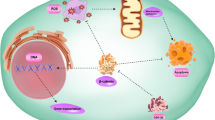
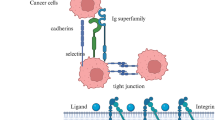
Abstract
Metastasis is a multi-step process that leads to the dissemination of tumor cells to new sites and, consequently, to multi-organ neoplasia. Although most lethal breast cancer cases are related to metastasis occurrence, little is known about the dysregulation of each step, and clinicians still lack reliable therapeutic targets for metastasis impairment. To fill these gaps, we constructed and analyzed gene regulatory networks for each metastasis step (cell adhesion loss, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, and angiogenesis). Through topological analysis, we identified E2F1, EGR1, EZH2, JUN, TP63, and miR-200c-3p as general hub-regulators, FLI1 for cell-adhesion loss specifically, and TRIM28, TCF3, and miR-429 for angiogenesis. Applying the FANMOD algorithm, we identified 60 coherent feed-forward loops regulating metastasis-related genes associated with distant metastasis-free survival prediction. miR-139-5p, miR-200c-3p, miR-454-3p, and miR-1301-3p, among others, were the FFL’s mediators. The expression of the regulators and mediators was observed to impact overall survival and to go along with metastasis occurrence. Lastly, we selected 12 key regulators and observed that they are potential therapeutic targets for canonical and candidate antineoplastics and immunomodulatory drugs, like trastuzumab, goserelin, and calcitriol. Our results highlight the relevance of miRNAs in mediating feed-forward loops and regulating the expression of metastasis-related genes. Altogether, our results contribute to understanding the multi-step metastasis complexity and identifying novel therapeutic targets and drugs for breast cancer management.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data utilized in this research are freely available in the referenced databases.
References
Agarwal R, Mori Y, Cheng Y et al (2009) Silencing of claudin-11 is associated with increased invasiveness of gastric cancer cells. PLoS One 4:e8002. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0008002
Ahirwar DK, Charan M, Mishra S et al (2021) Slit2 inhibits breast cancer metastasis by activating M1-like phagocytic and anti-fibrotic macrophages. Cancer Res 81:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-3909
Andrés-León E, Cases I, Alonso S, Rojas AM (2017) Novel miRNA-mRNA interactions conserved in essential cancer pathways. Sci Rep 7:46101. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep46101
Andrés-León E, Peña DG, Gómez-López G, Pisano DG (2015) MiRGate: a curated database of human, mouse and rat miRNA-mRNA targets. Database. Bav035 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1093/database/bav035
Barabási AL, Oltvai ZN (2004) Network biology: understanding the cell’s functional organization. Nat Rev Genet 5:101–113. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg1272
Bo C, Zhang H, Cao Y et al (2021) Construction of a TF–miRNA–gene feed-forward loop network predicts biomarkers and potential drugs for myasthenia gravis. Sci Rep 11:2416. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-81962-6
Brinton LT, Brentnall TA, Smith JA, Kelly KA (2012) Metastatic biomarker discovery through proteomics. Cancer Genomics Proteomics 9:345–356
Chen YW, Chou HC, Lyu PC et al (2011) Mitochondrial proteomics analysis of tumorigenic and metastatic breast cancer markers. Funct Integr Genomics 11:225–239. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-011-0210-y
Chénais B, Cornec M, Dumont S et al (2020) Transcriptomic response of breast cancer cells MDA-MB-231 to docosahexaenoic acid: downregulation of lipid and cholesterol metabolism genes and upregulation of genes of the pro-apoptotic er-stress pathway. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17:3746. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17103746
Cheng S, Huang Y, Lou C et al (2019) FSTL1 enhances chemoresistance and maintains stemness in breast cancer cells via integrin β3/Wnt signaling under miR-137 regulation. Cancer Biol Ther 20:328–337. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384047.2018.1529101
Chin CH, Chen SH, Wu HH et al (2014) cytoHubba: Identifying hub objects and sub-networks from complex interactome. BMC Syst Biol 8:S11. https://doi.org/10.1186/1752-0509-8-S4-S11
Cho C-Y, Lee K-T, Chen W-C et al (2016) MST3 promotes proliferation and tumorigenicity through the VAV2/Rac1 signal axis in breast cancer. Oncotarget 7:12. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.7542
Cockshott ID (2000) Clinical pharmacokinetics of goserelin. Clin Pharmacokinet 39(1):27–48. https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-200039010-00003
Colden M, Dar AA, Saini S et al (2017) MicroRNA-466 inhibits tumor growth and bone metastasis in prostate cancer by direct regulation of osteogenic transcription factor RUNX2. Cell Death Dis 8:e2572. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2017.15
Dujon AM, Capp JP, Brown JS et al (2021) Is there one key step in the metastatic cascade? Cancers (Basel) 13:3693. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13153693
Gray RJ (2002) Modeling survival data: extending the Cox model. J Am Stat Assoc 97:353–354. https://doi.org/10.1198/jasa.2002.s447
Grottke A, Ewald F, Lange T et al (2016) Downregulation of AKT3 increases migration and metastasis in triple negative breast cancer cells by upregulating S100A4. PLoS One 11:e0146370. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0146370
