Abstract
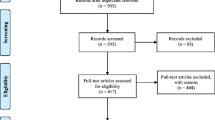
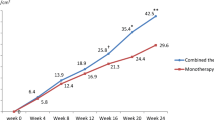
Laser sources have established their potential effect in inducing hair regrowth. No large cohort study has evaluated the effect of ablative fractional 2940-nm erbium yttrium aluminum garnet (Er: YAG) laser in the treatment of androgenetic alopecia (AGA). To investigate the efficacy and safety of the ablative fractional 2940-nm Er: YAG laser in combination with medication therapy for the treatment of AGA. We performed a retrospective study between first July 2021 to 30th December 2021. All included patients received oral finasteride and topical minoxidil, or combined with six sessions of Er: YAG laser at 2-week intervals. Patients were divided into medication or combined therapy groups. The efficacy of the two therapies was evaluated by the investigator’s Global Assessment (IGA) scores and the patient’s Likert satisfaction scale at week 12 and week 24. Changes in total, terminal and villous hair count, total and terminal hair diameter, and AGA grade were also recorded. Adverse events were evaluated at each follow-up. A total of 192 male patients with AGA were included, including 67 receiving combination treatment, and 125 receiving medication treatment. At week 24, the combination treatment afforded superior outcomes in the IGA score, patient’s global assessment, total and terminal hair counts, and diameters (all P<0.05). No severe adverse events were reported in both groups. The combined therapy of ablative fractional Er: YAG laser and medication was superior in treating male AGA than single medication therapy without serious adverse effects.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are not publicly available due to the privacy of research participants but are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Kanti V, Messenger A, Dobos G, Reygagne P, Finner A, Blumeyer A et al (2018) Evidence-based (S3) guideline for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia in women and in men - short version. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 32:11–22. https://doi.org/10.1111/jdv.14624
Huang CH, Fu Y, Chi CC (2021) Health-related quality of life, depression, and self-esteem in patients with androgenetic alopecia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol 157:963–970. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.2196
Adil A, Godwin M (2017) The effectiveness of treatments for androgenetic alopecia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol 77(136–41e5). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2017.02.054
Gupta AK, Bamimore MA, Foley KA (2022) Efficacy of non-surgical treatments for androgenetic alopecia in men and women: a systematic review with network meta-analyses, and an assessment of evidence quality. J Dermatolog Treat 33:62–72. https://doi.org/10.1080/09546634.2020.1749547
Manabe M, Tsuboi R, Itami S, Osada SI, Amoh Y, Ito T et al (2017) Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of male-pattern and female-pattern hair loss. J Dermatol 45:1031–1043. https://doi.org/10.1111/1346-8138.14470
Lee GY, Lee SJ, Kim WS (2011) The effect of a 1550 nm fractional erbium-glass laser in female pattern hair loss. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 25:1450–1454. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-3083.2011.04183.x
Suchonwanit P, Rojhirunsakool S, Khunkhet S (2019) A randomized, investigator-blinded, controlled, split-scalp study of the efficacy and safety of a 1550-nm fractional erbium-glass laser, used in combination with topical 5% minoxidil versus 5% minoxidil alone, for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia. Lasers Med Sci 34:1857–1864. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-019-02783-8
Day D, McCarthy M, Talaber I (2022) Non-ablative Er:YAG laser is an effective tool in the treatment arsenal of androgenetic alopecia. J Cosmet Dermatol 21:2056–2063. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocd.14370
Su YP, Wu XJ (2022) Ablative 2940 nm Er: YAG fractional laser for male androgenetic alopecia. Dermatol Ther 35:e15801. https://doi.org/10.1111/dth.15801
Cho SB, Goo BL, Zheng Z, Yoo KH, Kang JS, Kim H (2018) Therapeutic efficacy and safety of a 1927-nm fractionated thulium laser on pattern hair loss: an evaluator-blinded, split-scalp study. Lasers Med Sci 33:851–859. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-018-2437-5
