Abstract
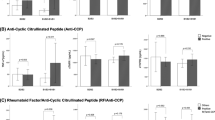
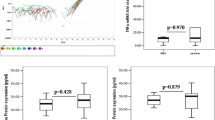
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a severely disabling chronic autoimmune disorder that leads to progressive inflammation of the joints and surrounding tissues. TNF-α, a potent proinflammatory cytokine, plays a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of RA. The endogenous formation of TNF-α may be influenced by TNF-α promoter polymorphisms. Hence, the present study was designed to explore any possible association between genetic polymorphism of TNF-α -308 G/A, messenger RNA (mRNA) expression, serum levels of TNF-α, and inflammatory markers in North Indian RA patients. A total of 214 controls and 187 RA patients were recruited according to the revised American College of Rheumatology 2010 criteria. TNF-α -308 G/A genetic polymorphism within promoter region was analyzed by using PCR-RFLP. Levels of inflammatory markers and serum TNF-α were estimated by ELISA. The mRNA expression of TNF-α gene was measured by quantitative real-time PCR. Higher levels of autoantibodies (RF and anti-CCP) were present in RA patients as compared to controls. We found a positive and significant correlation of circulating TNF-α levels with RF (r = 0.18), anti-CCP (r = 0.16), and mRNA expression of TNF-α gene (r = 0.57) in RA patients. The mRNA expression levels of TNF-α was 4.5-fold higher in patients with RA as compared to controls. The heterozygous mutant variants (G/A) and homozygous mutant variants (A/A) were found to be significantly associated with RA as compared to control (OR = 1.52 and 3.02, respectively). Our observations illustrated a significant association of allele -308 A TNF-α with progression of RA. Significant and positive correlation of TNF-α levels with mRNA expression and inflammatory marker levels suggests that serum TNF-α may be a susceptibility marker for RA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gibofsky A (2012) Overview of epidemiology, pathophysiology, and diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Manag Care 18(13 Suppl):S295–S302
Malaviya AN, Kapoor SK, Singh RR, Kumar A, Pande I (1993) Prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in the adult Indian population. Rheumatol Int 13(4):131–134
Yamamoto K, Okada Y, Suzuki A, Kochi Y (2015) Genetic studies of rheumatoid arthritis. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci 91(8):410
Barton A, Worthington J (2009) Genetic susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis: an emerging picture. Arthritis Care Res 61(10):1441–1446
Shafia S, Dilafroze SFA, Rasool R, Javeed S, Shah ZA (2014) Rheumatoid arthritis and genetic variations in cytokine genes: a population-based study in Kashmir Valley. Immunol Investig 43(4):349–359.
Harrison P, Pointon J, Chapman K, Roddam A, Wordsworth B (2008) Interleukin-1 promoter region polymorphism role in rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis of IL-1B-511A/G variant reveals association with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 47(12):1768–1770
Barton A, Platt H, Salway F, Symmons D, Barrett E, Bukhari M, Lunt M, Zeggini E, Eyre S, Hinks A (2004) Polymorphisms in the tumour necrosis factor gene are not associated with severity of inflammatory polyarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 63(3):280–284
Aguillón JC, Cruzat A, Aravena O, Salazar L, Llanos C, Cuchacovich M (2006) Could single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) affecting the tumour necrosis factor promoter be considered as part of rheumatoid arthritis evolution? Immunobiology 211(1):75–84
Song GG, Bae S-C, Kim J-H, Lee YH (2014) Association between TNF-α promoter –308 A/G polymorphism and rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis. Rheumatol Int 34(4):465–471
Hayashi K, Piras V, Tabata S, Tomita M, Selvarajoo K (2013) A systems biology approach to suppress TNF-induced proinflammatory gene expressions. Cell Commun Signal 11(1):84
Zhang B-B, Liu X-Z, Sun J, Yin Y-W, Sun Q-Q (2013) Association between TNF α gene polymorphisms and the risk of duodenal ulcer: a meta-analysis. PLoS One 8(2):e57167
Elahi MM, Asotra K, Matata BM, Mastana SS (2009) Tumor necrosis factor alpha− 308 gene locus promoter polymorphism: an analysis of association with health and disease. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) - Mol Basis Dis 1792(3):163–172
Keffer J, Probert L, Cazlaris H, Georgopoulos S, Kaslaris E, Kioussis D, Kollias G (1991) Transgenic mice expressing human tumour necrosis factor: a predictive genetic model of arthritis. EMBO J 10(13):4025
Feldmann M, Maini RN (2003) TNF defined as a therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune diseases. Nat Med 9(10):1245–1250
Mariaselvam CM, Sofiane S, Boukouaci W, Fortier C, Charron D, Krishnamoorthy R, Tamouza R, Negi VS (2014) TNF alpha promoter polymorphism may confer susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis and influence TNF alpha production but not the clinical phenotype and treatment response. J Mol Biomark Diagn 5(6):1
Nakano K, Boyle DL, Firestein GS (2013) Regulation of DNA methylation in rheumatoid arthritis synoviocytes. J Immunol 190(3):1297–1303
Kay J, Calabrese L (2004) The role of interleukin-1 in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology-Oxford 43(3):iii2
