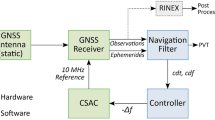
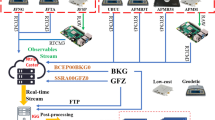
Abstract
Time-relative positioning (TRP), a global navigation satellite system (GNSS) dead reckoning method with low-cost and highly autonomous characteristics, accumulates the position increments calculated by time-differenced carrier phase (TDCP) between adjacent epochs to extrapolate position. It suffers from error accumulation over time, so it is necessary to judge the availability of positioning services based on predicted accuracy. We propose a new model to predict the accuracy (the root-mean-square error, RMSE) of TRP in real time by determining systematical errors and random errors. The proposed model consists of the following two steps: first, extracting the systematic errors and correlation of position increment errors before position extrapolation; second, predicting RMSE of the positioning results based on the error propagation law during position extrapolation. The experimental results show that after considering the correlation, the predicted RMSE sequences can envelop the actual positioning error more closely. In the case of having static observation before position extrapolation, the predicted RMSEs of extrapolation position in both horizontal and vertical directions decrease by approximately 53.8% compared to the results without considering correlation; in the case where real-time kinematic (RTK) dynamic results are obtained before extrapolation, the predicted RMSE of extrapolation position can decrease by 36.7% in horizontal direction and decrease by 27.9% in vertical direction. The proposed model will be able to provide an important accuracy reference to judge the availability of positioning services when the TRP method is used to extrapolate position under the condition of the augmentation information of RTK interruption.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Balard N, Santerre R, Cocard M, Bourgon S (2006) Single GPS receiver time-relative positioning with loop misclosure corrections. GPS Solut 10(1):56–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-005-0008-2
Bezcioglu M, Yigit CO, Karadeniz B, Dindar AA, El-Mowafy A, Avci O (2023) Evaluation of real-time variometric approach and real-time precise point positioning in monitoring dynamic displacement based on high-rate (20 Hz) GPS Observations. GPS Solut 27(1):43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-022-01381-6
Colosimo G, Crespi M, Mazzoni A (2011) Real-time GPS seismology with a stand-alone receiver: a preliminary feasibility demonstration. J Geophys Res 116:B11302. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010JB007941
Dong Y, Zhang L, Wang D, Li Q, Wu J, Wu M (2020) Low-latency, high-rate, high-precision relative positioning with moving base in real time. GPS Solut 24(2):56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-020-0969-1
Freda P, Angrisano A, Gaglione S, Troisi S (2015) Time-differenced carrier phases technique for precise GNSS velocity estimation. GPS Solut 19(2):335–341. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-014-0425-1
Guo J, Xu X, Zhao Q, Liu J (2016) Precise orbit determination for quad-constellation satellites at Wuhan University: strategy, result validation and comparison, procedure for the significance testing of unmodeled errors in GNSS observations. J Geod 90(2):143–159. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-015-0862-9
Han S, Wang J (2012) Integrated GPS/INS navigation system with dual-rate Kalman Filter. GPS Solut 16(3):389–404. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-011-0240-x
Han S, Rizos C (1996) Centimeter GPS kinematic or rapid static surveys without ambiguity resolution. J Surv Land Inf Syst 56(3):143–148
Hatch RR, Sharpe RT, Yang Y (2007) GPS navigation using successive differences of carrier-phase measurements. US Patent 7,212,155 B2
He K, Weng D, Ji S, Wang Z, Chen W, Lu Y, Nie Z (2021) Improving the performance of time-relative GNSS precise positioning in remote areas. Sensors 21(1):292. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21010292
Ji S, Sun Z, Weng D, Chen W, Wang Z, He K (2019) High-precision ocean navigation with single set of BeiDou short-message device. J Geod 93(9):1589–1602. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-019-01273-7
Li B, Zhang Z, Shen Y, Yang L (2018) A procedure for the significance testing of unmodeled errors in GNSS observations. J Geod 92(10):1171–1186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-018-1111-9
