Abstract
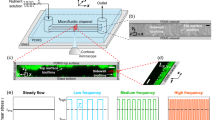
Biofilm accumulation in porous media can cause pore plugging and change many of the physical properties of porous media. Engineering bioplugging may have significant applications for many industrial processes, while improved knowledge on biofilm accumulation in porous media at porescale in general has broad relevance for a range of industries as well as environmental and water research. The experimental results by means of microscopic imaging over a T-shape microchannel clearly show that increase in fluid velocity could facilitate biofilm growth, but that above a velocity threshold, biofilm detachment and inhibition of biofilm formation due to high shear stress were observed. High nutrient concentration prompts the biofilm growth; however, the generated biofilm displays a weak adhesive strength. This paper provides an overview of biofilm development in a hydrodynamic environment for better prediction and modelling of bioplugging processes associated with porous systems in petroleum industry, hydrogeology and water purification.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bester E, Wolfaardt G, Joubert L, Garny K, Saftic S (2005) Planktonic-cell yield of a pseudomonad biofilm. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:7792–7798. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.71.12.7792-7798.2005
Billings N, Birjiniuk A, Samad TS, Doyle PS, Ribbeck K (2015) Material properties of biofilms—a review of methods for understanding permeability and mechanics. Rep Prog Phys 78:036601. https://doi.org/10.1088/0034-4885/78/3/036601
Brown LR (2010) Microbial enhanced oil recovery (MEOR). Curr Opin Microbiol 13:316–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2010.01.011
Cherifi T, Jacques M, Quessy S, Fravalo P (2017) Impact of nutrient restriction on the structure of Listeria monocytogenes biofilm grown in a microfluidic system. Front Microbiol 8:864. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.00864
Chua SL, Liu Y, Yam JKH, Chen Y, Vejborg RM, Tan BGC, Kjelleberg S, Tolker-Nielsen T, Givskov M, Yang L (2014) Dispersed cells represent a distinct stage in the transition from bacterial biofilm to planktonic lifestyles. Nat Commun 5:4462. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms5462
Cuzman OA, Rescic S, Richter K, Wittig L, Tiano P (2015) Sporosarcina pasteurii use in extreme alkaline conditions for recycling solid industrial wastes. J Biotechnol 214:49–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2015.09.011
David C, Bühler K, Schmid A (2015) Stabilization of single species Synechocystis biofilms by cultivation under segmented flow. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 42:1083–1089. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-015-1626-5
Dumitrache A, Wolfaardt G, Allen G, Liss SN, Lynd LR (2013) Form and function of Clostridium thermocellum biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:231–239. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02563-12
Dunsmore BC, Bass CJ, Lappin-Scott HM (2003) A novel approach to investigate biofilm accumulation and bacterial transport in porous matrices. Environ Microbiol 6:183–187. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1462-2920.2003.00546.x
Ezeuko CC, Sen A, Gates ID (2013) Modelling biofilm-induced formation damage and biocide treatment in subsurface geosystems. Microb Biotechnol 6:53–66. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.12002
Flemming H-C, Wingender J, Szewzyk U (2011) Biofilm highlights, vol 5. Springer Series on Biofilms. Heidelberg
Franco-Rivera A, Paniagua-Michel J, Zamora-Castro J (2007) Characterization and performance of constructed nitrifying biofilms during nitrogen bioremediation of a wastewater effluent. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 34:279–287. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-006-0196-y
Fujiwara K, Sugai Y, Yazawa N, Ohno K, Hong CX, Enomoto H (2004) Biotechnological approach for development of microbial enhanced oil recovery technique. Pet Biotechnol Dev Perspect 151:405–445
Garrett TR, Bhakoo M, Zhang Z (2008) Bacterial adhesion and biofilms on surfaces. Prog Nat Sci 18:1049–1056. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnsc.2008.04.001
Hao R, Meng C, Li J (2017) Impact of operating condition on the denitrifying bacterial community structure in a 3DBER-SAD reactor. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 44:9–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-016-1853-4
