022) Landslide detection and mapping based on SBAS-InSAR and PS-InSAR: a case study in Gongjue County. Remote sensing, Tibet, China. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194728
Zhang P, Guo ZH, Guo SF, Xia J (2022) Land Subsidence monitoring method in regions of variable radar reflection characteristics by integrating PS-InSAR and SBAS-InSAR techniques. Remote Sens. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14143265
Zheng ZZ, Xie CH, He Y, Zhu MC, Huang WF, Shao TM (2022) Monitoring potential geological hazards with different InSAR algorithms: the case of Western Sichuan. Remote Sens. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14092049
Zhou XB, Chang NB, Li SS (2009) Applications of SAR interferometry in earth and environmental science research. Sensors 9(3):1876–1912. https://doi.org/10.3390/s90301876
Zhou JG, Shi B, Liu GL, Ju SJ (2021) Accuracy analysis of dam deformation monitoring and correction of refraction with robotic total station. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0251281
Zhou X, Zhang SC, Zhang Q, Liu Q, Ma ZM, Wang T, Tian J, Li XR (2022) Research of deformation and soil moisture in loess landslide simultaneous retrieved with ground-based GNSS. Remote Sens. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225687
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Huibin Liang: conceptualization, methodology, software, visualization, formal analysis, investigation, writing — original draft, writing — review and editing. Han Zhang: conceptualization, methodology, validation, writing — review and editing. Jiacheng Guo: resources, writing — review and editing. Xia Xiang: supervision, writing — review and editing. Linsong Zhang: writing — review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, H., Zhang, H., Guo, J. et al. Safety monitoring and effect analysis of fracturing body on the right bank of Pubugou reservoir head in China based on space-ground-body monitoring mode. Landslides 21, 1221–1241 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-024-02230-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-024-02230-y