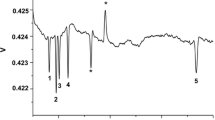
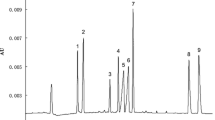
Abstract
Biogenic amines (BAs) are important compounds that can be used in the quality control of food and beverages. BA analysis is a challenging task that can be made easier by applying a derivatizing agent like dansyl chloride (DNS). The optimized capillary zone electrophoresis (CZE) separation of the DNS-BA derivates (derivates of cadaverine, histamine, putrescine, tryptamine, and tyramine) was performed using benzylamine as an internal standard, a potential of 18 kV, a temperature of 23 °C, a running buffer consisting of phosphoric acid, 120 mmol L−1, pH 2.5, and an hydrodynamic injection at 25 mBar for 6 s. All calibration curves had r2 higher than 0.99, and limits of detection (LODs) ranged from 7 to 50 µg L−1. The developed methodology was tested in cheese and yogurt samples. DNS showed to be an alternative derivatization reagent not only because it produced UV-detectable derivates (214 nm), but also because of its stability, aqueous solubility, high selectivity and sensitivity, reduced impurities, and simple preparation steps.
Graphic abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huang C-Y, Wang Y-X, Wang X-Z, Hu C-C, Chiu T-C (2019) Analysis of seven biogenic amines and two amino acids in wines using micellar electrokinetic chromatography. Appl Sci 9:1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9061193
Liu S-J, Xu J-J, Ma C-L, Guo C-F (2018) A comparative analysis of derivatization strategies for the determination of biogenic amines in sausage and cheese by HPLC. Food Chem 266:275–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.06.001
Karovičová J, Kohajdová Z (2005) Biogenic amines in food. Chem Pap 59:70–79
Milheiro J, Ferreira LC, Filipe-Ribeiro L, Cosme F, Nunes FM (2019) A simple dispersive solid phase extraction clean-up/concentration method for selective and sensitive quantification of biogenic amines in wines using benzoyl chloride derivatisation. Food Chem 274:110–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.08.116
Erdag D, Merhan O, Yildiz B (2019) Biochemical and pharmacological properties of biogenic amines. In: Proestos C (ed) Biogenic amines. IntechOpen, London, pp 1–19. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.81569
Papageorgiou M, Lambropoulou D, Morrison C, Kłodzińska E, Namieśnik J, Płotka-Wasylka J (2018) Literature update of analytical methods for biogenic amines determination in food and beverages. Trends Anal Chem 98:128–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2017.11.001
Adımcılar V, Öztekin N, Erim FB (2018) A direct and sensitive analysis method for biogenic amines in dairy products by capillary electrophoresis coupled with contactless conductivity detection. Food Anal Methods 11:1374–1379. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-017-1122-9
Francisco KCA, Brandão PF, Ramos RM, Gonçalves LM, Cardoso AA, Rodrigues JA (2020) Salting-out assisted liquid–liquid extraction with dansyl chloride for the determination of biogenic amines in food. Int J Food Sci Technol 55:248–258. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.14300
Ruiz-Capillas C, Herrero A (2019) Impact of biogenic amines on food quality and safety. Foods 8:62. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8020062
Ishimaru M, Muto Y, Nakayama A, Hatate H, Tanaka R (2019) Determination of biogenic amines in fish meat and fermented foods using column-switching high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. Food Anal Methods 12:166–175. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-018-1349-0
Erim FB (2013) Recent analytical approaches to the analysis of biogenic amines in food samples. Trends Anal Chem 52:239–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2013.05.018
Cao D, Xu X, Xue S, Feng X, Zhang L (2019) An in situ derivatization combined with magnetic ionic liquid-based fast dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for determination of biogenic amines in food samples. Talanta 199:212–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.02.065
Czajkowska-Mysłek A, Leszczyńska J (2018) Liquid chromatography–single-quadrupole mass spectrometry as a responsive tool for determination of biogenic amines in ready-to-eat baby foods. Chromatographia 81:901–910. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-018-3527-z
Shen N-Y, Zheng S-Y, Wang X-Q (2017) Determination of biogenic amines in pu-erh tea with precolumn derivatization by high-performance liquid chromatography. Food Anal Methods 10:1690–1698. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-016-0724-y