Rodríguez-Rodríguez L, González-Juanatey C, Palomino-Morales R, Vázquez-Rodríguez TR, Miranda-Filloy JA, Fernández-Gutiérrez B, Llorca J, Martin J, González-Gay MA (2011) TNFA− 308 (rs1800629) polymorphism is associated with a higher risk of cardiovascular disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Atherosclerosis 216(1):125–130
Ramos-Payán R, Aguilar-Medina M, Estrada-Parra S, González-y-Merchand J, Favila-Castillo L, Monroy-Ostria A, Estrada-Garcia ICE (2003) Quantification of cytokine gene expression using an economical real-time polymerase chain reaction method based on SYBR® Green I. Scand J Immunol 57(5):439–445
Myasoedova E, Kremers HM, Fitz-Gibbon P, Crowson C, Therneau T, Gabriel S (2009) Lipid profile improves with the onset of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 68 (Suppl3):78
Toms TE, Symmons DP, Kitas GD (2010) Dyslipidaemia in rheumatoid arthritis: the role of inflammation, drugs, lifestyle and genetic factors. Curr Vasc Pharmacol 8(3):301–326
Matuszewska A, Madej M, Wiland P (2015) Immunological markers of rheumatoid arthritis. Postepy Higi Med Dosw (Online) 70:251–257
Dörner T, Egerer K, Feist E, Burmester GR (2004) Rheumatoid factor revisited. Curr Opin Rheumatol 16(3):246–253
Aletaha D, Alasti F, Smolen JS (2015) Rheumatoid factor, not antibodies against citrullinated proteins, is associated with baseline disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis clinical trials. Arthritis Res Ther 17(1):229
Arnab B, Biswadip G, Arindam P, Shyamash M, Anirban G, Rajan P (2013) Anti-CCP antibody in patients with established rheumatoid arthritis: does it predict adverse cardiovascular profile? J Cardiovasc Dis Res 4(2):102–106
Shafiaa S, Shaha Z, Sofib F, Rasoola R, Gulla A (2016) Anti-CCP is associated with greater disease burden in Kashmiri population with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Sunnyvale) 6(190):2161–1149.1000190
Mjaavatten MD, van der Heijde D, Uhlig T, Haugen AJ, Nygaard H, Sidenvall G, Helgetveit K, Kvien TK (2010) The likelihood of persistent arthritis increases with the level of anti-citrullinated peptide antibody and immunoglobulin M rheumatoid factor: a longitudinal study of 376 patients with very early undifferentiated arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 12(3):R76. doi:10.1186/ar2995
Singh HV, Shrivastava AK, Raizada A, Singh SK, Pandey A, Singh N, Yadav D, Sharma H (2013) Atherogenic lipid profile and high sensitive C-reactive protein in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Biochem 46(12):1007–1012. doi:10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2013.03.023
Ghosh B (2016) Correlation of serum uric acid with disease activity and C-reactive protein in patients suffering from rheumatoid arthritis. Open J Rheumatol Autoimmun Dis 6(03):79
Ajay K, Pranshi M, Neelima S (2012) Study of non-enzymatic antioxidant and lipid peroxide levels in rheumatoid arthritis. UJMD 1:10–13
Danve A, Sehra S, Jaykumar D, Kulkarni S (2016) Tumor necrosis factor in-hibitors may improve glycemic control in patients rheumatoid arthritis and concomitant diabetes mellitus. Osteol Rheumatol Open J 1(1):17–19
Schett G (2012) Pathophysiology of subchondral bone erosions in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 14:1–8
Oregon-Romero E, Vazquez-Del Mercado M, Ruiz-Quezada SL, Navarro-Hernandez RE, Rangel-Villalobos H, Martinez-Bonilla G, Bernard-Medina AG, Armendariz-Borunda J, Garcia-Banuelos J, Munoz-Valle JF (2008) Tumor necrosis factor alpha-308 and -238 polymorphisms in rheumatoid arthritis. Association with messenger RNA expression and sTNF-alpha. J Investig Med 56(7):937–943.
Aranda F, Perés Wingeyer SD, Schneeberger E, Valerio M, Saint Martin E, Dal Pra F, Correa MÁ, Citera G, Martínez L, Mannucci P (2016) The− 308 G/A polymorphism in the tumor necrosis factor-α gene is not associated with development and progression of rheumatoid arthritis in Argentinean patients. Int J Rheum Dis 19(5):476–481
Gambhir D, Lawrence A, Aggarwal A, Misra R, Mandal SK, Naik S (2010) Association of tumor necrosis factor alpha and IL-10 promoter polymorphisms with rheumatoid arthritis in North Indian population. Rheumatol Int 30(9):1211–1217. doi:10.1007/s00296-009-1131-0
Priyanka R, Kawaljit M, Ajay K, Priyanka S, RubinaS AB (2014) Association of tumor necrosis factor-alpha -308 G>A polymorphism with rheumatoid arthritis in two north Indian cohorts. Arch Rheumatol 29:241–249
Lagha A, Zidi S, Stayoussef M, Gazouani E, Kochkar R, Kochbati S, Almawi W, Yacoubi-Loueslati B (2015) Interleukin-1β, interleukin1-Ra, interleukin-10, and tumor necrosis factor-α polymorphisms in Tunisian patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Pathol Biol 63(4):179–184
Li F, Xie X, Chen J, Gao J, Lu F (2015) Association of TNF-α gene polymorphisms with the risk of rheumatoid arthritis in Han Chinese population from Hunan. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban = J Cent S Univ Med Sci 40(9):945
Acknowledgements
One of the authors Mohd Jahid is thankful to the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) New Delhi for providing the Senior Research Fellowship (SRF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jahid, M., Rehan-Ul-Haq, Jha, P.K. et al. Tumor necrosis factor-α -308 polymorphism in North Indian rheumatoid arthritis patients and association with mRNA and serum TNF-α. Clin Rheumatol 36, 2209–2216 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-017-3774-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-017-3774-7