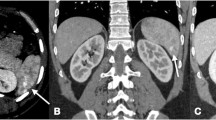
Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to review and compare the image quality and radiation dose of split-bolus single-pass computed tomography(CT) in the assessment of trauma patients in comparison to standard multi-phase CT techniques.
Methods
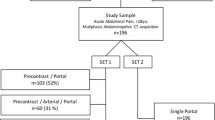
An online electronic database was searched using the MESH terms “split-bolus,” “dual phase,” and “single pass.” Inclusion criteria required the research article to compare a split contrast bolus protocol in a single-pass scan in the assessment of trauma patients. Studies using split-bolus CT technique in non-traumatic injury assessment were excluded. Six articles met the inclusion criteria.
Conclusions
Parenchymal and vascular image qualities, as well as subjective image quality assessments, were equal or superior in comparison to non-split-bolus multi-phase trauma CT protocols. Split-bolus single-pass CT decreased radiation exposure in all studies. Further research is required to determine the superior split-bolus protocol and the specificity and sensitivity of detecting blunt cerebrovascular injury screening, splenic parenchymal vascular lesions, and characterization of pelvic vascular extravasation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huber-Wagner S, Biberthaler P, Haberle S, Wierer M, Dobritz M, Rummeny E, van Griensven M, Kanz KG, Lefering R, TraumaRegister DGU (2013) Whole-body CT in haemodynamically unstable severely injured patients—a retrospective, multicentre study. PLoS One 8(7):e68880. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0068880
Huber-Wagner S, Lefering R, Qvick LM, Korner M, Kay MV, Pfeifer KJ, Reiser M, Mutschler W, Kanz KG, Working Group on Polytrauma of the German Trauma S (2009) Effect of whole-body CT during trauma resuscitation on survival: a retrospective, multicentre study. Lancet 373(9673):1455–1461. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60232-4
Sierink JC, Saltzherr TP, Beenen LF, Luitse JS, Hollmann MW, Reitsma JB, Edwards MJ, Hohmann J, Beuker BJ, Patka P, Suliburk JW, Dijkgraaf MG, Goslings JC, Group R-s (2012) A multicenter, randomized controlled trial of immediate total-body CT scanning in trauma patients (REACT-2). BMC Emerg Med 12:4. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-227X-12-4
Sierink JC, Saltzherr TP, Beenen LF, Luitse JS, Hollmann MW, Reitsma JB, Edwards MJ, Patka P, Beuker BJ, Suliburk JW, Hohmann J, Dijkgraaf MG, Goslings JC, Group R-S (2012) Randomised, controlled trial of immediate total-body computed tomography scanning in trauma patients. Emerg Med Australas 24(3):350–351. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-6723.2012.01558.x
Sierink JC, Saltzherr TP, Reitsma JB, Van Delden OM, Luitse JS, Goslings JC (2012) Systematic review and meta-analysis of immediate total-body computed tomography compared with selective radiological imaging of injured patients. Br J Surg 99(Suppl 1):52–58. https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs.7760
10 Leading Causes of Death by Age Group, United States (2014) Web-based Injury Statistics Query Reporting System [WISQARS] (2014) National Center for Injury Prevention and Control, CDC using WISQARS. Accessed Last reviewed February 25, 2016
Leung V, Sastry A, Woo TD, Jones HR (2015) Implementation of a split-bolus single-pass CT protocol at a UK major trauma centre to reduce excess radiation dose in trauma pan-CT. Clin Radiol 70(10):1110–1115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crad.2015.05.014
Stengel D, Ottersbach C, Matthes G, Weigeldt M, Grundei S, Rademacher G, Tittel A, Mutze S, Ekkernkamp A, Frank M, Schmucker U, Seifert J (2012) Accuracy of single-pass whole-body computed tomography for detection of injuries in patients with major blunt trauma. CMAJ 184(8):869–876. https://doi.org/10.1503/cmaj.111420
Pearce MS, Salotti JA, Little MP, McHugh K, Lee C, Kim KP, Howe NL, Ronckers CM, Rajaraman P, Sir Craft AW, Parker L, Berrington de Gonzalez A (2012) Radiation exposure from CT scans in childhood and subsequent risk of leukaemia and brain tumours: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet 380(9840):499–505. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60815-0
Mathews JD, Forsythe AV, Brady Z, Butler MW, Goergen SK, Byrnes GB, Giles GG, Wallace AB, Anderson PR, Guiver TA, McGale P, Cain TM, Dowty JG, Bickerstaffe AC, Darby SC (2013) Cancer risk in 680,000 people exposed to computed tomography scans in childhood or adolescence: data linkage study of 11 million Australians. BMJ 346:f2360. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.f2360
