Abstract
Purpose
To assess the removal performance of low-volume post-hemodiafiltration (HDF) with Japanese hemodiafilters and the removal performance with 20 % reduction in the total dialysate flow rate (Qdtotal).
Methods
Subjects were 8 patients undergoing pre-HDF. Study 1: Post-HDF was performed at a blood flow rate (Qb) of 250 mL/min and a total volume of substitution fluid (Vs) of 12 L/session(s) for 4 hrs using Fineflux-210Seco (FIX), ABH-21PA (ABH), and NVF-21H (NVF). We assessed removal efficiency of small molecular solutes, low-molecular-weight-proteins and the amount of albumin loss. Study 2: Post-HDF was performed at Vs of 12 L/s under G-1, Qdtotal of 500 and Qb of 250 mL/min; G-2, Qdtotal of 400 and Qb of 250 mL/min; and G-3, Qdtotal of 400 and Qb of 300 mL/min. Removal efficiency was compared and analyzed between these conditions.
Results
Study 1: The results using FIX, ABH and NVF are shown in order. The Kt/V were 1.8, 1.9 and 1.8. The β2-Microglobulin (MG) removal rate (RR) (%) were 81.2, 83.1 and 82.8, and the α1-MG RR were 37.4, 40.2 and 38.5, respectively. Study 2: The results in G-1, 2 and 3 are shown in order. The Kt/V and the RR of small solutes, were significantly higher in G-3. The β2-MG RR (%) were 81.2, 80.1 and 81.0, and the α1-MG RR were 37.4, 37.5 and 38.0, respectively.
Conclusions
Low-volume post-HDF performed at Qb of 250 mL/min with Japanese high-performance hemodiafilters exhibited favorable removal efficiency for all solutes. Even with 20 % reduction in Qdtotal, the removal performance was also favorable.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
At the end of 2017, in Japan, there were 334,505 dialysis patients, 21.1 % of whom were receiving online (OL) hemodiafiltration (HDF). In Japan, the pre-dilution OL-HDF (pre-HDF) is used in 84.4 % of patients on OL-HDF. Kikuchi et al. reported that pre-HDF with a volume of substitution fluid (Vs) of 40 L or more favorably affects patient prognosis compared to pre-HDF with Vs of 40 L or less and hemodialysis (HD) [1]. Conversely, in Europe, OL-HDF has been performed in the post-dilution OL-HDF (post-HDF). High-volume post-HDF with a high blood flow rate (Qb) has been reported to improve patient prognosis, and its effect has been reported to be enhanced with increased Vs [2,3,4].
In Japan, post-HDF has not been widely accepted, mainly because albumin (Alb) loss was difficult to control in post-HDF and because hemodialysis with high Qb was not preferable. We previously reported that pre-HDF was superior to post-HDF in terms of biocompatibility [5]. Later, we reported that post-HDF using recent high-performance hemodiafilter efficiently removed low-molecular-weight protein (LMWP), caused only mild Alb loss, and was comparable with pre-HDF in terms of biocompatibility [6]. Our study showed that high-efficiency post-HDF could be achieved without high Qb and high Vs by selecting an appropriate hemodiafilter.
In Study 1 of the present study, post-HDF was performed with 3 types of Japanese high-performance hemodiafilters at Vs of 12 L/session (s) and Qb of 250 mL/min, and the removal performance was assessed. Then, we examined whether this low-volume post-HDF with moderate Qb exhibited removal efficiency adequate for HDF. In Study 2, removal performance of post-HDF with fixed Vs of 12 L/s and 20 % reduction in the total dialysate flow rate (Qdtotal) was assessed to examine whether the dialysate volume could be reduced.
Patients and methods
Ethical approval
All subjects enrolled in this research have given their informed consent. The study has been approved by our institutional committee on human and/or animal research, and this protocol has been found acceptable by them (approved number: 2019-05).
Study design and population
This prospective, single-center study included 8 stable dialysis patients undergoing maintenance dialysis by pre-HDF in our clinic (Table 1). Each patient had received pre-HDF 3 times per week (i.e., on Monday, Wednesday, and Friday or on Tuesday, Thursday, and Saturday) for 6 months or longer (Fig. 1).
Study 1 In the patients, pre-HDF was switched to post-HDF on Friday or Saturday, and post-HDF was performed 3 times under the same conditions. In the third session (on the middle day of the week), samples were collected. According to this dialysis schedule, post-HDF was repeated using 3 types of hemodiafilters for 3 weeks. The hemodiafilters used were Fineflux-210Seco (FIX) (asymmetric triacetate [ATA] membrane, Nipro Co., Osaka, Japan) in the first week, ABH-21PA (ABH) (polysulfone [PS] membrane, Asahi Kasei Medical Co., Ltd. Tokyo, Japan) in the second week, and NVF-21H (NVF) (PS membrane, Toray Medical Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) in the third week (Table 2). Post-HDF was performed at Qb of 250 mL/min and Vs of 12 L/s for 4 hrs (Table 3).
