Abstract
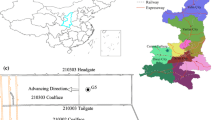
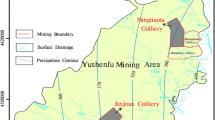
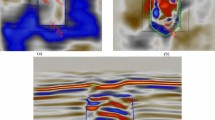
Formation of a zone of interconnected fractures during coal mining is a key factor in mine flooding. Coal mines in western China are characterized by thick coal seams with mechanically weak overburden. In situ studies including drill core analysis, drilling fluid loss measurement, and borehole video monitoring were used at the working face 101 in Shaanxi Jinjitan coal mine to explore the maximum height of the interconnected fractures zone (IFZ). Also, tests on a scaled physical model and numerical simulation based on the drilling data were used to study the formation of the fractured zone. By considering data from other mines with similar mining conditions, a logarithmic relationship was found between the maximum height of the IFZ and the thickness of coal excavation. The maximum height of the IFZ was found to be 27 times the thickness of the excavated coal seam, which is far more than in coal mining areas in eastern China. Also, the IFZ in overlying strata of the study area was arch-shaped, not saddle-shaped, as had been observed in previous studies.
Zusammenfassung
Die Ausbildung einer Zone von verbundenen Bruchzone während des Kohleabbaus ist ein Schlüsselfaktor bei der Grubenflutung. Die Kohlebergwerke in Westchina sind durch mächtige Kohleflöze und bruchanfälligem Deckgebirge charakterisiert. Diese unterscheiden sich deutlich von Kohlebergwerken in Ostchina. Vor-Ort-Untersuchungen, welche Bohrkernanalysen, Messung von Bohrspülungsverlusten und Kameraüberwachungen im Bohrloch beinhalteten, wurden am Arbeitsgebiet 101 im Shaanxi Jinjitan-Kohlebergwerk genutzt, um die maximale Ausdehnung der Bruchzone zu erkunden. Weiterhin wurden Tests an einem maßstabsgetreuen physikalischen Modell und numerische Modellrechnungen basierend auf den Bohrdaten durchgeführt, um die Bildung der Bruchzone zu untersuchen. Unter Berücksichtigung von Daten aus anderen Bergwerken mit ähnlichen Abbaubedingungen wurde eine logarithmische Beziehung zwischen der maximalen Ausdehnung der Bruchzone und der Mächtigkeit des Kohleabbaus gefunden. Die maximale Ausdehnung der Bruchzone beträgt demnach etwa das 27-fache der Mächtigkeit des abgebauten Kohleflözes, die damit deutlich größer ist als in den Kohlebergbaugebieten in Ostchina. Darüber hinaus war im Gegensatz zu früheren Studien die Bruchzone im Hangenden des Untersuchungsgebietes bogenförmig und nicht sattelförmig.
Resumen
La formación de una zona de fracturas interconectadas durante la explotación minera de carbón, es un factor clave en la inundación de la mina. Las minas de carbón en el este de China están caracterizadas por la presencia de gruesas vetas de carbón en rocas mecánicamente débiles, que difiere mucho de las minas de carbón en el este de China. Estudios in situ que incluyeron el análisis del corazón de la perforación, la medida de la pérdida de fluido en la perforación y el videomonitoreo del pozo, se usaron en la cara de trabajo 101 en la mina de carbón Shaanxi Jinjitan, para conocer la máxima altura de la zona de fracturas interconectadas (IFZ). Los ensayos sobre un modelo físico escalado y la simulación numérica sobre los datos de la perforación también fueron usados para estudiar la formación de la zona de fractura. Teniendo en cuenta datos de otras minas con iguales condiciones, se encontró una relación logarítmica entre la altura máxima del IFZ y el grosor de la excavación. La máxima altura del IFZ fue 27 veces mayor que el grosor de la veta de carbón excavada que es mucho mayor que la que se encuentra en áreas mineras del este de China. También, el IFZ en estratos superpuestos del área de estudio fue en forma de arco y no en forma de montura como fuera observado en estudios previos.