Hinzpeter R, Boehm T, Boll D, Constantin C, Del Grande F, Fretz V, Leschka S, Ohletz T, Bronnimann M, Schmidt S, Treumann T, Poletti PA, Alkadhi H (2016) Imaging algorithms and CT protocols in trauma patients: survey of Swiss emergency centers. Eur Radiol 27:1922–1928. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-016-4574-1
Beenen LF, Sierink JC, Kolkman S, Nio CY, Saltzherr TP, Dijkgraaf MG, Goslings JC (2015) Split bolus technique in polytrauma: a prospective study on scan protocols for trauma analysis. Acta Radiol 56(7):873–880. https://doi.org/10.1177/0284185114539319
Loupatatzis C, Schindera S, Gralla J, Hoppe H, Bittner J, Schroder R, Srivastav S, Bonel HM (2008) Whole-body computed tomography for multiple traumas using a triphasic injection protocol. Eur Radiol 18(6):1206–1214. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-008-0875-3
Stedman JM, Franklin JM, Nicholl H, Anderson EM, Moore NR (2014) Splenic parenchymal heterogeneity at dual-bolus single-acquisition CT in polytrauma patients-6-months experience from Oxford, UK. Emerg Radiol 21(3):257–260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10140-013-1186-9
Yaniv G, Portnoy O, Simon D, Bader S, Konen E, Guranda L (2013) Revised protocol for whole-body CT for multi-trauma patients applying triphasic injection followed by a single-pass scan on a 64-MDCT. Clin Radiol 68(7):668–675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crad.2012.12.011
Biffl WL, Moore EE, Offner PJ, Brega KE, Franciose RJ, Elliott JP, Burch JM (1999) Optimizing screening for blunt cerebrovascular injuries. Am J Surg 178(6):517–522
Burlew CC, Biffl WL, Moore EE, Barnett CC, Johnson JL, Bensard DD (2012) Blunt cerebrovascular injuries: redefining screening criteria in the era of noninvasive diagnosis. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 72(2):330–335; discussion 336-337, quiz 539. https://doi.org/10.1097/TA.0b013e31823de8a0
Geddes AE, Burlew CC, Wagenaar AE, Biffl WL, Johnson JL, Pieracci FM, Campion EM, Moore EE (2016) Expanded screening criteria for blunt cerebrovascular injury: a bigger impact than anticipated. Am J Surg 212(6):1167–1174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjsurg.2016.09.016
Miller PR, Fabian TC, Croce MA, Cagiannos C, Williams JS, Vang M, Qaisi WG, Felker RE, Timmons SD (2002) Prospective screening for blunt cerebrovascular injuries: analysis of diagnostic modalities and outcomes. Ann Surg 236(3):386–393; discussion 393-385. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.SLA.0000027174.01008.A0
Boscak AR, Shanmuganathan K, Mirvis SE, Fleiter TR, Miller LA, Sliker CW, Steenburg SD, Alexander M (2013) Optimizing trauma multidetector CT protocol for blunt splenic injury: need for arterial and portal venous phase scans. Radiology 268(1):79–88. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.13121370
Biffl WL, Cothren CC, Moore EE, Kozar R, Cocanour C, Davis JW, McIntyre RC Jr, West MA, Moore FA (2009) Western trauma association critical decisions in trauma: screening for and treatment of blunt cerebrovascular injuries. J Trauma 67(6):1150–1153. https://doi.org/10.1097/TA.0b013e3181c1c1d6
Eastman AL, Muraliraj V, Sperry JL, Minei JP (2009) CTA-based screening reduces time to diagnosis and stroke rate in blunt cervical vascular injury. J Trauma 67(3):551–556; discussion 555-556. https://doi.org/10.1097/TA.0b013e3181b84408
Roberts DJ, Chaubey VP, Zygun DA, Lorenzetti D, Faris PD, Ball CG, Kirkpatrick AW, James MT (2013) Diagnostic accuracy of computed tomographic angiography for blunt cerebrovascular injury detection in trauma patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Surg 257(4):621–632. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0b013e318288c514
Nguyen D, Platon A, Shanmuganathan K, Mirvis SE, Becker CD, Poletti PA (2009) Evaluation of a single-pass continuous whole-body 16-MDCT protocol for patients with polytrauma. AJR Am J Roentgenol 192(1):3–10. https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.07.3702
Bruns BR, Tesoriero R, Kufera J, Sliker C, Laser A, Scalea TM, Stein DM (2014) Blunt cerebrovascular injury screening guidelines: what are we willing to miss? J Trauma Acute Care Surg 76(3):691–695. https://doi.org/10.1097/TA.0b013e3182ab1b4d
Gunn ML (2012) Imaging of aortic and branch vessel trauma. Radiol Clin N Am 50(1):85–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rcl.2011.08.002