Study 2 The patients who participated in Study 2 were the same as those who participated in Study 1. Post-HDF using FIX was performed at a fixed Vs of 12 L/s, Qd reduced to 400 mL/min, and Qb of 250 mL/min in Group 2 (G-2) or 300 mL/min in Group 3 (G-3). The removal efficiency in these groups was compared with that of post-HDF performed at total Qd (Qdtotal) of 500 mL/min and Qb of 250 mL/min in Group 1 (G-1: this was done in the first term of study 1). In Study 2, post-HDF was also performed 3 times under the same conditions, and samples were collected in the third session (Table 4).
Data collection
To assess removal performance, we measured the standardized dialysis dose (Kt/V); the removal rates and amounts of urea [molecular weight (MW): 60 Da], creatinine (MW: 113 Da), phosphorus (MW: 30.97 Da), ß2-microglobulin (MG) (MW: 11.8 kDa), and α1-MG (MW: 33 kDa); and the removal rate of prolactin (MW: 22 kDa). To measure the removal amount of each solute and the amount of Alb loss, spent dialysate was pooled at 2 L/h. At the end of a post-HDF session, the pooled fluid was thoroughly stirred, and then samples were collected.
Filtration fractions for post-HDF with blood flow and plasma flow were calculated with the equations presented as follows [7]:
Of the laboratory data, those affected by concentration due to ultrafiltration after dialysis were corrected for the hematocrit values.
Statistical analysis
All results are expressed as a mean and standard deviation. The Friedman test was performed to analyze all parameters using StatMate III for Windows (ATMS Corp., Tokyo, Japan). A p value less than 5 % was considered as the significance level.
Results
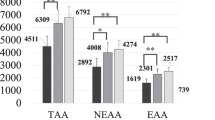
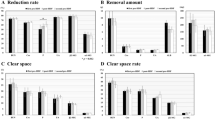
Study 1 The respective results are presented in the order of FIX, ABH, and NVF. Kt/V values were 1.82 ± 0.29, 1.89 ± 0.32, and 1.83 ± 0.31. There were significant differences between FIX and ABH, and between ABH and NVF in Kt/V. The removal rates of urea (%) were 76.9 ± 4.8, 78.3 ± 4.9, and 77.3 ± 5.1, with a significant difference between ABH and NVF. Removal rates of ß2-MG (%) were 81.2 ± 2.6, 83.1 ± 4.3, and 82.8 ± 3.7. Removal rates of prolactin (%) were 80.2 ± 3.2, 78.0 ± 9.9 and 77.9 ± 7.3, and removal rates of α1-MG (%) were 37.4 ± 3.9, 40.2 ± 8.2 and 38.5 ± 7.0, respectively. Amounts of Alb loss (g/s) were 3.4 ± 0.7, 5.4 ± 2.1, and 5.4 ± 2.8, but no significant difference was observed. Ratios of α1-MG/Alb (mg/g) were 44.4 ± 9.3, 33.0 ± 9.7, and 36.9 ± 10.5. For 1 g of Alb loss, the removal amount of α1-MG was higher for FIX, but it did not significantly differ between the hemodiafilters (Table 5). During post-HDF, the increase in transmembrane pressure (TMP) was mild for all hemodiafilters, and it remained at 100 mmHg or lower until the end of each session.
Study 2 The respective results are presented in the order of G-1, G-2, and G-3. Kt/V values were 1.82 ± 0.29, 1.77 ± 0.28, and 2.02 ± 0.36. As with the removal rates of urea and creatinine, Kt/V was significantly highest in G-3. Removal rates of ß2-MG (%) were 81.2 ± 2.6, 80.1 ± 4.2, and 81.0 ± 3.6; the rate in G-1 was significantly higher than that in G-2 (p < 0.05). Removal rates of prolactin (%) were 80.2 ± 3.2, 79.6 ± 5.1, and 80.5 ± 5.0. Removal rates of α1-MG (%) were 37.4 ± 3.9, 37.5 ± 6.5, and 38.0 ± 5.8. Amounts of Alb loss (g/s) were 3.4 ± 0.7, 3.8 ± 1.1, and 4.0 ± 0.8, showing no significant difference. Removal amounts of ß2-MG (g) were 0.222 ± 0.03, 0.199 ± 0.03, and 0.198 ± 0.03; the amount was significantly highest in G-1. Removal amounts of α1-MG (g) were 0.146 ± 0.033, 0.163 ± 0.03, and 0.180 ± 0.005; the amount was significantly highest in G-3. In addition, ratios of α1-MG/Alb were 44.4 ± 9.3, 40.2 ± 9.6, and 42.0 ± 8.2 (Table 6).
