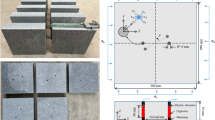
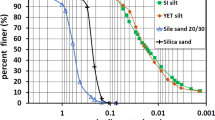
Abstract
The repose angle and characteristics of the vertical stress distribution beneath the sandpile can help to understand the physical and mechanical properties of the granular matter and guide the foundation design of the rock-soil deposits such as the rockfill dam and the storage structures of granular materials. Researches previously found that the stress dip phenomenon exists in piles constructed by the localized-source procedure, where the maximum vertical stress underneath the pile deviates from the center. The repose angle and the stress dip are affected by many internal and external factors and exhibit highly nonlinear and sensitive characteristics. However, the variation of the repose angle and the stress dip with influencing factors and the cause of the stress dip have not yet been fully explored. Based on the localized-source conical sandpile experiments and the discrete element method (DEM) simulation analysis, this paper studied the influences of the internal friction angle of granular matter and the construction history (the slowly raising funnel method SRFM and the fixed funnel method FFM) on the repose angle and the vertical stress dip beneath the pile; while the formation mechanism of the stress dip phenomenon was analyzed. The experimental results showed that the repose angle, physically different from the internal friction angle, has a relatively larger value and is positively related to the internal friction angle in the sandpile constructed by the FFM; the localized-source procedure and the internal friction angle are conducive to the formation of the macroscopic force chain arch structure in granular matter, which produces the arching effect and the stress shielding effect and leads to the stress dip beneath the pile; and the ratio of the stress dip RSD decreases with the increase of the local impact effect and the internal friction angle.
Graphic abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gennes. P. G. D.: Granular matter: a tentative view. Rev. Mod. Phys. 71(2) (1999).
Fang, Y., Li, B.: Multiscale problems and analysis of soil mechanics. Mech. Mater. 103, 55–67 (2016)
Feng, D., Fang, Y.: Theoretical analysis and experimental research on multiscale mechanical properties of soil. Int. J. Geomech. 16(4), 04015094 (2016)
Kadanoff, L.P.: Built upon sand: theoretical ideas inspired by granular flows. Rev. Mod. Phys. 71(1), 435–444 (1999)
Metcalf, J.R.: Angle of repose and internal friction. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr. 3(2), 155–161 (1966)
Rackl, M., Grtsch, F.E., Willibald A. G.: Angle of repose revisited: when is a heap a cone? In: Powders and Grains —International Conference on Micromechanics on Granular Media (2017)
Hamzah, M., Beakawi Al-Hashemi, O.S., Al-Amoudi, B.: A review on the angle of repose of granular materials. Powder Technol., 330, 397–417 (2018).
Zhou, Z.Y., Zou, R.P., Pinson, D., Yu, A.B.: Angle of repose and stress distribution of sandpiles formed with ellipsoidal particles. Granular Matter 16(5), 695–709 (2014)
Dai, B.B., Yang, J., Zhou, C.Y.: Micromechanical origin of angle of repose in granular materials. Granular Matter 19(2), 24 (2017)
Shorts, D.C., Feitosa, K.: Experimental measurement of the angle of repose of a pile of soft frictionless grains. Granular Matter 20(1), 2 (2018)
Liu, M., Dong, P., Zhong, R.: A rapid method for estimating the angle of repose and volume of grain piles using terrestrial laser scanning. Remote Sensing Lett. 11(7), 707–713 (2020)
Mitchell, J.K., Soga, K.: Fundamentals of Soil Behavior (Vol. 3). New York (2005).