Wojnowski W, Namieśnik J, Płotka-Wasylka J (2019) Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction combined with gas chromatography–mass spectrometry for in situ determination of biogenic amines in meat: estimation of meat’s freshness. Microchem J 145:130–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2018.10.034
Papageorgiou M, Lambropoulou D, Morrison C, Namieśnik J, Płotka-Wasylka J (2018) Direct solid phase microextraction combined with gas chromatography–mass spectrometry for the determination of biogenic amines in wine. Talanta 183:276–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.02.006
Mohammadi M, Kamankesh M, Hadian Z, Mortazavian AM, Mohammadi A (2017) Determination of biogenic amines in cheese using simultaneous derivatization and microextraction method followed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Chromatographia 80:119–126. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-016-3217-7
Huang J, Gan N, Lv F, Cao Y, Ou C, Tang H (2016) Environmentally friendly solid-phase microextraction coupled with gas chromatography and mass spectrometry for the determination of biogenic amines in fish samples. J Sep Sci 39:4384–4390. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201600893
Almeida C, Fernandes JO, Cunha SC (2012) A novel dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction (DLLME) gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC–MS) method for the determination of eighteen biogenic amines in beer. Food Control 25:380–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2011.10.052
Chiu T-C, Lin Y-W, Huang Y-F, Chang H-T (2006) Analysis of biologically active amines by CE. Electrophoresis 27:4792–4807. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.200600126
Płotka-Wasylka JM, Morrison C, Biziuk M, Namieśnik J (2015) Chemical derivatization processes applied to amine determination in samples of different matrix composition. Chem Rev 115:4693–4718. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr4006999
Woźniakiewicz M, Woźniakiewicz A, Nowak PM, Kłodzińska E, Namieśnik J, Płotka-Wasylka J (2018) CE-MS and GC-MS as “Green” and complementary methods for the analysis of biogenic amines in wine. Food Anal Methods 11:2614–2627. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-018-1219-9
Daniel D, dos Santos VB, Vidal DTR, do Lago CL (2015) Determination of biogenic amines in beer and wine by capillary electrophoresis–tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1416:121–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2015.08.065
Santos B, Simonet BM, Ríos A, Valcárcel M (2004) Direct automatic determination of biogenic amines in wine by flow injection-capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry. Electrophoresis 25:3427–3433. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.200405991
Li W, Pan Y, Liu Y, Zhang X, Ye J, Chu Q (2014) Simultaneous determination of eight typical biogenic amines by CZE with capacitively coupled contactless conductivity detection. Chromatographia 77:287–292. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-013-2595-3
Ginterová P, Marák J, Staňová A, Maier V, Ševčík J, Kaniansky D, Staňová S, Maier V, Jurajševčík JJ, Kaniansky D (2012) Determination of selected biogenic amines in red wines by automated on-line combination of capillary isotachophoresis–capillary zone electrophoresis. J Chromatogr B 904:135–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2012.07.018
Dossi N, Toniolo R, Pizzariello A, Susmel S, Bontempelli G (2011) A modified electrode for the electrochemical detection of biogenic amines and their amino acid precursors separated by microchip capillary electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 32:906–912. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.201000690
An D, Chen Z, Zheng J, Chen S, Wang L, Huang Z, Weng L (2015) Determination of biogenic amines in oysters by capillary electrophoresis coupled with electrochemiluminescence. Food Chem 168:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.07.019
Fekete A, Lahaniatis M, Lintelmann J, Schmitt-Kopplin P (2008) Determination of aliphatic low-molecular-weight and biogenic amines by capillary zone electrophoresis. In: Schmitt-Kopplin P (ed) Capillary electrophoresis, vol 384. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 65–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-59745-376-9_4
Moraes MP, Gonçalves LM, Pereira EA (2018) Determination of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid by capillary electrophoresis with indirect detection using pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylic acid or 3,5-dinitrobenzoic acid. Int J Environ Anal Chem 98:258–270. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2018.1446528
Baker DR (1995) Capillary electrophoresis. Wiley, New York