Discussion
The FIX series consists of 4 types of products (i.e., FIX-U, -S, -E, and -M), and the NVF series consists of 3 types of products (i.e., NVF-P, -H, and -M). The membranes of the FIX-U and NVF-P have the largest pore size among the respective series. From these products, we selected and used the FIX-S and NVF-H, with which post-HDF was assumed to yield adequate removal performance for LMWP and to keep Alb loss within the adequate range. As for ABH-PA, which is the only available type of the product, there was no alternative.
In the present study, because post-HDF was performed at Qdtotal of 500 mL/min and Vs of 12 L/s, the net Qd was 450 mL/min. Under this condition, the efficiency in removing small molecular solutes by diffusion was expressed as Kt/V of 1.8 or higher and removal rates of 75 % or higher for urea and 70 % for creatinine, which were favorable. We previously reported that HDF should be set with target removal rates of 80 % for ß2-MG and 35 % for α1-MG when dialysis patients with various complications are treated [8, 9]. Post-HDF performed under the conditions set in the present study was a therapeutic strategy demonstrating the original features of HDF (i.e., efficient removal of middle- to large-molecular-weight solutes), because the removal rates were 80 % or higher for ß2-MG and 35 % or higher for α1-MG.
The European style of post-HDF requires a high Vs (15–30 L/s) to improve efficiency in removing solutes by convection [10]. High Vs inevitably leads to high Qb to prevent hemoconcentration. For example, in the ESHOL study, Qb and Vs were reported to be 384–392 mL/min and 20.8–21.8 L/s, respectively [3]. There is no other way but to state that high Vs and high Qb are required, because the removal performance of hemodiafilters used for HDF in Europe is unsatisfactory for substances in the LMWP range.
The European style of post-HDF at high Qb is associated with 2 disadvantages. The first disadvantage is the risk of excessive loss of amino acids. Because amino acids are small molecular solutes, their loss increases with higher Qb. Excessive loss of amino acids obviously has an adverse effect on the nutritional status of patients. The second disadvantage is the increased risk of the development of micro air-bubbles in the blood tube circuit. Stegmayr et al. reported that when Qb is 300 mL/min or higher, micro air-bubbles always develop in the blood tube circuit, enter the body via a dialysis membrane, and adversely affect the body [11,12,13]. With Qb of 250 mL/min, at which post-HDF was performed in the present study, the risk of the development of micro air-bubbles is low. Based on these 2 disadvantages, the Japanese style of post-HDF, characterized by low-volume of substitution fluid and moderate Qb using Japanese high-performance hemodiafilters, clearly appears to be superior to the European style of post-HDF. Furthermore, the former may also be superior in biocompatibility, because the increase in TMP during post-HDF is mild [14].
Among the 3 types of hemodiafilters used in the present study, Kt/V, removal rate of urea, removal rate and amount of β2-MG showed significant differences in several comparisons. However, it is unlikely that these differences could result in a problem in clinical practice. There was no significant difference in the amount of Alb loss. When using FIX, however, even though the serum level of Alb was high, the amount of Alb loss was low and its standard deviation was also small. The ratio of α1-MG/Alb was also at its highest when FIX was used (Table 5). These results indicate that FIX is capable of suppressing Alb loss and efficiently removing α1-MG to some extent. These findings imply that the radii of pores on the FIX vary within a small range, and that there are none or only a few shunt pores (i.e., non-standard, large pores). Because the problem with conventional post-HDF is the difficulty in controlling Alb loss, under the present circumstances, the FIX appears to be the most appropriate hemodiafilter for post-HDF among those 3 types of hemodiafilters.
When post-HDF was performed at Vs of 12 L/s for 4 hrs with 20 % reduction in Qdtotal (i.e., Qdtotal of 400 mL/min), the net Qd was 350 mL/min, and the removal efficiency for small molecular solutes was only slightly decreased. Furthermore, because Vs remained the same, it is not surprising that the removal efficiency for LMWP was unchanged. When Qb was 300 mL/min, the removal efficiency for small molecular solutes was significantly improved. However, it should be kept in mind that the loss of amino acids and the risk of development of micro-air-bubbles increase with higher Qb.