K. Terzaghi.: Theoretical soil mechanics. USA (1943).
George, H., Hentschel, E., Prabhat, K.J., Chandana, M., Itamar, P., Jacques, Z.: The sandpile revisited: computer assisted determination of constitutive relations and the breaking of scaling. Soft Matter 13, 5008–5020 (2017)
Zhao, H., An, X., Dong, K., Yang, R., Xu, F., Fu, H., et al.: Macro-and microscopic analyses of piles formed by Platonic solids. Chem. Eng. Sci. 205, 391–400 (2019)
Zhao, H., An, X., Gou, D., Zhao, B., Yang, R.: Attenuation of pressure dips underneath piles of spherocylinders. Soft Matter 14(21), 4404–4410 (2018)
Wittmer, J.P., Claudin, P., Cates, M.E., Bouchaud, J.P.: An explanation for the central stress minimum in sand piles. Nature 382(6589), 336–338 (1996)
Watson, A.: Searching for the sand-pile pressure dip. Science 273(5275), 579–580 (1996)
Cates, M.E., Wittmer, J.P., Bouchaud, J.P., Claudin, P.: Jamming and static stress transmission in granular materials. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 9(3), 511–522 (1999)
Liu, Y., Yeung, A.T., Ding, L., Yan, R.: Experimental study on the effect of particle shape on stress dip in granular piles. Powder Technol. 319, 415–425 (2017)
Vanel, L., Howell, D., Clark, D., Behringer, R.P., Clément, E.: Memories in sand: experimental tests of construction history on stress distributions under sandpiles. Phys. Rev. E 60(5), R5040 (1999)
Geng, J., Longhi, E., Behringer, R.P., Howell, D.W.: Memory in two-dimensional heap experiments. Phys. Rev. E 64, 060301 (2001)
Altshuler, E., Ramos, O., Martínez, E., Batista-Leyva, A.J., Rivera, A., Bassler, K.E.: Sandpile formation by revolving rivers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91(1), 014501 (2003)
Krimer, D.O., Pfizner, M., Brauer, K., et al.: Granular elasticity: general considerations and stress dip in sand piles. Phys. Rev. E 74, 061310 (2006)
Jiang, Y., Liu, M.: From elasticity to hypoplasticity: dynamics of granular solids. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99(10), 105501.1–10550.14 (2007)
Jiang, Y., Liu, M.: Granular solid hydrodynamics. Granular Matter 11(3), 139–156 (2009)
Bouchaud, J.P., Cates, M.E., Claudin, P.: Stress distribution in granular media and nonlinear wave equation. J. Phys. I 5(6), 639–656 (1995)
Zheng, Q., Yu, A.: Why have continuum theories previously failed to describe sandpile formation? Phys. Rev. Lett. 113(6), 068001 (2014)
Horabik, J., Parafiniuk, P., Molenda, M.: Discrete element modeling study of force distribution in a 3D pile of spherical particles. Powder Technol. 312, 194–203 (2017)
Atman, A.P.F., Brunet, P., Geng, J., Reydellet, G., Clauidn, P., Behringer, R.P., Clément, E.: From the stress reponse function (back) to the sand pile “dip.” Eur. Phys. J. E. 17, 93–100 (2005)
Peters, J.F., Muthuwamy, M., Wibowo, J., Tordesillas, A.: Characterization of force chains in granular material. Phys. Rev. E 72, 041307 (2005)
Campbell, C.S.: A problem related to stability of force chains. Granular Matter 5, 129–134 (2003)
Sanfratello, L., Fukushima, E., Behringer, R.P.: Using MR elastography to image the 3D force chain structure of a quasi-static granular assembly. Granular Matter 11, 1–6 (2009)
Fu, L., Zhou, S., Guo, P., Wang, S., Luo, Z.: Induced force chain anisotropy of cohesionless granular materials during biaxial compression. Granular Matter 21, 52 (2019)
Zuriguel, I., Mullin, T.: Effect of particle shape on stress dip under a sandpile. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 028001 (2007)
Zuriguel, I., Mullin, T.: The role of particle shape on the stress distribution in a sandpile. Proc. R. Soc. A. 464, 99–116 (2008)
Ostojic, S., Somfai, E., Nienhuis, B.: Scale invariance and universality of force networks in static granular matter. Nature 439, 828–830 (2006)
Grima, A.P., Wypych, P.W.: Discrete element simulations of granular pile formation. Eng. Comput. 28(3), 314–339 (2011)
Fang, Y., Guo, L., Hou, M.: Arching effect analysis of granular media based on force chain visualization. Powder Technol. 363, 621–628 (2020)
Silbert, L.E., Grest, G.S., Landry, J.W.: Statistics of contact network in frictional and frictionless granular packings. Phys. Rev. E 66, 061303 (2002)
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge financial support from the State Key Lab of Subtropical Building Science, South China University of Technology (Grant No.2017 KB16), the National Key Scientific Instruments and Equipment Development Projects of China (Grant No.41827807), and the Open Research Fund of the State Key Laboratory of Geomechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Institute of Rock and Soil Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. Z018019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, Y., Li, X., Guo, L. et al. The experiment and analysis of the repose angle and the stress arch-caused stress dip of the sandpile. Granular Matter 24, 7 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-021-01171-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-021-01171-w