He K, Li WX, Guan D et al (2019) Regulatory network reconstruction of five essential microRNAs for survival analysis in breast cancer by integrating miRNA and mRNA expression datasets. Funct Integr Genomics 19:645–658. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-019-00670-7
He Y, Davies CM, Harrington BS et al (2020) CDCP1 enhances Wnt signaling in colorectal cancer promoting nuclear localization of β-catenin and E-cadherin. Oncogene 39:219–233. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-019-0983-3
Huang J, Sun Y, Chen H et al (2019) ADAMTS5 acts as a tumor suppressor by inhibiting migration, invasion and angiogenesis in human gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer 22:287–301. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10120-018-0866-2
Hulsbergen AFC, Claes A, Kavouridis VK et al (2020) Subtype switching in breast cancer brain metastases: a multicenter analysis. Neuro Oncol 22:1173–1181. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/noaa013
Jin H, Liu P, Kong L et al (2019) Identification of re1-silencing transcription factor as a promoter of metastasis in pancreatic cancer. Front Oncol 9:291. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2019.00291
Jurmeister S, Baumann M, Balwierz A et al (2012) MicroRNA-200c represses migration and invasion of breast cancer cells by targeting actin-regulatory proteins FHOD1 and PPM1F. Mol Cell Biol 32:633–651. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.06212-11
Kravchenko DS, Frolova EI, Kravchenko JE, Chumakov SP (2016) Role of PDLIM4 and c-Src in breast cancer progression. Mol Biol 50:59–68. https://doi.org/10.1134/S002689331601009X
Krishnan K, Steptoe AL, Martin HC et al (2013) miR-139-5p is a regulator of metastatic pathways in breast cancer. RNA 19:1767–1780. https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.042143.113
Lánczky A, Győrffy B (2021) Web-based survival analysis tool tailored for medical research (KMplot): development and implementation. J Med Internet Res 23:e27633. https://doi.org/10.2196/27633
Li R, Qu H, Wang S et al (2018) GDCRNATools: an R/bioconductor package for integrative analysis of lncRNA, miRNA and mRNA data in GDC. Bioinformatics 34:2515–2517. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty124
Liang J, Chen M, Hughes D et al (2018) CDK8 selectively promotes the growth of colon cancer metastases in the liver by regulating gene expression of TIMP3 and matrix metalloproteinases. Cancer Res 78:6594–6606. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-1583
Liberzon A, Birger C, Thorvaldsdóttir H et al (2015) The molecular signatures database hallmark gene set collection. Cell Syst 1:417–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cels.2015.12.004
Lignitto L, LeBoeuf SE, Homer H et al (2019) Nrf2 Activation Promotes Lung Cancer Metastasis by Inhibiting the Degradation of Bach1. Cell 178:316–329.e18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2019.06.003
Liu X, Wang S, Meng F et al (2013) SM2miR: a database of the experimentally validated small molecules’ effects on microRNA expression. Bioinformatics 29:409–411. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts698
Martin TA, Ye L, Lane J, Jiang WG (2013) Cancer invasion and metastasis: molecular and cellular perspective. In: Jandial R, Hunter K (eds) On: metastatic cancer: integrated organ system and biological approach. Clinical and Biological Perspectives. Landes Bioscience, Austin, TX, pp 135–168
Matsunuma R, Chan DW, Kim BJ et al (2018) DPYSL3 modulates mitosis, migration, and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in claudin-low breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115:E11978–E11987. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1810598115
Mohammad T, Singh P, Jairajpuri DS et al (2022) Differential gene expression and weighted correlation network dynamics in high-throughput datasets of prostate cancer. Front Oncol 12:881246. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.881246
Moore HCF, Unger JM, Phillips K-A et al (2015) Goserelin for ovarian protection during breast-cancer adjuvant chemotherapy. N Engl J Med 372:923–932. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1413204
Parra E, Ferreira J (2010) The effect of siRNA-Egr-1 and camptothecin on growth and chemosensitivity of breast cancer cell lines. Oncol Rep 23:1159–1165. https://doi.org/10.3892/or_00000746
Qu W, Shi S, Sun L et al (2018) Construction of a microRNA-associated feed-forward loop network that identifies regulators of cardiac hypertrophy and acute myocardial infarction. Int J Mol Med 42:2062–2070. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2018.3790
Rody A, Loibl S, von Minckwitz G, Kaufmann M (2005) Use of goserelin in the treatment of breast cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 5:591–604. https://doi.org/10.1586/14737140.5.4.591
Rouillard AD, Gundersen GW, Fernandez NF et al (2016) The harmonizome: a collection of processed datasets gathered to serve and mine knowledge about genes and proteins. Database (Oxford) 2016:baw100. https://doi.org/10.1093/database/baw100
Saha SK, Riazul Islam SM, Saha T et al (2021) Prognostic role of EGR1 in breast cancer: a systematic review. BMB Rep 54:497–504. https://doi.org/10.5483/BMBRep.2021.54.10.087
Seyfried TN, Huysentruyt LC (2013) On the origin of cancer metastasis. Crit Rev Oncog 18(1–2):43–73. https://doi.org/10.1615/critrevoncog.v18.i1-2.40