Li X, Ge M, Guo B, Wickert J, Schuh H (2013) Temporal point positioning approach for real-time GNSS seismology using a single receiver. Geophys Res Lett 40:5677–5682. https://doi.org/10.1002/2013GL057818
Li X, Guo B, Lu C, Ge M, Wickert J, Schuh H (2014) Real-time GNSS seismology using a single receiver. Geophys J Int 198(1):72–89. https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggu113
Liu Z, Ji S, Chen W, Ding X (2013) New fast precise kinematic surveying method using a single dual-frequency GPS receiver. J Surv Eng 139(1):19–33. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)SU.1943-5428.0000092
Mao Y, Sun R, Wang J, Cheng Q, Kiong LC, Ochieng WY (2022) New time-differenced carrier phase approach to GNSS/INS integration. GPS Solut 26:122. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-022-01314-3
Michaud S, Santerre R (2001) Time-relative positioning with a single civil GPS receiver. GPS Solut 5(2):71–77. https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00012888
Olynik M, Petovello MG, Cannon ME, Lachapelle G (2002) Temporal variability of GPS error sources and their effect on relative positioning accuracy. In: Proceedings of the national technical meeting of the institute of navigation
Qu W, Chen H, Zhang Q, Gao Y, Wang Q, Hao M (2021) A robust estimation algorithm for the increasing breakdown point based on quasi-accurate detection and its application to parameter estimation of the GNSS crustal deformation model. J Geod 95(11):125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-021-01574-w
Sun R, Cheng Q, Wang J (2020) Precise vehicle dynamic heading and pitch angle estimation using time-differenced measurements from a single GNSS antenna. GPS Solut 24(3):84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-020-01000-2
Tang W, Li Y, Deng C, Zou X, Wang Y, Qi K (2021) Stability analysis of position datum for real-time GPS/BDS/INS positioning in a platform system with multiple moving devices. Remote Sens 13(23):4764. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13234764
Traugott J, Holzapfel F, Sachs G (2010) Conceptual approach for precise relative positioning with miniaturized GPS loggers and experimental results. From: https://www.sto.nato.int/publications/STO%20Educational%20Notes/RTO-EN-SET-116-2010/EN-SET-116(2010)-04.pdf. Accessed 1 Feb 2010
Ulmer K, Hwang P, Disselkoen B, Wagner M (1995) Accurate azimuth from a single PLGR + GLS DoD GPS receiver using time relative positioning. In: Proceedings of ION GPS-95, Palm Springs, California, pp 1733–1741
Van Grass F, Soloviev A (2004) Precise velocity estimation using a stand-alone GPS receiver. Navigation 51(4):283–292. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.2161-4296.2004.tb00359.x
Wang H, Ou J, Yuan Y (2011) Strategy of Data Processing for GPS Rover and Reference Receivers Using Different Sampling Rates. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 49(3):1144–1149. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2010.2070509
Zangeneh-Nejad F, Amiri-Simkooei AR, Sharifi MA, Asgari J (2017) Cycle slip detection and repair of undifferenced single-frequency GPS carrier phase observations. GPS Solut 21(4):1593–1603. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-017-0633-6
Zhang L, Lv H, Wang D, Hou Y, Wu J (2015) Asynchronous RTK precise DGNSS positioning method for deriving a low-latency high-rate output. J Geod 89(7):641–653. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-015-0803-7
Acknowledgements
We are very grateful to the reviewers and editor for their helpful remarks in improving the manuscript. This study is financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2021YFC3000504), the Key Research and Development Program of Technology Evolution Plan of Hubei Province (Grant No. 2023BAB068), the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province, China (Grant No. 2024JJ8377), and the Research Foundation of the Department of Natural Resources of Hunan Province (Grant No. 20230104CH).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XZ and ZL wrote the main manuscript text; WT designed the structure and ideas of the paper; YW and YL conducted testing and verification and prepared Tables 1, 2; SZ and YZ assisted in completing data analysis and prepared all figures. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zou, X., Li, Z., Tang, W. et al. A real-time accuracy prediction model on time-relative positioning method considering the correlation of position increment errors. GPS Solut 28, 110 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-024-01654-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-024-01654-2