Platt JF, Glazer GM (1988) IV contrast material for abdominal CT: comparison of three methods of administration. AJR Am J Roentgenol 151(2):275–277. https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.151.2.275
Cademartiri F, Mollet NR, van der Lugt A, McFadden EP, Stijnen T, de Feyter PJ, Krestin GP (2005) Intravenous contrast material administration at helical 16-detector row CT coronary angiography: effect of iodine concentration on vascular attenuation. Radiology 236(2):661–665. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2362040468
Uyeda JW, LeBedis CA, Penn DR, Soto JA, Anderson SW (2014) Active hemorrhage and vascular injuries in splenic trauma: utility of the arterial phase in multidetector CT. Radiology 270(1):99–106. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.13121242
Soto JA, Anderson SW (2012) Multidetector CT of blunt abdominal trauma. Radiology 265(3):678–693. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.12120354
Marovic P, Beech PA, Koukounaras J, Kavnoudias H, Goh GS (2017) Accuracy of dual bolus single acquisition computed tomography in the diagnosis and grading of adult traumatic splenic parenchymal and vascular injury. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol 61(6):725–731. https://doi.org/10.1111/1754-9485.12619
Anderson SW, Soto JA, Lucey BC, Burke PA, Hirsch EF, Rhea JT (2008) Blunt trauma: feasibility and clinical utility of pelvic CT angiography performed with 64-detector row CT. Radiology 246(2):410–419. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2462070082
Godt JC, Eken T, Schulz A, Johansen CK, Aarsnes A, Dormagen JB (2018) Triple-split-bolus versus single-bolus CT in abdominal trauma patients: a comparative study. Acta Radiol 284185117752522. https://doi.org/10.1177/0284185117752522
Scialpi M, Pierotti L, Gravante S, Rebonato A, Piscioli I, D’Andrea A, Schiavone R, Palumbo B (2016) Split-bolus multidetector-row computed tomography technique for characterization of focal liver lesions in oncologic patients. Iran J Radiol 13(2):e20143. https://doi.org/10.5812/iranjradiol.20143
Hakim W, Kamanahalli R, Dick E, Bharwani N, Fetherston S, Kashef E (2016) Trauma whole-body MDCT: an assessment of image quality in conventional dual-phase and modified biphasic injection. Br J Radiol 89(1063):20160160. https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr.20160160
Sedlic A, Chingkoe CM, Tso DK, Galea-Soler S, Nicolaou S (2013) Rapid imaging protocol in trauma: a whole-body dual-source CT scan. Emerg Radiol 20(5):401–408. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10140-013-1139-3
Gunn ML, Kool DR, Lehnert BE (2015) Improving outcomes in the patient with polytrauma: a review of the role of whole-body computed tomography. Radiol Clin N Am 53(4):639–656, vii. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rcl.2015.02.006
Hutter M, Woltmann A, Hierholzer C, Gartner C, Buhren V, Stengel D (2011) Association between a single-pass whole-body computed tomography policy and survival after blunt major trauma: a retrospective cohort study. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med 19:73. https://doi.org/10.1186/1757-7241-19-73
Healy DA, Hegarty A, Feeley I, Clarke-Moloney M, Grace PA, Walsh SR (2014) Systematic review and meta-analysis of routine total body CT compared with selective CT in trauma patients. Emerg Med J 31(2):101–108. https://doi.org/10.1136/emermed-2012-201892
Wurmb TE, Quaisser C, Balling H, Kredel M, Muellenbach R, Kenn W, Roewer N, Brederlau J (2011) Whole-body multislice computed tomography (MSCT) improves trauma care in patients requiring surgery after multiple trauma. Emerg Med J 28(4):300–304. https://doi.org/10.1136/emj.2009.082164
Beenen LF, Scheerder MJ, Veling EA, De Jong VM, Bredebeke-Kaufmann D, Lobe N (2017) Whole body CT protocols in mass casualty incidents. Paper presented at the American Society of Emergency Radiology 2017 annual scientific meeting and postgraduate course. Toronto, Ontario, Canada, September 6-9
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Author Dr. Martin Gunn contributes to Research Support for Philips Healthcare, USA. The other authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeavons, C., Hacking, C., Beenen, L.F. et al. A review of split-bolus single-pass CT in the assessment of trauma patients. Emerg Radiol 25, 367–374 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10140-018-1591-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10140-018-1591-1