Abstract
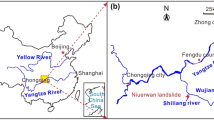
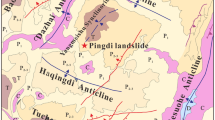
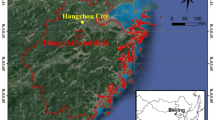
At approximately 3:50 a.m. (UTC + 8) on August 21, 2020, a massive rainfall-induced landslide occurred in Zhonghaicun, Fuquan town, Hanyuan County, Sichuan Province, China, forming an approximately 40.85 × 104 m3 landslide accumulation, burying eight houses and approximately 100 m of roads, and causing long-term traffic interruptions. The landslide was comprehensively evaluated through field investigation, UAV photography, borehole drilling, and laboratory tests. According to movement and accumulation characteristics, the landslide is divided into the main sliding zones (the source area, impact sliding area, shoveling-accumulation area, and accumulation area) and landslide-affected zones. The deformation and failure of the Zhonghaicun landslide are related to the lithology (existence of a weak interlayer), geomorphology (microrelief changes), and antecedent rainfall. However, the main trigger of the landslide is continuous rainfall, which increases the landslide saturation and pore water pressure and reduces the mechanical strength of the weak layer. The landslide failure mode is complex. The upper slope is affected by rainfall and loses stability first. Under the impact of the sliding mass, sliding of the lower slope is triggered. This study of the Zhonghaicun landslide characterizes the evolution process of a complex rainfall-induced landslide and provides ways to mitigate landslide disasters.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bezak N, Jež J, Sodnik J, Jemec Auflič M, Mikoš M (2020) An extreme May 2018 debris flood case study in northern Slovenia: analysis, modelling, and mitigation. Landslides 17:2373–2383. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-019-01325-1
Bhardwaj A, Wasson RJ, Ziegler AD, Chow WTL, Sundriyal YP (2019) Characteristics of rain-induced landslides in the Indian Himalaya: a case study of the Mandakini Catchment during the 2013 flood. Geomorphology 330(APR.1):100–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2019.01.010
Duan Z, Dong C, Zheng W, Tang H, Ma J (2020) liquefaction mechanism of terrace sandy silt under landslide impact. J Eng Geol 28(6):1362–1371. https://doi.org/10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2019-491
Emanuel K (2005) Increasing destructiveness of tropical cyclones over the past 30 years. Nature 436(7051):686–688. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03906
Fan L, Lehmann P, McArdell B et al (2017a) Linking rainfall-induced landslides with debris flows runout patterns towards catchment scale hazard assessment. Geomorphology 280(MAR.1):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2016.10.007
Fan X, Xu Q, Scaringi G, Dai L, Li W, Dong X, Zhu X, Pei X, Dai K, Havenith HB (2017b) Failure mechanism and kinematics of the deadly June 24 2017 Xinmo landslide, Maoxian, Sichuan, China. Landslides 14(6):2129–2146. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-017-0907-7
Geertsema M, Hungr O, Schwab JW, Evans SG (2006) A large rockslide–debris avalanche in cohesive soil at Pink Mountain, northeastern British Columbia, Canada. Eng Geol 83(1-3):64–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2005.06.025
Geological Bureau of Sichuan Province (1971) Yingjing Geological Map (1:200000). Map No. H-48-XIX. (In Chinese)
Guzzetti F, Peruccacci S, Rossi M, Stark CP (2007) Rainfall thresholds for the initiation of landslides in central and southern Europe. Meteorog Atmos Phys 98(3):239–267. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-007-0262-7
He K, Liu B, Hu X (2020) Preliminary reports of a catastrophic landslide occurred on August 21, 2020, in Hanyuan County, Sichuan Province, China. Landslides. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-020-01566-5
Hungr O, Leroueil S, Picarelli L (2014) The Varnes classification of landslide types, an update. Landslides 11(2):167–194. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-013-0436-y
Kotlyakov VM, Rototaeva OV, Nosenko GA (2004) The September 2002 Kolka glacier catastrophe in North Ossetia, Russian Federation: evidence and analysis. Mt Res Dev 24(1):78–83. https://doi.org/10.1659/0276-4741(2004)024[0078:TSKGCI]2.0.CO;2
Li Y, Ma C, Wang Y (2019) Landslides and debris flows caused by an extreme rainstorm on July 21 2012 in mountains near Beijing, China. B Eng Geol Environ 78(2):1265–1280. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-017-1187-0
Ma P, Peng J, Wang Q, Zhuang J, Zhang F (2019a) The mechanisms of a loess landslide triggered by diversion-based irrigation: a case study of the South Jingyang Platform, China. B Eng Geol Environ 78(7):4945–4963. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-019-01467-5
Ma S, Xu C, Xu X (2019b) Volume expansion rates of seismic landslides and influencing factors: a case study of the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake. J Mt Sci-Engl 16(8):1731–1742. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-019-5479-7
Meng XY, Zhang JF, Yu SB et al (1999) The variation of porewater pressure and its relationship with liquefaction and densification in saturated sand under impact loading. Chin J Geotech Eng 03:7–11
Peng JB, Ma PH, Wang QY et al (2018) Interaction between landsliding materials and the underlying erodible bed in a loess flowslide. Eng Geol 01:38–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.01.001