Conclusions
Low-volume post-HDF with moderate Qb using Japanese high-performance hemodiafilters can efficiently remove small-, middle-, and large-molecular-weight solutes. In addition, even when Qdtotal is reduced by 20 %, favorable removal performance is achieved for all solutes. Thus, post-HDF will be presumably performed more often, and the European style of high-volume post-HDF is considered unnecessary in Japan.
References
Kikuchi K, Hamano T, Wada A, Nakai S, Masakane I. Predilution online hemodiafiltration is associated with improved survival compared with hemodialysis. Kidney Int. 2019;95:929–38.
Grooteman MP, van den Dorpel MA, Bots ML, Penne EL, van der Weerd NC, Mazairac AH, den Hoedt CH, van der Tweel I, Lévesque R, Nubé MJ, ter Wee PM, Blankestijn PJ, CONTRAST Investigators. Effect of online hemodiafiltration on all-cause mortality and cardiovascular outcomes. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012;23:1087–96.
Maduell F, Moreso F, Pons M, Ramos R, Mora-Macià J, Carreras J, Soler J, Torres F, Campistol JM, Martinez-Castelao A, ESHOL Study Group. High-efficiency postdilution online hemodiafiltration reduces all-cause mortality in hemodialysis patients. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013;24:487–97.
Ok E, Asci G, Toz H, Ok ES, Kircelli F, Yilmaz M, Hur E, Demirci MS, Demirci C, Duman S, Basci A, Adam SM, Isik IO, Zengin M, Suleymanlar G, Yilmaz ME, Ozkahya M, Turkish Online Haemodiafiltration Study. Mortality and cardiovascular events in online haemodiafiltration (OL-HDF) compared with high-flux dialysis: results from TURKISH OL-HDF Study. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013;28:192–202.
Sakurai K, Saito T, Yamauchi F, Asahi D, Hosoya H. Comparison of the effects of predilution and postdilution hemodiafiltration on neutrophils, lymphocytes and platelets. J Artif Organs. 2013;16:316–21.
Sakurai K, Saito T, Yamauchi F, Hosoya H, Kurihara Y, Suzuki A, Kurozawa K, Yoshida K, Ishii D, Iwamura M, Kokubo K. Comparison of the effects of pre-dilution and post-dilution on-line hemodiafiltration on the cell surface marker of platelets and cytokines. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2018;33:i186–i189189.
Chapdelaine I, van Zuijdewijn CL, Mostovaya IM, Lévesque R, Davenport A, Blankestijn PJ, Wanner C, Nubé MJ, Grooteman MP, EUDIAL Group, Blankestijn PJ, Davenport A, Basile C, Locatelli F, Maduell F, Mitra S, Ronco C, Shroff R, Tattersall J, Wanner C. Optimization of the convection volume in online post-dilution haemodiafiltration: practical and technical issues. Clin Kidney J. 2015;8:191–8.
Sakurai K. Biomarker for evaluation of clinical outcomes of hemodiafiltration. Blood Purif. 2013;35:64–8.
Masakane I, Sakurai K. Current approaches to middle molecule removal: room for innovation. Nehrol Dial Transplant. 2018;33:12–211.
Basile C, Davenport A, Blankestijn PJ. Why choose high volume online post-dilution hemodiafiltration? J Nephrol. 2017;30:181–6.
Stegmayr CJ, Jonsson P, Forsberg U, Stegmayr BG. Development of air micro bubbles in the venous outlet line: an in vitro analysis of various air traps used for hemodialysis. Artif Organs. 2007;31:483–8.
Forsberg U, Jonsson P, Stegmayr C, Stegmayr B. Microemboli, developed during haemodialysis, pass the lung barrier and may cause ischaemic lesions in organs such as the brain. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2010;25:2691–5.
Stegmayr B. Air contamination during hemodialysis should be minimized. Hemodial Int. 2017;21:168–72.
Gritters-van den Oever M, Grooteman MP, Bartels PC, Blankestijn PJ, Bots ML, van den Dorpel MA, Schoorl M, Schoorl M, Ter Wee PM, Nubé MJ. Post-dilution haemodiafiltration and low-flux have dissimilar effects on platelets: a side study of CONTRAST. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009;24:3461–8.
Acknowledgements
This study received no external funding and was self-funded by Kenji Sakurai.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Sakurai, K., Hosoya, H., Kurihara, Y. et al. Evaluation of low-volume post-dilution online hemodiafiltration with Japanese high-performance hemodiafilters. J Artif Organs 23, 234–239 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10047-020-01167-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10047-020-01167-y