Shang S, Ji X, Zhang L et al (2019) Macrophage ABHD5 suppresses NFκB-dependent matrix metalloproteinase expression and cancer metastasis. Cancer Res 79:5513–5526. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-1059
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O et al (2003) Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res 13:2498–2504. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.1239303
Shivram H, Le SV, Iyer VR (2019) MicroRNAs reinforce repression of PRC2 transcriptional targets independently and through a feed-forward regulatory network. Genome Res 29:184–192. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.238311.118
Spugnini EP, Logozzi M, di Raimo R et al (2018) A role of tumor-released exosomes in paracrine dissemination and metastasis. Int J Mol Sci 19:3968. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123968
Steeg PS, Theodorescu D (2008) Metastasis: a therapeutic target for cancer. Nat Clin Pract Oncol 5:206–219. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncponc1066
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL et al (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71:209–249. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660
Wang L, Zhang S, Wang X (2021a) The Metabolic Mechanisms of Breast Cancer Metastasis. Front Oncol 10:602416. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.602416
Wang S, Pei L, Hu T et al (2021b) Protective effect of goserelin on ovarian reserve during (neo)adjuvant chemotherapy in young breast cancer patients: a prospective cohort study in China. Human Reproduction 36:976–986. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/deaa349
Wang Y, Xu H, Zhu B et al (2018) Systematic identification of the key candidate genes in breast cancer stroma. Cell Mol Biol Lett 23:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11658-018-0110-4
Wei L-L, Wu X-J, Gong C-C, Pei D-S (2017) Egr-1 suppresses breast cancer cells proliferation by arresting cell cycle progression via down-regulating cyclins. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 10(10):10212–10222
Weinstein JN, Collisson EA, Mills GB et al (2013) The cancer genome atlas pan-cancer analysis project. Nat Genet 45:1113–1120. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2764
Wernicke S, Rasche F (2006) FANMOD: A tool for fast network motif detection. Bioinformatics 22:1152–1153. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btl038
Wishart DS, Knox C, Guo AC et al (2008) DrugBank: a knowledgebase for drugs, drug actions and drug targets. Nucleic Acids Res 36:D901-6. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkm958
Wong KM, Song J, Wong YH (2021) CTCF and EGR1 suppress breast cancer cell migration through transcriptional control of Nm23-H1. Sci Rep 11:491. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-79869-9
Zhang G, Zhang W, Li B et al (2017) MicroRNA-200c and microRNA- 141 are regulated by a FOXP3-KAT2B axis and associated with tumor metastasis in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Research 19:1–3. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13058-017-0858-x
Zhang HM, Kuang S, Xiong X et al (2013) Transcription factor and microRNA co-regulatory loops: Important regulatory motifs in biological processes and diseases. Brief Bioinform 16:45–58. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbt085
Zhang XD, Song J, Bork P, Zhao XM (2016) The exploration of network motifs as potential drug targets from post-translational regulatory networks. Sci Rep 6:1–2. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep20558
Zhang YL, Xing X, Cai LB et al (2018) Integrin α9 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by rho GTPase signaling. J Immunol Res, eCollection 2018. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/4602570
Zhao L, Gu C, Ye M et al (2018) Integration analysis of microRNA and mRNA paired expression profiling identifies deregulated microRNA-transcription factor-gene regulatory networks in ovarian endometriosis. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 16:4. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12958-017-0319-5
Zheng JZ, Huang YN, Yao L et al (2018) Elevated miR-301a expression indicates a poor prognosis for breast cancer patients. Sci Rep 8:2225. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-20680-y
Funding
This research was funded by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior-Brasil (CAPES) and Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) Process: 408730/2018-8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Alexandre Luiz Korte de Azevedo: conceptualization, formal analysis, investigation, writing—original draft, and visualization. Tamyres Mingorance Carvalho: formal analysis, investigation, and writing—original draft. Cristiane Sato Mara and Igor Samesima Giner: formal analysis and investigation. Daniela Fiore Gradia, Jaqueline Carvalho de Oliveira, Enilze Maria de Souza Fonseca Ribeiro, and Iglenir João Cavalli: conceptualization, writing—review and editing, and supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
All authors agree for publication
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(ZIP 8440 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
de Azevedo, A.L.K., Carvalho, T.M., Mara, C.S. et al. Major regulators of the multi-step metastatic process are potential therapeutic targets for breast cancer management. Funct Integr Genomics 23, 171 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01097-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01097-x