Abstract
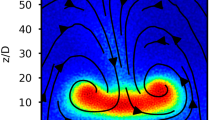
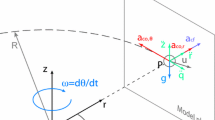
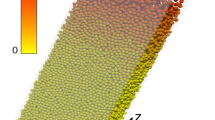
In a hopper with cylindrical symmetry and an aperture of radius R, the vertical velocity of granular flow \(v_z\) depends on the distance from the hopper’s center r and the height above the aperture z and \(v_z = v_z (r,z;\,R)\). We propose that the scaled vertical velocity \(v_{z}(r,z;\,R)/v_{z} (0,0;\,R)\) is a function of scaled variables \(r/R_r\) and \(z/R_z\), where \(R_{ r}=R- 0.5 d\) and \(R_{ z}=R-k_2 d\) with the granule diameter d and a parameter \(k_2\) to be determined. After scaled by \(v_{ z}^2 (0,0;\,R)/R_z \), the effective acceleration \(a_{\mathrm{eff}} (r,z;\,R)\) derived from \(v_z\) is a function of \(r/R_r\) and \(z/R_z\) also. The boundary condition \(a_\mathrm{eff} (0,0;\,R)=-\,g\) of granular flows under earth gravity g gives rise to \(v_{ z} (0,0;\,R) \propto \sqrt{g}\left( R -k_2 d\right) ^{1/2}\). Our simulations using the discrete element method and GPU program in the three-dimensional and the two-dimensional hoppers confirm the size scaling relations of \(v_{ z} (r,z;\,R)\) and \(v_{ z} (0,0;\,R)\). From the size scaling relations, we obtain the mass flow rate of D-dimensional hopper \(W \propto \sqrt{g } (R-0.5 d)^{D-1} (R-k_2 d)^{1/2}\), which agrees with the Beverloo law at \(R\gg d\). It is the size scaling of vertical velocity field that results in the dimensional R-dependence of W in the Beverloo law.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguirre, M.A., Grande, J.G., Calvo, A., Pugnaloni, L.A., Géminard, J.C.: Pressure independence of granular flow through an aperture. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104(23), 238002 (2010)
Aguirre, María Alejandra, Grande, Juan Gabriel, Calvo, Adriana, Pugnaloni, Luis A, Géminard, Jean-Christophe: Granular flow through an aperture: pressure and flow rate are independent. Phys. Rev. E 83(6), 061305 (2011)
Beverloo, W.A., Leniger, H.A., van de Velde, J.: The flow of granular solids through orifices. Chem. Eng. Sci. 15(3), 260–269 (1961)
Brilliantov, Nikolai V., Spahn, Frank, Hertzsch, Jan-Martin, Pöschel, Thorsten: Model for collisions in granular gases. Phys. Rev. E 53, 5382–5392 (1996)
Brown, R.L.: Minimum energy theorem for flow of dry granules through apertures. Nature 191(4787), 458–461 (1961)
Cundall, P.A., Strack, O.D.L.: A discrete numerical model for granular assemblies. Géotechnique 29(1), 47–65 (1979)
De-Song, Bao, Zhang Xun-Sheng, Xu, Guang-Lei, Pan Zheng-Quan, Xiao-Wei, Tang, Kun-Quan, Lu: Critical phenomenon of granular flow on a conveyor belt. Phys. Rev. E 67, 062301 (2003)
Dorbolo, S., Maquet, L., Brandenbourger, M., Ludewig, F., Lumay, G., Caps, H., Vandewalle, N., Rondia, S., Mélard, M., van Loon, J., Dowson, A., Vincent-Bonnieu, S.: Influence of the gravity on the discharge of a silo. Granul. Matter 15(3), 263–273 (2013)
Fisher, Michael E., Barber, Michael N.: Scaling theory for finite-size effects in the critical region. Phys. Rev. Lett. 28(23), 8–11 (1972)
Janda, Alvaro, Zuriguel, Iker, Maza, Diego: Flow rate of particles through apertures obtained from self-similar density and velocity profiles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108(24), 248001 (2012)
Johnson, K.L.: Contact Mechanics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1985)
Lin, P., Zhang, S., Qi, J., Xing, Y.M., Yang, L.: Numerical study of free-fall arches in hopper flows. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 417, 29–40 (2015)
Mankoc, C., Janda, A., Arévalo, R., Pastor, J.M., Zuriguel, I., Garcimartín, A., Maza, D.: The flow rate of granular materials through an orifice. Granul. Matter 9(6), 407–414 (2007)
Mankoc, Cristian, Garcimartín, Angel, Zuriguel, Iker, Maza, Diego, Pugnaloni, Luis A: Role of vibrations in the jamming and unjamming of grains discharging from a silo. Phys. Rev. E 80(1), 011309 (2009)
Nedderman, R.M., Tzn, U., Savage, S.B., Houlsby, G.T.: The flow of granular materials—I. Chem. Eng. Sci. 37(11), 1597–1609 (1982)
Rubio-Largo, S.M., Janda, A., Maza, D., Zuriguel, I., Hidalgo, R.C.: Disentangling the free-fall arch paradox in silo discharge. Phys. Rev. Lett. 114(23), 238002 (2015)
Schwager, Thomas, Pöschel, Thorsten: Coefficient of restitution for viscoelastic spheres: the effect of delayed recovery. Phys. Rev. E 78, 051304 (2008)
Tian, Y., Lin, P., Zhang, S., Wang, C.L., Wan, J.F., Yang, L.: Study on free fall surfaces in three-dimensional hopper flows. Adv. Powder Technol. 26(4), 1191–1199 (2015)
Tighe, Brian P, Sperl, Matthias: Pressure and motion of dry sand: translation of Hagen’s paper from 1852. Granul. Matter 9(3–4), 141–144 (2007)
Zhu, H.P., Yu, A.B.: Steady-state granular flow in a three-dimensional cylindrical hopper with flat bottom: microscopic analysis. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 37(10), 1497 (2004)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Magnetic Confinement Fusion Science Program of China under Grant No. 2014GB104002, the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences under Grant No. XDA03030100, and the National natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 11421063.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, G., Lin, P., Zhang, Y. et al. Size scaling relation of velocity field in granular flows and the Beverloo law. Granular Matter 21, 21 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-019-0872-z
Received:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-019-0872-z