Abstract
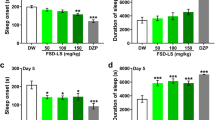
γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA), a primary inhibitory neurotransmitter, and tryptophan (Trp), a substrate for melatonin, are found in functional foods and exert hypnotic effects. The hypnotic effects of 3 doses of GABA and a combined-preparation of GABA and Trp (GABA+Trp) were investigated in mice. Hypnotic activity was evaluated using pentothal-induced sleep time testing. Treatments included low, middle, and high doses of GABA and GABA+Trp. Low doses of GABA (low-GABA) and low-GABA+Trp reduced sleep latency and significantly (p<0.05) prolonged the sleep time induced by pentothal, compared with controls, although the melatonin concentration in the serum was not affected. On the other hand, the adenosine A1 receptor (AA1R) immunoreactivity in the suprachiasmatic nucleus of the hypothalamus was significantly (p<0.05) increased after administration of low-GABA and/or low-GABA+Trp, compared to controls. Low doses of GABA and/or Trp cause hypnotic effects that may be related to AA1R activation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Watanabe M, Maemura K, Kanbara K, Tamayama T, Hayasaki H. GABA and GABA receptors in the central nervous system and other organs. Int. Rev. Cytol. 213: 1–47 (2002)
Rodrigo-Angulo ML, Heredero S, Rodriguez-Veiga E, Reinoso-Suarez F. GABAergic and non-GABAergic thalamic, hypothalamic and basal forebrain projections to the ventral oral pontine reticular nucleus: Their implication in REM sleep modulation. Brain Res. 1210: 116–125 (2008)
Wang Y, Zhan L, Zeng W, Li K, Sun W, Xu ZC, Xu E. Downregulation of hippocampal GABA after hypoxia-induced seizures in neonatal rats. Neurochem. Res. 36: 2409–2416 (2011)
Bagosi Z, Jaszberenyi M, Telegdy G. The effects of endomorphins on striatal [3H]GABA release induced by electrical stimulation: An in vitro superfusion study in rats. Neurochem. Res. 34: 905–908 (2009)
Zhang H, Yao HY, Chen F. Accumulation of gamma-aminobutyric acid in rice germ using protease. Biosci. Biotech. Bioch. 70: 1160–1165 (2006)
Inoue K, Shirai T, Ochiai H, Kasao M, Hayakawa K, Kimura M, Sansawa H. Blood-pressure-lowering effect of a novel fermented milk containing gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in mild hypertensives. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 57: 490–495 (2003)
Abdou AM, Higashiguchi S, Horie K, Kim M, Hatta H, Yokogoshi H. Relaxation and immunity enhancement effects of gammaaminobutyric acid (GABA) administration in humans. Biofactors 26: 201–208 (2006)
Yoto A, Murao S, Motoki M, Yokoyama Y, Horie N, Takeshima K, Masuda K, Kim M, Yokogoshi H. Oral intake of gamma-aminobutyric acid affects mood and activities of central nervous system during stressed condition induced by mental tasks. Amino Acids 43: 1331–1337 (2012)
Hartmann E. Effects of L-tryptophan on sleepiness and on sleep. J. Psychiatr. Res. 17: 107–113 (1982)
Silber BY, Schmitt JA. Effects of tryptophan loading on human cognition, mood, and sleep. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 34: 387–407 (2010)
dos Santos TS, Meneghelli C, Hoeller AA, Paschoalini MA, Arckens L, Lino-de-Oliveira C, Marino-Neto J. Behavioral profile and Fos activation of serotonergic and non-serotonergic raphe neurons after central injections of serotonin in the pigeon (Columba livia). Behav. Brain Res. 220: 173–184 (2011)
Szabo N, Kincses ZT, Toldi J, Vecsei L. Altered tryptophan metabolism in Parkinson’s disease: A possible novel therapeutic approach. J. Neurol. Sci. 310: 256–260 (2011)
Feria-Velasco A, Mena-Munguia S, Carabez-Torres J, Gomez-Medrano A, Recendiz-Hurtado F, Orozco-Suarez S, Beas-Zarate C. Low tryptophan and protein in the diet during development increase the susceptibility to convulsions in adult rats. Neurochem. Res. 33: 1484–1491 (2008)