Hosseininoosheri P, Lashgari HR, Sepehrnoori K (2016) A novel method to model and characterize in situ bio-surfactant production in microbial enhanced oil recovery. Fuel 183:501–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2016.06.035
Hsi CD, Dudzik DS, Lane RH, Buettner JW, Neira RD (1994) Formation injectivity damage due to produced water reinjection. Paper presented at the SPE Formation Damage Control Symposium, Lafayette, Louisiana, 1994/1/1
Hunt SM, Werner EM, Huang B, Hamilton MA, Stewart PS (2004) Hypothesis for the role of nutrient starvation in biofilm detachment. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:7418–7425. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.70.12.7418-7425.2004
Joshi S, Goyal S, Mukherjee A, Reddy MS (2017) Microbial healing of cracks in concrete: a review. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 44:1511–1525. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-017-1978-0
Karambeigi MS, Schaffie M, Fazaelipoor MH (2013) Improvement of water flooding efficiency using mixed culture of microorganisms in heterogeneous micro-models. Pet Sci Technol 31:923–931. https://doi.org/10.1080/10916466.2010.506461
Karimi M, Mahmoodi M, Niazi A, Al-Wahaibi Y, Ayatollahi S (2012) Investigating wettability alteration during MEOR process, a micro/macro scale analysis. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 95:129–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2012.02.035
Khajepour H, Mahmoodi M, Biria D, Ayatollahi S (2014) Investigation of wettability alteration through relative permeability measurement during MEOR process: a micromodel study. J Pet Sci Eng 120:10–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2014.05.022
Kirby BJ (2010) Passive scalar transport: dispersion, patterning, and mixing. In: Micro- and nanoscale fluid mechanics: transport in microfluidic devices. Cambridge University Press, New York. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511760723.006
Klueglein N, Kögler F, Adaktylou IJ, Wuestner ML, Mahler E, Scholz J, Herold A, Alkan H (2016) Understanding selective plugging and biofilm formation of a halophilic bacterial community for MEOR application. In: Society of Petroleum Engineers SPE-179620-MS
Lam RH, Cui X, Guo W, Thorsen T (2016) High-throughput dental biofilm growth analysis for multiparametric microenvironmental biochemical conditions using microfluidics. Lab Chip 16:1652–1662. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6lc00072j
Landa-Marbán D, Liu N, Pop IS, Kumar K, Pettersson P, Bødtker G, Skauge T, Radu FA (2018) A pore-scale model for permeable biofilm: numerical simulations and laboratory experiments. Transp Porous Media. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-018-1218-8
Lane DJ (1991) 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In: Stackebrandt E, Goodfellow M (eds) Nucleic acid techniques in bacterial systematics. Wiley, London, pp 115–175
Lee JH, Kaplan JB, Lee WY (2008) Microfluidic devices for studying growth and detachment of Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilms. Biomed Microdevices 10:489–498. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-007-9157-0
Muyzer G, Dewaal EC, Uitterlinden AG (1993) Profiling of complex microbial-populations by denaturing gradient gel-electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes-coding for 16S ribosomal-RNA. Appl Environ Microb 59:695–700
Myhr S, Lillebo BL, Sunde E, Beeder J, Torsvik T (2002) Inhibition of microbial H2S production in an oil reservoir model column by nitrate injection. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 58:400–408. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-001-0881-8
Ohashi A, Harada H (1994) Adhesion strength of biofilm developed in an attached-growth reactor. Water Sci Technol 29:8
Oka GK, Pinder GF (2017) Multiscale model for assessing effect of bacterial growth on intrinsic permeability of soil: model description. Transp Porous Med 119:267–284. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-017-0870-8
Park A, Jeong H-H, Lee J, Kim KP, Lee C-S (2011) Effect of shear stress on the formation of bacterial biofilm in a microfluidic channel. BioChip J 5:236–241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-011-5307-9
Peszynska M, Trykozko A, Iltis G, Schlueter S, Wildenschild D (2016) Biofilm growth in porous media: experiments, computational modeling at the porescale, and upscaling. Adv Water Resour 95:288–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2015.07.008
Rabiei A, Sharifinik M, Niazi A, Hashemi A, Ayatollahi S (2013) Core flooding tests to investigate the effects of IFT reduction and wettability alteration on oil recovery during MEOR process in an Iranian oil reservoir. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:5979–5991. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-4863-4