Ruiz-Jiménez J, de Castro MDL (2006) Pervaporation as interface between solid samples and capillary electrophoresis. J Chromatogr A 1110:245–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2006.01.081
He L, Xu Z, Hirokawa T, Shen L (2017) Simultaneous determination of aliphatic, aromatic and heterocyclic biogenic amines without derivatization by capillary electrophoresis and application in beer analysis. J Chromatogr A 1482:109–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2016.12.067
Arce L, Rı́os A, Valcárcel M (1998) Direct determination of biogenic amines in wine by integrating continuous flow clean-up and capillary electrophoresis with indirect UV detection. J Chromatogr A 803:249–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9673(97)01255-7
Timm M, Jørgensen BM (2002) Simultaneous determination of ammonia, dimethylamine, trimethylamine and trimethylamine-n-oxide in fish extracts by capillary electrophoresis with indirect UV-detection. Food Chem 76:509–518. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0308-8146(01)00289-8
Lista AG, Arce L, Rı́os A, Valcárcel M (2001) Analysis of solid samples by capillary electrophoresis using a gas extraction sampling device in a flow system. Anal Chim Acta 438:315–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(00)01267-8
Kataoka H (1996) Derivatization reactions for the determination of amines by gas chromatography and their applications in environmental analysis. J Chromatogr A 733:19–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9673(95)00726-1
Křı́žek M, Pelikánová T (1998) Determination of seven biogenic amines in foods by micellar electrokinetic capillary chromatography. J Chromatogr A 815:243–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9673(98)00464-6
Su SC, Chou SS, Chang PC, Hwang DF (2000) Determination of biogenic amines in fish implicated in food poisoning by micellar electrokinetic capillary chromatography. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 749:163–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4347(00)00403-5
Male KB, Luong JHT (2001) Derivatization, stabilization and detection of biogenic amines by cyclodextrin-modified capillary electrophoresis–laser-induced fluorescence detection. J Chromatogr A 926:309–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9673(01)01056-1
Gray WR (1972) [8] End-group analysis using dansyl chloride. Methods Enzymol 25:121–138
Jia S, Kang YP, Park JH, Lee J, Kwon SW (2012) Determination of biogenic amines in Bokbunja (Rubus coreanus Miq.) wines using a novel ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole-time of flight mass spectrometry. Food Chem 132:1185–1190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.11.069
Dugo GM, Vilasi F, La Torre GL, Pellicanò TM (2006) Reverse phase HPLC/DAD determination of biogenic amines as dansyl derivatives in experimental red wines. Food Chem 95:672–676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2005.07.001
Gaš B, van de Muijselaar CS, Griend P (2018) High performance capillary electrophoresis—a primer 5990-3777EN. https://www.agilent.com/cs/library/applications/5990-5244EN.pdf
Petruci JFDS, Pereira EA, Cardoso AA (2013) Determination of 2-methylimidazole and 4-methylimidazole in caramel colors by capillary electrophoresis. J Agric Food Chem 61:2263–2267. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf3048274
Ramos RM, Brandão PF, Rodrigues JA (2020) Development of a SALLE-HPLC-FLD analytical method for the simultaneous determination of ten biogenic amines in cheese. Food Anal Methods. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-020-01730-6
Altria KD (1995) Capillary electrophoresis guidebook. Humana Press, New Jersey
Pacheco JG, Valente IM, Gonçalves LM, Rodrigues JA, Barros AA (2010) Gas-diffusion microextraction. J Sep Sci 33:3207–3212. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201000351
Valente IM, Santos CM, Gonçalves LM, Rodrigues JA, Barros AA (2012) Application of gas-diffusion microextraction for high-performance liquid chromatographic analysis of aliphatic amines in fermented beverages. Anal Methods 4:2569. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2ay25272d
Donegatti TA, Lobato A, Gonçalves LM, Pereira EA (2019) Cyclohexane-1,3-dione as a derivatizing agent for the analysis of aldehydes by micelar electrokinetic chromatography with diode array detection. Electrophoresis. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.201900171
de Lima LF, Brandão PF, Donegatti TA, Ramos RM, Gonçalves LM, Cardoso AA, Pereira EA, Rodrigues JA (2018) 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid as a derivatizing agent for aldehyde analysis by HPLC-UV and CE-DAD. Talanta 187:113–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.04.091
