Abstract
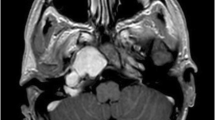
Giant intrapetrous internal carotid aneurysms (petrous ICA aneurysm) are rare. A giant petrous ICA aneurysm presenting with otorrhagia and coil exposure to the external auditory meatus (EAM) after endovascular treatment has never been documented before. The authors report here a case of successful surgical trapping with bypass intervention of a giant petrous ICA aneurysm presenting with coil exposure after endovascular treatment. A 58-year-old man presented with persistent otorrhagia having been admitted to our hospital because of the recurrence of a giant petrous ICA aneurysm after repeated embolization treatments with coils. An electronic otoscope examination demonstrated that a piece of coil escaped into his right EAM. After multidisciplinary consultation, an extracranial-intracranial (EC-IC) bypass with ICA occlusion and coil removal with a closed EAM filling were performed in stages. The patient recovered quickly without any neurological deficits. A digital subtraction angiography confirmed the absence of the aneurysm and patency of the bypass graft.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe H, Takemoto K, Higashi T, Inoue T (2011) Surgical treatment for aneurysms in the cavernous-petrous portion of the internal carotid artery. Acta Neurochir Suppl 112:77–83. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7091-0661-7_14
Akhtar MU, Akram M, Ahmed TM, Bhatti AM (2017) Superficial temporal artery-middle cerebral artery bypass for internal carotid artery petrous aneurysm: a case report. JPMA J Pak Med Assoc 67:128–130
Bien AG, Cress MC, Nguyen SB, Westgate SJ, Nanda A (2013) Endovascular treatment of a temporal bone pseudoaneurysm presenting as bloody otorrhea. J Neurol Surg Rep 74:88–91. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0033-1348954
Chen JB, Sun H, Zhou LX, He M, Lei D (2013) Successful endovascular treatment of carotid aneurysms in a patient with vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. J Neurol Surg Part A Cent Eur Neurosurg 74(Suppl 1):e85–e88. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0032-1322591
Cinar C, Bozkaya H, Parildar M, Oran I (2013) Endovascular management of vascular injury during transsphenoidal surgery. Interv Neuroradiol 19:102–109. https://doi.org/10.1177/159101991301900116
Cloft HJ, Kallmes DF (2002) Cerebral aneurysm perforations complicating therapy with Guglielmi detachable coils: a meta-analysis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1706–1709
Cohen JE, Grigoriadis S, Gomori JM (2007) Petrous carotid artery pseudoaneurysm in bilateral carotid fibromuscular dysplasia: treatment by means of self-expanding covered stent. Surg Neurol 68:216–220; discussion 220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surneu.2006.08.082
Couldwell WT, Zuback J, Onios E, Ahluwalia BS, Tenner M, Moscatello A (2001) Giant petrous carotid aneurysm treated by submandibular carotid-saphenous vein bypass: case report. J Neurosurg 94:806–810. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2001.94.5.0806
Depauw P, Defreyne L, Dewaele F, Caemaert J (2003) Endovascular treatment of a giant petrous internal carotid artery aneurysm. Case report and review of the literature. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 46:250–253. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2003-42358
Ferroli P, Bisleri G, Nakaji P, Albanese E, Acerbi F, Polvani G, Broggi G (2009) Endoscopic radial artery harvesting for U-clip EC-IC bypass in the treatment of a giant petrous internal carotid artery aneurysm: technical case report. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 52:186–189. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0028-1105901
Hamamoto Filho PT, Machado VC, Macedo-de-Freitas CC (2013) A giant aneurysm from the petrous carotid presenting with isolated peripheral facial palsy. Rev Assoc Med Bras 59:531–533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ramb.2013.07.004
Kadkhodayan Y, Shetty VS, Blackburn SL, Reynolds MR, Cross DT 3rd, Moran CJ (2013) Pipeline embolization device and subsequent vessel sacrifice for treatment of a bleeding carotid pseudoaneurysm at the skull base: a case report. J Neurointerv Surg 5:e31. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2012-010394
Mangat SS, Nayak H, Chandna A (2011) Horner’s syndrome and sixth nerve paresis secondary to a petrous internal carotid artery aneurysm. Semin Ophthalmol 26:23–24. https://doi.org/10.3109/08820538.2010.541321
Mascitelli JR, De Leacy RA, Oermann EK, Skovrlj B, Smouha EE, Ellozy SH, Patel AB (2014) Cervical-petrous internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysm presenting with otorrhagia treated with endovascular techniques. BMJ Case Rep. https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr-2014-011286
Mascitelli JR, De Leacy RA, Oermann EK, Skovrlj B, Smouha EE, Ellozy SH, Patel AB (2015) Cervical-petrous internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysm presenting with otorrhagia treated with endovascular techniques. J Neurointerv Surg 7:e25. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2014-011286.rep
Morantz RA, Kirchner FR, Kishore P (1976) Aneurysms of the petrous portion of the internal carotid artery. Surg Neurol 6:313–318
Orru E, Roccatagliata L, Cester G, Causin F, Castellan L (2013) Complications of endovascular treatment of cerebral aneurysms. Eur J Radiol 82:1653–1658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2012.12.011
Oyama H, Hattori K, Tanahashi S, Kito A, Maki H, Tanahashi K (2010) Ruptured pseudoaneurysm of the petrous internal carotid artery caused by chronic otitis media. Neurol Med Chir 50:578–580
Palacios E, Gomez J, Alvernia JE, Jacob C (2010) Aneurysm of the petrous portion of the internal carotid artery at the foramen lacerum: anatomic, imaging, and otologic findings. Ear, Nose, Throat J 89:303–305
Singh H, Thomas J, Hoe WL, Sethi DS (2008) Giant petrous carotid aneurysm: persistent epistaxis despite internal carotid artery ligation. J Laryngol Otol 122:e18. https://doi.org/10.1017/s002221510800282x
Tsang AC, Leung KM, Lee R, Lui WM, Leung GK (2015) Primary endovascular treatment of post-irradiated carotid pseudoaneurysm at the skull base with the pipeline embolization device. J Neurointerv Surg 7:603–607. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2014-011154
Wang B, Gao BL, Xu GP, Xiang C, Liu XS (2015) Endovascular embolization is applicable for large and giant intracranial aneurysms: experience in one center with long-term angiographic follow-up. Acta Radiol 56:105–113. https://doi.org/10.1177/0284185113520312
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Yin-Xia (Chief of the Otorhinolaryngology Department, Beijing Tiantan Hospital, Capital Medical University) for general support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethics approval
This report was approved by the patient and the institutional ethical review board of Beijing Tiantan Hospital.
Informed consent
The patient approved the publication of this case presentation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, LB., Zhang, D., Yang, SH. et al. Surgical management of giant intrapetrous internal carotid aneurysm presenting with coil exposure after endovascular treatment. Neurosurg Rev 41, 891–894 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-018-0964-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-018-0964-y