Abstract
Background
Aneurysms of the petrosal segment of the internal carotid artery are rare in children and are usually found secondary to trauma and infection or can have a congenital origin. Management includes endovascular therapy, surgery, and in rare cases observation.
Discussion
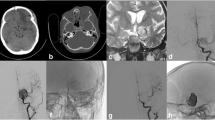
Here, we report our experience with a giant petrous internal carotid artery aneurysm in a 16-year-old boy successfully managed endovascularly by parent artery occlusion.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhtar MU, Akram M, Ahmed TM, Bhatti AM (2017) Superficial temporal artery - middle cerebral artery bypass for internal carotid artery petrous aneurysm: a case report. J Pak Med Assoc 67:128–130
Auyeung KM, Lui WM, Chow LC, Chan FL (2003) Massive epistaxis related to petrous carotid artery pseudoaneurysm after radiation therapy: emergency treatment with covered stent in two cases. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1449–1452
Busby DR, Slemmons DH, TFJ M (1968) Fatal epistaxis via carotid aneurysm and eustachian tube. Arch Otolaryngol 87:295–298
Cohen JE, Grigoriadis S, Gomori JM (2007) Petrous carotid artery pseudoaneurysm in bilateral carotid fibromuscular dysplasia: treatment by means of self-expanding covered stent. Surg Neurol 68:216–220
Coley SC, Clifton A, Britton J (1998) Giant aneurysm of the petrous internal carotid artery: diagnosis and treatment. J Laryngol Otol 112:196–198
Conley J, Hildyard V (1969) Aneurysm of the internal carotid artery presenting in the middle ear. Arch Otolaryngol 90(1):35–38
Date I, Sugiu K, Ohmoto T (1999) A giant thrombosed aneurysm of the petrous carotid artery presenting with cavernous sinus syndrome: case report. Skull Base Surg 9:65–70
De Witte, Cross DT 3rd, Moran CJ, Brown AP, Oser AB, Goldberg DE, Diego J (1995) Endovascular treatment of epistaxis in a patient with tuberculosis and a giant petrous carotid pseudoaneurysm. AJNR 16:1084–1086
Depauw P, Defreyne L, Dewaele F, Caemaert J (2003) Endovascular treatment of a giant petrous internal carotid artery aneurysm. Case report and review of the literature. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 46:250–253
Frank E, Brown BM, Wilson DF (1989) Asymptomatic fusiform aneurysm of the petrous carotid artery in a patient with von Recklinghausen’s neurofibromatosis. Surg Neurol 32:75–78
Gross BA, Moon K, Ducruet AF, Albuquerque FC (2017) A rare but morbid neurosurgical target: petrous aneurysms and their endovascular management in the stent/flow diverter era. J Neurointerv Surg 9:381–383. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2016-012668
Guha A, Montanera W, Hoffman HJ (1990) Congenital aneurismal dilatation of the petrous-cavernous carotid artery and vertebral basilar junction in a child. Neurosurgery 26:322–327
Guirguis S, Tadros FW (1961) An internal carotid aneurysm in the petrous temporal bone. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 24:84–85
Gum GK, Nadell JA, Numaguchi Y, Robinson AE (1998) Giant aneurysms of bilateral internal carotid arteries in a child. Childs Nerv Syst 4:161–163
Halbach VV, Higashida RT, Hieshima GB, Dowd CF, Barnwell SL, Edwards MS, Melicharek M (1990) Aneurysms of the petrous portion of the internal carotid artery: results of treatment with endovascular or surgical occlusion. AJNR 11:253–257
Lee SH, Jang JH, Kim KH, Kim YZ (2015) Stent-assisted coil embolization of petrous ICA in a teenager with neurofibromatosis. J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg 17:252–256. https://doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2015.17.3.252
Liu JK, Gottfried ON, Amini A, Couldwell WT (2004) Aneurysms of the petrous internal carotid artery: anatomy, origins, and treatment. Neurosurg Focus 15:1–9
Mangat SS, Nayak H, Chandna A (2011) Horner’s syndrome and sixth nerve paresis secondary to a petrous internal carotid artery aneurysm. Semin Ophthalmol 26:23–24. https://doi.org/10.3109/08820538.2010.541321
Mascitelli JR, De Leacy RA, Oermann EK, Skovrlj B, Smouha EE, Ellozy SH, Patel AB (2014) Cervical-petrous internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysm presenting with otorrhagia treated with endovascular techniques. BMJ Case Rep 30:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr-2014-011286
Mukherjee P, Huilgol R, Graham A, Fagan P (2016) Open and endovascular repair of aneurysms affecting the distal extracranial internal carotid artery: case series. J Laryngol Otol 130(4):S29–S34. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022215116000694
Oyama H, Hattori K, Tanahashi S, Kito A, Maki H, Tanahashi K (2010) Ruptured pseudoaneurysm of the petrous internal carotid artery caused by chronic otitis media. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 50:578–580
Stallings JO, McCabe BF (1969) Congenital middle ear aneurysm of internal carotid. Arch Otolaryngol 90:39–43
Tranmer BI, Humphreys RP, Chuang SH (1985) Microsurgical recovery of a migrated balloon from the internal carotid artery of a child. Neurosurgery 16:381–386
Vasama JP, Ramsay H, Markkola A (2001) Petrous internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysm due to gunshot injury. Ann Othol Rhinol Laryngol 110:491–493
Wemple JB, Smith GW (1966) Extracranial carotid aneurysm. J Neurosurg 24:667–671
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 13 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Borha, A., Patron, V., Huet, H. et al. Endovascular management of a giant petrous internal carotid artery aneurysm in a child. Case report and literature review. Childs Nerv Syst 35, 183–186 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-018-3941-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-018-3941-4