摘要
煤矿突水的一个重要因素是与矿井开采过程中形成的导水裂缝带(IFZ)有关。而在中国西部矿区具有煤厚、覆岩强度低等特点,与东部矿区有显著不同。为了探测位于中国西部的陕西金鸡滩煤矿开采101工作面形成的最大导水裂缝带高度,采用钻孔岩芯分析、钻孔冲洗液漏失量观测和钻孔彩色电视三种手段对其现场实测。同时,依据钻井数据建立物理模型和数值模型研究裂缝带的形成机理。结合周边其他相似矿区的裂缝带实测数据,发现西部矿区导水裂缝带高度与煤层开采厚度之间存在一个对数的关系,并且裂缝带最大高度可以达到27倍以上的采厚,其数值远高于东部矿区。另外,在所研究区域得到的裂缝带的发育形态为弧形,并非先前认为的马鞍形








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai M, Elsworth D (1990) Some aspects of mining under aquifers in China. Min Sci Tech 10(1):81–91
China Coal Industry Bureau (2000) Measuring method on height of water flowing fractured zone using losses of drilling fluid. Coal Ind Stand People’s Repub China MT/T 865–2000:1–3 [in Chinese]
Hu G, Li WP, Cheng W (2008) Study on the law of fractured full-mechanized caving mining in Huainan coal. Coal Eng 5:74–76 [in Chinese]
Kendorski FS (1993) Effect of high-extraction coal mining on surface and ground waters. In: Proceedings of the 12th conference ground control in mining, West Virginia University, Morgantown, WV, USA
Kratzsch H (1983) Mining subsidence engineering. Springer, Berlin
Liu TQ (1981) Coal Mine Ground Movement and Strata Failure. Coal Industry Publ House, Beijing [in Chinese]
Lv WH (2014) Measure and simulation for development height of water conducted crack zone in overburden roof. J Xi’an Univ Sci Technol 34(3):309–313 [in Chinese]
Ma YJ, Wu Q, Zhang ZY, Hong YQ, Guo LW, Tian HS, Zhang LG (2008) Research on prediction of water conducted fissure height in roof of coal mining seam. J China Coal Sci Technol 36(5):59–62 [in Chinese]
Ma XD, Wang WK, Zhu L (2010) Mining impact on springs in ecologically fragile area. J China Coal Geol 22(1):32–36 [in Chinese]
Palchik V (2002) Influence of physical characteristics of weak rock mass on height of caved zone over abandoned subsurface coal mines. Environ Geol 42(1):92–101
Peng SP, Zhang JC (2007) Engineering geology for underground rocks. Springer, Berlin
Ren W, Guo C, Peng Z, Wang Y (2010) Model experimental research on deformation and subsidence characteristics of ground and wall rock due to mining under thick overlying terrane. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 47:614–624
SAWS, SACMS (2009) Coal Mine Water Prevention and Control Regulations. China Coal Industry Publ House, Beijing. ISBN 978-7-5020-3586-0 [in Chinese]
Shen H, Coal Group Company (2012) Research of effect on groundwater resources and ecology by modern coal mining technology in Shendong mining area. China Univ Min Technol Press, Beijing [in Chinese]
Turchaninov IA, Iofis MA, Kasparian EV (1977) Principles of rock mechanics. Nedra, Leningrad
Venticinque GA (2013) Advanced numer`ical modeling of fracture propagation in rock. Univ of Wollongong, Australia
Wang YN (1982) Prediction of the height of water conducting fissured zone by amazing the stress distribution in overlying strata. J China Coal Soc 1:92–99 [in Chinese]
Wang Y (2013) Research on the technical scheme of coal mining under water-containing condition in Yushuwan coal mine. Xi’an Univ Sci Technol Press, Xi’an [in Chinese]
Wu K, Jin J, Dai Z, Jiang J (2002) An experimental study on the transmission of mining subsidence in soil. J China Coal Soc 27(06):601–603 [in Chinese]
Zhang YJ, Kang YH (2005) Summarize and estimation of the development on the exploration of overburden failure law. J China Coal Min Technol 10(2):10–12 [in Chinese]
Zhang JX, Jiang HQ, Deng XJ, Ju F (2014) Prediction of the height of the water-conducting zone above the mined panel in solid backfill mining. Mine Water Environ 33:317–326
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the support of Shaanxi Future Energy Company for this research. This research was financially supported by National Nature Science Foundation of China (41372290, 41402250), National Nature Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2013EEQ 019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, J., Wu, F., Yin, H. et al. Formation and Height of the Interconnected Fractures Zone after Extraction of Thick Coal Seams with Weak Overburden in Western China. Mine Water Environ 36, 59–66 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-016-0396-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-016-0396-2