Rochex A, Lebeault JM (2007) Effects of nutrients on biofilm formation and detachment of a Pseudomonas putida strain isolated from a paper machine. Water Res 41:2885–2892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2007.03.041
Rukavina Z, Vanic Z (2016) Current trends in development of liposomes for targeting bacterial biofilms. Pharmaceutics 8:18. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics8020018
Sarafzadeh P, Niazi A, Oboodi V, Ravanbakhsh M, Hezave AZ, Ayatollahi SS, Raeissi S (2014) Investigating the efficiency of MEOR processes using Enterobacter cloacae and Bacillus stearothermophilus SUCPM# 14 (biosurfactant-producing strains) in carbonated reservoirs. J Pet Sci Eng 113:46–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2013.11.029
Skolimowski M, Nielsen MW, Emneus J, Molin S, Taboryski R, Sternberg C, Dufva M, Geschke O (2010) Microfluidic dissolved oxygen gradient generator biochip as a useful tool in bacterial biofilm studies. Lab Chip 10:2162–2169. https://doi.org/10.1039/c003558k
Stoodley P, Cargo R, Rupp CJ, Wilson S, Klapper I (2002) Biofilm material properties as related to shear-induced deformation and detachment phenomena. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 29:361–367. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jim.7000282
Stoodley P, Dodds I, Boyle JD, Lappin‐Scott HM (1999) Influence of hydrodynamics and nutrients on biofilm structure. J Appl Microbiol 85:7
Sun D-L, Jiang X, Wu QL, Zhou N-Y (2013) Intragenomic heterogeneity of 16S rRNA genes causes overestimation of prokaryotic diversity. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:5962–5969. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01282-13
Sunde E, Thorstenson T, Torsvik T (1990) Growth of bacteria on water injection additives. In: Society of petroleum engineers SPE 20690, pp 301–316
Suthar H, Hingurao K, Desai A, Nerurkar A (2009) Selective plugging strategy based microbial enhanced oil recovery using Bacillus licheniformis TT33. J Microbiol Biotechnol 19:8. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.0904.04043
Tahirbegi IB, Ehgartner J, Sulzer P, Zieger S, Kasjanow A, Paradiso M, Strobl M, Bouwes D, Mayr T (2017) Fast pesticide detection inside microfluidic device with integrated optical pH, oxygen sensors and algal fluorescence. Biosens Bioelectron 88:188–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.08.014
Tsai YP (2005) Impact of flow velocity on the dynamic behaviour of biofilm bacteria. Biofouling 21:267–277. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927010500398633
Vilcáez J, Li L, Wu D, Hubbard SS (2013) Reactive transport modeling of induced selective plugging by Leuconostoc mesenteroides in carbonate formations. Geomicrobiol J 30:813–828. https://doi.org/10.1080/01490451.2013.774074
Weiss N, Obied KE, Kalkman J, Lammertink RG, van Leeuwen TG (2016) Measurement of biofilm growth and local hydrodynamics using optical coherence tomography. Biomed Opt Express 7:3508–3518. https://doi.org/10.1364/BOE.7.003508
Yawata Y, Nguyen J, Stocker R, Rusconi R (2016) Microfluidic studies of biofilm formation in dynamic environments. J Bacteriol 198:2589–2595. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00118-16
Yuan B, Wood DA (2018) Chapter one—overview of formation damage during improved and enhanced oil recovery. In: Yuan B, Wood DA (eds) Formation damage during improved oil recovery. Gulf Professional Publishing, Houston, pp 1–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-813782-6.00001-4
Zhang YD, Li C, Wu YC, Zhang YL, Zhou Z, Cao B (2019) A microfluidic gradient mixer-flow chamber as a new tool to study biofilm development under defined solute gradients. Biotechnol Bioeng 116:54–64. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.26852
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank Edin Alagic, Rikke H. Ulvøen and Tove L. Eide for technical assistance. This work was supported by the Research Council of Norway and industry partner GOE-IP through the Project IMMENS No. 255426.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, N., Skauge, T., Landa-Marbán, D. et al. Microfluidic study of effects of flow velocity and nutrient concentration on biofilm accumulation and adhesive strength in the flowing and no-flowing microchannels. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 46, 855–868 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-019-02161-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-019-02161-x