Donegatti TA, Gonçalves LM, Pereira EAEA (2017) Derivatizing assay for the determination of aldehydes using micellar electrokinetic chromatography. Electrophoresis 38:1068–1074. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.201600483
Jastrzębska A, Piasta A, Szłyk E (2014) Simultaneous determination of selected biogenic amines in alcoholic beverage samples by isotachophoretic and chromatographic methods. Food Addit Contam Part A 31:83–92. https://doi.org/10.1080/19440049.2013.855326
Dadáková E, Křížek M, Pelikánová T (2009) Determination of biogenic amines in foods using ultra-performance liquid chromatography (UPLC). Food Chem 116:365–370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.02.018
Ramos RM, Valente IM, Rodrigues JA (2014) Analysis of biogenic amines in wines by salting-out assisted liquid-liquid extraction and high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorimetric detection. Talanta 124:146–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2014.02.026
de Moraes M, de Moraes SL, Pereira EA, Tavares MFM (2009) Estratégias de pré-concentração em eletroforese capilar (CE): parte 1. Manipulação da velocidade eletroforética do analito. Quim Nova 32:1041–1046. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-40422009000400036
Gonçalves LM, Valente IM, Rodrigues JA (2017) Recent advances in membrane-aided extraction and separation for analytical purposes. Sep Purif Rev 46:179–194. https://doi.org/10.1080/15422119.2016.1235050
Restuccia D, Spizzirri UG, Puoci F, Cirillo G, Curcio M, Parisi OI, Iemma F, Picci N (2011) A new method for the determination of biogenic amines in cheese by LC with evaporative light scattering detector. Talanta 85:363–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2011.03.080
Kovács Á, Simon-Sarkadi L, Ganzler K (1999) Determination of biogenic amines by capillary electrophoresis. J Chromatogr A 836:305–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9673(98)00912-1
Uzaşçı S, Başkan S, Erim FB (2012) Biogenic amines in wines and pomegranate molasses—a non-ionic mcellar electrokinetic chromatography sssay with laser-induced fluorescence detection. Food Anal Methods 5:104–108. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-011-9220-6
Başkan S, Tezcan F, Köse S, Öztekin N, Erim FB (2010) Non-ionic micellar electrokinetic chromatography with laser-induced fluorescence: a new method tested with biogenic amines in brined and dry-salted fish. Electrophoresis 31:2174–2179. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.200900683
Cortacero-Ramírez S, Arráez-Román D, Segura-Carretero A, Fernández-Gutiérrez A (2007) Determination of biogenic amines in beers and brewing-process samples by capillary electrophoresis coupled to laser-induced fluorescence detection. Food Chem 100:383–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2005.09.037
Liu X, Yang L-X, Lu Y-T (2003) Determination of biogenic amines by 3-(2-furoyl)quinoline-2-carboxaldehyde and capillary electrophoresis with laser-induced fluorescence detection. J Chromatogr A 998:213–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9673(03)00637-X
Zhang B, Cai X, Yin Y, Li X, Lu H, Wu X (2017) Analysis of biogenic amines in foods by capillary electrochromatography coupled with laser induced fluorescence detection. Chin J Chromatogr 35:344. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1123.2016.10031
Guo J, Chen Y, Zhao L, Sun P, Li H, Zhou L, Wang X, Pu Q (2016) A strategy to modulate the electrophoretic behavior in plastic microchips using sodium polystyrene sulfonate. J Chromatogr A 1477:132–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2016.11.042
Zhang N, Wang H, Zhang Z, Deng Y, Zhang H (2008) Sensitive determination of biogenic amines by capillary electrophoresis with a new fluorogenic reagent 3-(4-fluorobenzoyl)-2-quinolinecarboxaldehyde. Talanta 76:791–797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2008.04.027
Płotka-Wasylkam J, Kłodzińska E, Namieśnik J (2017) Determination of biogenic amines in wine using micellar electrokinetic chromatography. J Res Anal 3:62–66
Acknowledgements
Authors wish to acknowledge Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES: 001), MSc fellowship granted to JOFM by Programa de Pós-Graduação em Biotecnologia e Monitoramento, UFSCAr (Campus Sorocaba), Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq 132680/2019-0), and Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP 2019/03582-7 and 2018/14425-7) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mantoanelli, J.O.F., Gonçalves, L.M. & Pereira, E.A. Dansyl Chloride as a Derivatizing Agent for the Analysis of Biogenic Amines by CZE-UV. Chromatographia 83, 767–778 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-020-03896-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-020-03896-x