Markus CR, Firk C, Gerhardt C, Kloek J, Smolders GF. Effect of different tryptophan sources on amino acids availability to the brain and mood in healthy volunteers. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 201: 107–114 (2008)
Steinberg LA, O’Connell NC, Hatch TF, Picciano MF, Birch LL. Tryptophan intake influences infants’ sleep latency. J. Nutr. 122: 1781–1791 (1992)
Srinivasan V, Pandi-Perumal SR, Trahkt I, Spence DW, Poeggeler B, Hardeland R, Cardinali DP. Melatonin and melatonergic drugs on sleep: possible mechanisms of action. Int. J. Neurosci. 119: 821–846 (2009)
Doghramji K. The epidemiology and diagnosis of insomnia. Am. J. Manag. Care. 12: S214–S220 (2006)
Roth T, Drake C. Evolution of insomnia: Current status and future direction. Sleep Med. 5(Suppl. 1): S23–S30 (2004)
Fang X, Hao JF, Zhou HY, Zhu LX, Wang JH, Song FQ. Pharmacological studies on the sedative-hypnotic effect of Semen Ziziphi spinosae (Suanzaoren) and Radix et Rhizoma Salviae miltiorrhizae (Danshen) extracts and the synergistic effect of their combinations. Phytomedicine 17: 75–80 (2010)
Gyllenhaal C, Merritt SL, Peterson SD, Block KI, Gochenour T. Efficacy and safety of herbal stimulants and sedatives in sleep disorders. Sleep Med. Rev. 4: 229–251 (2000)
Darias V, Abdala S, Martin-Herrera D, Tello ML, Vega S. CNS effects of a series of 1,2,4-triazolyl heterocarboxylic derivatives. Pharmazie 53: 477–481 (1998)
Ma Y, Ma H, Eun JS, Nam SY, Kim YB, Hong JT, Lee MK, Oh KW. Methanol extract of Longanae Arillus augments pentobarbitalinduced sleep behaviors through the modification of GABAergic systems. J. Ethnopharmacol. 122: 245–250 (2009)
Lee CH, Park JH, Yoo KY, Choi JH, Hwang IK, Ryu PD, Kim DH, Kwon YG, Kim YM, Won MH. Pre- and post-treatments with escitalopram protect against experimental ischemic neuronal damage via regulation of BDNF expression and oxidative stress. Exp. Neurol. 229: 450–459 (2011)
Gottesmann C. GABA mechanisms and sleep. Neuroscience. 111: 231–239 (2002)
Borja NL, Daniel KL. Ramelteon for the treatment of insomnia. Clin. Ther. 28: 1540–1555 (2006)
Lu J, Greco MA. Sleep circuitry and the hypnotic mechanism of GABAA drugs. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2: S19–S26 (2006)
Beulens JW, Bindels JG, de Graaf C, Alles MS, Wouters-Wesseling W. Alpha-lactalbumin combined with a regular diet increases plasma Trp-LNAA ratio. Physiol. Behav. 81: 585–593 (2004)
Basheer R, Strecker RE, Thakkar MM, McCarley RW. Adenosine and sleep-wake regulation. Prog. Neurobiol. 73: 379–396 (2004)
Zhang J, Yin D, Wu F, Zhang G, Jiang C, Li Z, Wang L, Wang K. Microinjection of adenosine into the hypothalamic ventrolateral preoptic area enhances wakefulness via the A1 receptor in rats. Neurochem. Res. 38: 1616–1623 (2013)
Liu ZW, Gao XB. Adenosine inhibits activity of hypocretin/orexin neurons by the A1 receptor in the lateral hypothalamus: A possible sleep-promoting effect. J. Neurophysiol. 97: 837–848 (2007)
Sodickson DL, Bean BP. Neurotransmitter activation of inwardly rectifying potassium current in dissociated hippocampal CA3 neurons: Interactions among multiple receptors. J. Neurosci. 18: 8153–8162 (1998)
Dunwiddie TV, Masino SA. The role and regulation of adenosine in the central nervous system. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 24: 31–55 (2001)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahn, J.H., Im, C., Park, J.H. et al. Hypnotic effect of GABA from rice germ and/or tryptophan in a mouse model of pentothal-induced sleep. Food Sci Biotechnol 23, 1683–1688 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-014-0229-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-014-0229-7