Abstract
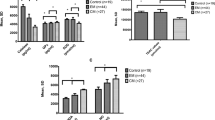
Tension-type headache (TTH) is one of the most common and costly primary types of headache in clinical practice, with an unknown etiology. This study assessed to investigate oxidative and antioxidative status in patients with chronic tension-type headache (CTTH), and to evaluate possible effect of medical treatment. The study included 41 CTTH patients and 19 age- and sex-matched healthy subjects without headache as controls. The CTTH group comprised 20 patients receiving treatment and 21 untreated patients. We evaluated oxidant/antioxidant status by measuring serum malondialdehyde (MDA) levels and activities of antioxidant enzymes, namely glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) and catalase (CAT). Comparison of oxidative parameters in the patient and control groups revealed significantly lower CAT activities and higher MDA level and GSH-Px activities in the patient group. In the CTTH group, serum CAT activities were found to be significantly decreased in patient groups, while serum MDA levels and GSH-Px activities were found to be higher in the untreated CTTH patients. These findings suggest that oxidative stress is increased in the patients with CTTH, and medical treatment abolishes the stress in part. It has been concluded that antioxidant support might be helpful for the patients with CTTH to prevent oxidant stress and peroxidation damages further.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lj Stovner, Hagen K, Jensen R, Katsarava Z, Lipton R, Scher A et al (2007) The global burden of headache: a documentation of headache prevalence and disability worldwide. Cephalalgia 27(3):193–210
Rasmussen BK (2001) Epidemiology of headache. Cephalalgia 21:774–777
Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (1988) Classification and diagnostic criteria for headache disorders, cranial neuralgias and facial pain. Cephalalgia 8(Suppl 7):1–96
Headache Classification Subcommittee of the International Headache Society (2004) The international classification of headache disorders. Cephalalgia 24(Suppl 1):1–160
Bendtsen L, Jensen R (2006) Tension-type headache: the most common, but also the most neglected, headache disorder. Curr Opin Neurol 19:305–309
Bendtsen L (2000) Central sensitization in tension-type headache–possible pathophysiological mechanisms. Cephalalgia 20(5):486–508
Dahle LK, Hill EG, Holman RT (1962) The thiobarbituric acid reaction and the autoxidations of polyunsaturated fatty acid methyl esters. Arch Biochem Biophys 98:53–261
Aebi H (1974) Catalase. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) Methods of enzymatic analysis. Academic Press, New York, pp 673–677
Paglia DE, Valentine WN (1967) Studies on the quantitative and qualitative characterization of erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase. J Lab Clin Med 70(1):158–169
Jensen R, Symon D (2005) Epidemiology of tension-type headaches. In: Olesen J, Goadsby PJ, Ramadan N et al (eds) The Headaches, 3rd edn. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 621–624
Fernandez-de-Las-Peñas C, Cuadrado ML, Arendt-Nielsen L, Ge HY, Pareja JA (2007) Increased pericranial tenderness, decreased pressure pain threshold, and headache clinical parameters in chronic tension-type headache patients. Clin J Pain 23(4):346–352
Buchgreitz L, Lyngberg AC, Bendtsen L, Jensen R (2007) Increased prevalence of tension-type headache over a 12-year period is related to increased pain sensitivity. A population study. Cephalalgia 27(2):145–152
Bendtsen L, Evers S, Linde M, Mitsikostas DD, Sandrini G, Schoenen J, EFNS (2010) EFNS guideline on the treatment of tension-type headache–report of an EFNS task force. Eur J Neurol 17(11):1318–1325
Moja PL, Cusi C, Sterzi RR, Canepari C (2005) Selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitors (SSRIs) for preventing migraine and tension-type headaches. Cochrane Datab Syst Rev 3:19
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC (1999) Free radicals in biology and medicine, 3rd edn. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Rao AL, Bharani M, Pallavi V (2006) Role of antioxidants and free radicals in health and disease. Adv Pharmacol Toxicol 7:29–38
Boćkowski L, Sobaniec W, Kulak W, Smigielska-Kuzia J (2008) Serum and intraerythrocyte antioxidant enzymes and lipid peroxides in children with migraine. Pharmacol Rep 60:542–548
Gaweł S, Wardas M, Niedworok E, Wardas P (2004) Malondialdehyde (MDA) as a lipid peroxidation marker. Wiad Lek 57(9–10):453–455
Witztum JL (1994) The oxidation hypothesis of atherosclerosis. Lancet 344(8925):793–795
Gupta R, Pathak R, Bhatia MS, Banerjee BD (2009) Comparison of oxidative stress among migraineurs, tension-type headache subjects, and a control group. Ann Indian Acad Neurol 12(3):167–172
Shimomura T, Kowa H, Nakano T, Kitano A, Marukawa H, Urakami K et al (1994) Platelet superoxide dismutase in migraine and tension-type headache. Cephalalgia 14:215–218
Bolayir E, Celik K, Kugu N, Yilmaz A, Topaktas S, Bakir S (2004) Intraerythrocyte antioxidant enzyme activities in migraine and tension-type headaches. J Chin Med Assoc 67(6):263–267
Neyal M, Yimenicioglu F, Aydeniz A, Taskin A, Saglam S, Cekmen M et al (2013) Plasma nitrite levels, total antioxidant status, total oxidant status, and oxidative stress index in patients with tension-type headache and fibromyalgia. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 115(6):736–740
Acknowledgments
The authors had no funding sources for this study.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed on human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gökçe Çokal, B., Aytaç, B., Durak, Z.E. et al. Serum oxidant and antioxidant status of patients with chronic tension-type headache: possible effects of medical treatment. Neurol Sci 36, 1771–1775 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-015-2240-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-015-2240-z