Abstract
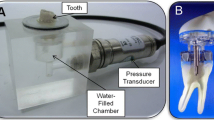
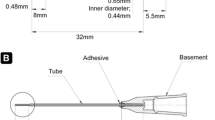
Apical pressure during root canal irrigation is regarded as a key factor affecting the risk of irrigant extrusion. The aim of this study was to examine the effect of apical size on the apical pressure by positive and negative pressure syringe-needle and multisonic negative pressure irrigation. An extracted maxillary first molar with two separate buccal roots, one palatal root and four canals was selected. The roots of the molar were fixed in a specially made apparatus to acquire the apical pressure of the four root canals separately. The apical sizes tested were from sizes 10, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 110. Multisonic negative pressure irrigation protocol was as recommended by the manufacturer (45 mL/min), syringe-needle irrigation was done using 30-G side-vented needle 3 mm from the working length at 5 mL/min as a conventional positive pressure irrigation (SNI), and as negative pressure irrigation (NPSNI) using suction. Apical pressure by SNI was measured also at 10 mL/min with an open-ended 30G needle, for the smallest and largest apical sizes. Apical pressures by SNI stayed positive, except when suction was used (NPSNI). The apical pressure by multisonic negative pressure irrigation remained negative in all situations. With increasing apical size, apical pressure by SNI decreased, whereas with multisonic negative pressure irrigation and NPSNI, it was not affected by apical size. Large apical size did not result in higher apical pressure values compared to small apical sizes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haapasalo M, Shen Y, Qian W, Gao Y. Irrigation in endodontics. Dent Clin N Am. 2010;54(2):291–312.
Azim AA, Aksel H, Jefferson MM, Huang GTJ. Comparison of sodium hypochlorite extrusion by five irrigation systems using an artificial root socket model and a quantitative chemical method. Clin Oral Invest. 2018;22(2):1055–61.
Kishor N. Oral tissue complications during endodontic irrigation-a literature review. NY St Dent J. 2013;79(3):37–42.
Guivarc’h M, Ordioni U, Ahmed HMA, et al. Sodium hypochlorite accident: a systematic review. J Endod. 2017;43(1):16–24.
Gu LS, Kim JR, Ling J, et al. Review of contemporary irrigant agitation techniques and devices. J Endod. 2009;35(6):791–804.
Gu LS, Kim JR, Ling J, Choi KK, Pashley DH, Tay FR. Review of contemporary irrigant agitation techniques and devices. J Endod. 2013;39(4):529–33.
Charara K, Friedman S, Sherman A, et al. Assessment of apical extrusion during root canal irrigation with the novel GentleWave system in a simulated apical environment. J Endod. 2016;42(1):135–9.
Haapasalo M, Shen Y, Wang Z, et al. Apical pressure created during irrigation with the GentleWaveTM system compared to conventional syringe irrigation. Clin Oral Investig. 2016;20(7):1525–34.
Boutsioukis C, Gogos C, Verhaagen B, Versluis M, Kastrinakis E, van der Sluis LWM. The effect of apical preparation size on irrigant flow in root canals evaluated using an unsteady computational fluid dynamics model. Int Endod J. 2010;43(10):874–81.
Boutsioukis C, Lambrianidis T, Verhaagen B, et al. The effect of needle-insertion depth on the irrigant flow in the root canal: evaluation using an unsteady computational fluid dynamics model. J Endod. 2010;36(10):1664–8.
Shen Y, Gao Y, Qian W, et al. Three-dimensional numeric simulation of root canal irrigant flow with different irrigation needles. J Endod. 2010;36(5):884–9.
Khan S, Niu L, Eid AA, et al. Periapical pressures developed by nonbinding irrigation needles at various irrigation delivery rates. J Endod. 2013;39(4):529–33.
Park E, Shen Y, Khakpour M, Haapasalo M. Apical pressure and extent of irrigant flow beyond the needle tip during positive-pressure irrigation in an in vitro root canal model. J Endod. 2013;39(4):511–5.
Yost RA, Bergeron BE, Kirkpatric TC, et al. Evaluation of 4 different irrigating systems for apical extrusion of sodium hypochlorite. J Endod. 2015;41(9):1530–4.
Huang Q, Barnes JB, Schoeffel GJ, et al. Effect of canal anastomosis on periapical fluid pressure build-up during needle irrigation in single roots with double canals using a polycarbonate model. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):1582.
Psimma Z, Boutsioukis C, Kastrinakis E, et al. Effect of needle insertion depth and root canal curvature on irrigant extrusion ex vivo. J Endod. 2013;39(4):521–4.
Acknowledgements
Supported by Canada Foundation for Innovation (CFI: 32623) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81873714).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
One of the authors (MH) consults to Sonendo Inc. and has a commercial interest in the product used for irrigation in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, B., Shen, Y., Ma, J. et al. Effect of apical size on apical pressure during syringe-needle and multisonic negative pressure irrigation. Odontology 109, 625–631 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10266-020-00586-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10266-020-00586-w