Abstract
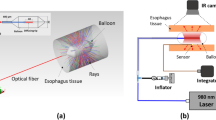
Barrett’s esophagus (BE) is associated with an intestinal metaplasia that replaces normal squamous epithelium by columnar epithelium. The aim of the current study was to evaluate the feasible endoscopic treatment on esophageal tissue with circumferential laser irradiation. A 532-nm laser was used to deliver 10 W in a continuous manner through a balloon catheter-integrated diffuser. Ex vivo leporine esophagus was tested to identify thermal responses at various irradiation times. In vivo testing in a porcine model was performed to evaluate the feasibility of endoscopic application with the integrated device for BE treatment. Goniometric measurements confirmed that the proposed device yielded uniform radial irradiation (i.e., 0.9 ± 0.1 in arbitrary unit). Emission profiles were well correlated with temperature distribution along the device. Ex vivo leporine testing demonstrated that the temperature rise increased with irradiation time. The maximum temperature increase was around 38 °C after 60-s irradiation (transient increase rate = 0.62 °C/s), and the corresponding thermal coagulation reached esophageal submucosa (1.5 ± 0.2 mm). In vivo porcine testing evidently presented circumferential thermal denaturation around the lumen along with mild inflammatory reaction and the degenerated squamous epithelium. The overall thickness of the irreversible thermal coagulation was 3.1 ± 0.2 mm. The proposed photothermal therapy can be a feasible endoscopic method to treat BE with the aid of circumferential irradiation and mechanical expansion. Further chronic in vivo testing will be pursued to understand chronic tissue response in terms of wound healing and complication.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coleman HG, Bhat SK, Murray LJ, McManus DT, O'Neill OM, Gavin AT, Johnston BT (2014) Symptoms and endoscopic features at barrett's esophagus diagnosis: implications for neoplastic progression risk. Am J Gastroenterol 109(4):527–534. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2014.10
Shaheen NJ, Falk GW, Iyer PG, Gerson LB (2016) ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Barrett's Esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol 111(1):30–50. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2015.322
Boeckxstaens G, El-Serag HB, Smout AJ, Kahrilas PJ (2014) Symptomatic reflux disease: the present, the past and the future. Gut 63(7):1185–1193. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2013-306393
El-Serag HB, Sweet S, Winchester CC, Dent J (2014) Update on the epidemiology of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: a systematic review. Gut 63(6):871–880. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2012-304269
Eloubeidi MA, Mason AC, Desmond RA, El-Serag HB (2003) Temporal trends (1973-1997) in survival of patients with esophageal adenocarcinoma in the United States: a glimmer of hope? Am J Gastroenterol 98(7):1627–1633. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1572-0241.2003.07454.x
Mitry E, Rachet B, Quinn MJ, Cooper N, Coleman MP (2008) Survival from cancer of the oesophagus in England and Wales up to 2001. Br J Cancer 99(Suppl 1):S11–S13. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6604572
Domper Arnal MJ, Ferrandez Arenas A, Lanas Arbeloa A (2015) Esophageal cancer: Risk factors, screening and endoscopic treatment in Western and Eastern countries. World J Gastroenterol 21(26):7933–7943. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i26.7933
Tomizawa Y, Iyer PG, Wong Kee Song LM, Buttar NS, Lutzke LS, Wang KK (2013) Safety of endoscopic mucosal resection for Barrett's esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol 108(9):1440–1447. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2013.187
Garman KS, Shaheen NJ (2011) Ablative therapies for Barrett's esophagus. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 13(3):226–239. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11894-011-0182-z
Phoa KN, Pouw RE, van Vilsteren FGI, Sondermeijer CMT, Ten Kate FJW, Visser M, Meijer SL, van Berge Henegouwen MI, Weusten B, Schoon EJ, Mallant-Hent RC, Bergman J (2013) Remission of Barrett's esophagus with early neoplasia 5 years after radiofrequency ablation with endoscopic resection: a Netherlands cohort study. Gastroenterology 145(1):96–104. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2013.03.046
Dumot J (2013) The use of cryotherapy for treatment of barrett esophagus. Gastroenterol Hepatol 9(12):811–813
Sanchez A, Reza M, Blasco JA, Callejo D (2010) Effectiveness, safety, and cost-effectiveness of photodynamic therapy in Barrett's esophagus: a systematic review. Dis Esophagus 23(8):633–640. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1442-2050.2010.01078.x
Sengupta N, Ketwaroo GA, Bak DM, Kedar V, Chuttani R, Berzin TM, Sawhney MS, Pleskow DK (2015) Salvage cryotherapy after failed radiofrequency ablation for Barrett's esophagus-related dysplasia is safe and effective. Gastrointest Endosc 82(3):443–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2015.01.033
Ertan A, Zaheer I, Correa AM, Thosani N, Blackmon SH (2013) Photodynamic therapy vs radiofrequency ablation for Barrett's dysplasia: efficacy, safety and cost-comparison. World J Gastroenterol 19(41):7106–7113. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i41.7106
Nguyen TH, Rhee YH, Ahn JC, Kang HW (2015) Circumferential irradiation for interstitial coagulation of urethral stricture. Opt Express 23(16):20829–20840. https://doi.org/10.1364/oe.23.020829
Lee HS, Kim SW, Oak C, Ahn YC, Kang HW, Chun BK, Lee KD (2015) Rabbit model of tracheal stenosis induced by prolonged endotracheal intubation using a segmented tube. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 79(12):2384–2388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2015.10.049
Bak J, Kang HW (2017) Temperature-monitored optical treatment for radial tissue expansion. Lasers Med Sci 32(5):993–999. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-017-2199-5
Bak J, Hwang J, Park S, Kang HW (2017) Integration of optical applicator with balloon catheter for photothermal treatment of biliary stricture. Lasers Surg Med 49(8):781–786. https://doi.org/10.1002/lsm.22688
Truong VG, Tran VN, Hwang J, Kang HW (2018) Effect of spatial light distribution on the thermal response of vascular tissue. Biomed Opt Express 9(7):3037–3048. https://doi.org/10.1364/boe.9.003037
Welch AJ, van Gemert MJC (1995) Optical-thermal response of laser-irradiated tissue. Plenum Press, New York
Abdelhamid A, Jouini M, Bel Haj Amor H, Mzoughi Z, Dridi M, Ben Said R, Bouraoui A (2018) Phytochemical Analysis and Evaluation of the Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, and Antinociceptive Potential of Phlorotannin-Rich Fractions from Three Mediterranean Brown Seaweeds. Mar Biotechnol 20(1):60–74. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-017-9787-z
Acknowledgment
This research was supported by a grant of the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (grant number: HI16C1017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeong, S., Bak, J., Kim, S.M. et al. Feasibility study of endoscopic thermal coagulation with circumferential laser irradiation for treating esophageal tissue . Lasers Med Sci 35, 893–900 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-019-02877-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-019-02877-3