Rahardjo H, Lee TT, Leong EC, Rezaur RB (2005) Response of a residual soil slope to rainfall. Can Geotech J 42(2):340–351. https://doi.org/10.1139/t04-101
Rahmani H, Naeini SA (2020) Influence of non-plastic fine on static iquefaction and undrained monotonic behavior of sandy gravel. Eng Geol 275:105729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105729
Sassa K, Wang G, Fukuoka H, Wang F, Ochiai T, Sugiyama M, Sekiguchi T (2004) Landslide risk evaluation and hazard zoning for rapid and long-travel landslides in urban development areas. Landslides 1:221–235. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-004-0028-y
Scheidegger AE (1973) On the prediction of the reach and velocity of catastrophic landslides. Rock Mech 5(4):231–236. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01301796
Shrestha S, Kang T (2019) Assessment of seismically-induced landslide susceptibility after the 2015 Gorkha earthquake, Nepal. B Eng Geol Environ 78(3):1829–1842. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-017-1191-4
Tang H, Wasowski J, Juang CH (2019) Geohazards in the three Gorges Reservoir Area, China — lessons learned from decades of research. Eng Geol 261:105267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.105267
Wang G, Sassa K, Fukuoka H (2003) Downslope volume enlargement of a debris slide-debris flow in the 1999 Hiroshima, Japan, rainstorm. Eng Geol 69(3-4):309–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-7952(02)00289-2
Wang J, Xiao L, Zhang J, Zhu Y (2020) Deformation characteristics and failure mechanisms of a rainfall-induced complex landslide in Wanzhou County, Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Landslides 17:419–431. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-019-01317-1
Wu L, Huang R, Li X (2020) Hydro-mechanical analysis of rainfall-induced landslides. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-0761-8_3
Xu C, Xu X, Shen L, Yao Q, Tan X, Kang W, Ma S, Wu X, Cai J, Gao M, Li K (2016) Optimized volume models of earthquake-triggered landslides. Sci Rep 6(1):29797. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep29797
Yang S, Su L, Zhang C, Li C, Hu l (2020) Analysis of seepage characteristics and stability of Xigada Formation slope under heavy rainfall. J Civil Environ Eng 42(4):19–27. https://doi.org/10.11835/j.issn.2096-6717.2020.024
Yin Y, Wang H, Gao Y, Li X (2010) Real-time monitoring and early warning of landslides at relocated Wushan Town, the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Landslides 7(3):339–349. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-010-0220-1
Yin Y, Zheng W, Li X, Sun P, Li B (2011) Catastrophic landslides associated with the M8.0 Wenchuan earthquake. B Eng Geol Environ 70(1):15–32. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-010-0334-7
Yu H, Li C, Zhou J, Chen W, Long J, Wang X, Peng T (2020) Recent rainfall- and excavation-induced bedding rockslide occurring on October 22 2018 along the Jian-En expressway, Hubei, China. Landslides 17:2619–2629. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-020-01468-6
Yu X, Xiong Q, Song Y, He C (2012) Preliminary analysis on the characteristics of slide-prone strata of Xigeda formation in Hanyuan County, Sichuan Province. Res Environ Eng 26(B04):36–38. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1671-1211.2012.z1.009
Zhang F, Liu G, Chen W, Liang S, Chen R, Han W (2012) Human-induced landslide on a high cut slope: a case of repeated failures due to multi-excavation. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 4(4):367–374. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1235.2012.00367
Zhang J F, Meng X Y (2003) Build-up and dissipation of excess pore water pressure in saturated sand under impact loading. Chin J Rock Mech Eng, (9): 1463–1468.
Zhu B, Wu X (2008) An analysis of rainfall-induced landslide in colluvial and eluvial soils overlying Xigeda strata, Southwestern Sichuan, China. J Eng Geol 16(Suppl.): 487–494.
Acknowledgements
We are very grateful to the Sichuan Institute of Geological Engineering Investigation Group Co. Ltd. for providing borehole data and geotechnical exploration reports. We also grateful for the DOMs and DEMs provided by the 606 Brigade of Sichuan Metallurgical Geological Survey Bureau. The authors also thank the Hanyuan County Meteorological Bureau for providing rainfall data. We would like to thank our team Weikong Zeng, Jinnan Han, and Jiawei Dun, in the College of Environment and Civil Engineering, for cooperating during site investigation and laboratory testing for samples taken from the Zhonghaicun landslide. We also thank the anonymous referees and the editor for their constructive feedbacks and suggestions that encourage us to improve the quality of this paper.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 41977252, U2005205) and the State Key Laboratory of Geohazard Prevention and Geoenvironment Protection Independent Research Project (Grant No. SKLGP2020Z001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yi, X., Feng, W., Bai, H. et al. Catastrophic landslide triggered by persistent rainfall in Sichuan, China: August 21, 2020, Zhonghaicun landslide. Landslides 18, 2907–2921 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-021-01701-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-021-01701-w