Salah M, Samy N, Fawzy MM, Farrag AR, Shehata H, Hany A (2022) The effect of the fractional carbon dioxide laser on improving minoxidil delivery for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia. J Lasers Med Sci 11:29–36. https://doi.org/10.15171/jlms.2020.06
Bae JM, Jung HM, Goo B, Park YM (2015) Hair regrowth through wound healing process after ablative fractional laser treatment in a murine model. Lasers Surg Med 47:433–440. https://doi.org/10.1002/lsm.22358
Meephansan J, Ungpraphakorn N, Ponnikorn S, Suchonwanit P, Poovorawan Y (2018) Efficacy of 1,550-nm erbium-glass fractional laser treatment and its effect on the expression of insulin-like growth factor 1 and Wnt/β-Catenin in androgenetic alopecia. Dermatol Surg 44:1295–1303. https://doi.org/10.1097/DSS.0000000000001619
Connolly D, Vu HL, Mariwalla K, Saedi N (2017) Acne scarring-pathogenesis, evaluation, and treatment options. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol 10:12–23
Walsh JT Jr, Flotte TJ, Deutsch TF (1989) Er:YAG laser ablation of tissue: effect of pulse duration and tissue type on thermal damage. Lasers Surg Med 9:314–326. https://doi.org/10.1002/lsm.1900090403
Langley RG, Feldman SR, Nyirady J, van de Kerkhof P, Papavassilis C (2015) The 5-point Investigator’s Global Assessment (IGA) Scale: a modified tool for evaluating plaque psoriasis severity in clinical trials. J Dermatolog Treat 26:23–31. https://doi.org/10.3109/09546634.2013.865009
Dourado GB, Volpato GH, de Almeida-Pedrin RR, Pedron Oltramari PV, Freire Fernandes TM, de Castro Ferreira Conti AC (2021) Likert scale vs visual analog scale for assessing facial pleasantness. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop 160:844–852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajodo.2020.05.024
Katzer T, Leite Junior A, Beck R, da Silva C (2019) Physiopathology and current treatments of androgenetic alopecia: going beyond androgens and anti-androgens. Dermatol Ther 32:e13059. https://doi.org/10.1111/dth.13059
Devjani S, Ezemma O, Kelley KJ, Stratton E, Senna M (2023) Androgenetic alopecia: therapy update. Drugs 83:701–715. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-023-01880-x
Wat H, Wu DC, Chan HH (2017) Fractional resurfacing in the Asian patient: current state of the art. Lasers Surg Med 49:45–59. https://doi.org/10.1002/lsm.22579
Verma N, Yumeen S, Raggio BS (2023) Ablative Laser Resurfacing. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Treasure Island (FL):Last Update: April 23, 2023
Ke J, Guan H, Li S, Xu L, Zhang L, Yan Y (2015) Erbium: YAG laser (2,940 nm) treatment stimulates hair growth through upregulating wnt 10b and β-catenin expression in C57BL/6 mice. Int J Clin Exp Med 8:20883–20889
Perper M, Aldahan AS, Fayne RA, Emerson CP, Nouri K (2017) Efficacy of fractional lasers in treating alopecia: a literature review. Lasers Med Sci 32:1919–1925. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-017-2306-7
Nieboer MJ, Meesters AA, Almasian M, Georgiou G, de Rie MA, Verdaasdonk RM et al (2022) Enhanced topical cutaneous delivery of indocyanine green after various pretreatment regimens: comparison of fractional CO2 laser, fractional Er:YAG laser, microneedling, and radiofrequency. Lasers Med Sci 35:1357–1365. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-020-02950-2
Funding
This research was funded by Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82103754 and 82373503).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RD, XY and XW contributions to conception and design of study, analysis and interpretation of data. RD and YS involved in acquisition of data and implementing of the research. RD wrote the manuscript. XW gave final approval of the version to be published. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the Human Ethics Committee of Zhejiang University School of Medicine Second Affiliated Hospital (IRB-2021-1686) and performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dai, R., Yang, X., Su, Y. et al. Effectiveness and safety of the ablative fractional 2940-nm Er: YAG laser for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia. Lasers Med Sci 39, 128 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-024-04074-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-024-04074-3