Abstract
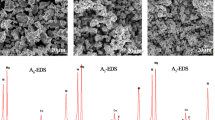
The binary TiFe alloy was synthesized by mechanical alloying (MA) under argon atmosphere at room temperature. The effect of ball to powder weight ratio on the microstructures was characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD). The effect of milling time on the electrochemical and activation properties was investigated by scanning electron microscope (SEM), galvanostatic charging and discharging, constant potential discharge, and potentiodynamic polarization techniques. Relationships between electrochemical properties, such as polarization, variation of electrochemical discharge capacity, \( \frac{D_{\mathrm{H}}}{a^2} \) ratio exchange current density, and Nernst potential and alloy compositions were evaluated. XRD results showed that with increasing ball to powder weight ratio, the amorphization process is accelerating and powders milled with a ratio of 1:8 have the highest conversion rate to TiFe. SEM observations reveal that particles show cleavage fracture morphology and size distribution is generally normalized. TiFe milled during 40 h was easily activated within 5 cycles and showed the best discharge capacity equal to 147 mAh g−1. A good cycling was observed after 20 cycles at ambient temperature for the alloy milled for 30 h. A correlation between alloy composition, \( \frac{D_{\mathrm{H}}}{a^2} \) report, exchange current density, and Nernst potential on one hand and the variation of the electrochemical discharge capacity during cycling for different milling times on the other hand was observed.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Khaldi C, Boussami S, Tliha M, Azizi S, Fenineche N, ElKedim O, Mathlouthi H, Lamloumi J (2013) The effect of the temperature on the electrochemical properties of the hydrogen storage alloy for nickel–metal hydride accumulators. J Alloys Compd 574:59–66
Abdul Wahab M, Jia Y, Yang D, Zhao H, Yao X (2013) Enhanced hydrogen desorption from Mg(BH4)2 by combining nanoconfinement and a Ni catalyst. J Mater Chem A 1:3471–3478
Schlapbach L, Zuttel A (2001) Hydrogen-storage materials for mobile applications. Nature 414:353–358
Zhu J, Ma L, Liang F, Wang L (2015) Effect of Sc substitution on hydrogen storage properties of Ti–V–Cr–Mn alloys. Int J Hydrog Energy 40:6860–6865
Kadir K, Sakai T, Uehara I (1999) Structural investigation and hydrogen capacity of YMg2Ni9 and (Y0.5Ca0.5)(MgCa)Ni9: new phases in the AB2C9 system isostructural with LaMg2Ni9. J Alloys Compd 287:264–270
Kadir K, Kuriyama N, Sakai T, Uehara I, Eriksson L (1999) Structural investigation and hydrogen capacity of CaMg2Ni9: a new phase in the AB2C9 system isostructural with LaMg2Ni9. J Alloys Compd 284:145–154
Baddour-Hadjcan R, Meyer L, Pereira-Ramos JP, Latroche M, Percheron-Guégan A (2001) An electrochemical study of new La1−xCexY2Ni9 (0≤x≤1) hydrogen storage alloys. Electrochim Acta 46:2385–2393
Mathlouthi H, Lamloumi J, Latroche M, Percheron-Guégan A (1997) Study of poly-substituted intermetallic hydrides: electrochemical applications. Ann Chim Sci Mater 22:241–244
Sakintuna B, Lamari-Darkrim F, Hirscher M (2007) Metal hydride materials for solid hydrogen storage: a review. Int J Hydrog Energy 32:1121–1140
Zhang X, Sun D, Yin W, Chai Y, Zhao M (2006) Crystallographic and electrochemical characteristics of La0.7Mg0.3Ni3.5-x(Al0.5Mo0.5)x (x=0–0.8) hydrogen storage alloys. J Power Sources 154:290–297
Zhang XB, Sun DZ, Yin WY, Chai YJ, Zhao MS (2005) Effect of Mn content on the structure and electrochemical characteristics of La0.7Mg0.3Ni2.975-xCo0.525Mnx (x=0–0.4) hydrogen storage alloys. Electrochim Acta 50:2911–2918
Zhang XB, Sun DZ, Yin WY, Chai YJ, Zhao MS (2005) Crystallographic and electrochemical characteristics of La0.7Mg0.3Ni5.0-x(Al0.5Mo0.5)x hydrogen-storage alloys. Chem Phys Chem 6:520–525
Qu H, Du J, Pu C, Niu Y, Huang T, Li Z, Lou Y, Wu Z (2015) Effects of Co introduction on hydrogen storage properties of Ti–Fe–Mn alloys. Int J Hydogen Energy 40:2729–2735
Emami H, Edalati K, Matsuda J, Akiba E, Horita Z (2015) Hydrogen storage performance of TiFe after processing by ball milling. Acta Mater 88:190–195
Jain P, Gosselin C, Huot J (2015) Effect of Zr, Ni and Zr7Ni10 alloy on hydrogen storage characteristics of TiFe alloy. Int J Hydrog Energy 40:16921–16927
Ćirić KD, Kocjan A, Gradišek A, Koteski VJ, Kalijadis AM, Ivanovski VN, Laušević ZV, Stojić DL (2012) A study on crystal structure, bonding and hydriding properties of Ti–Fe–Ni intermetallics—behind substitution of iron by nickel. Inter J Hydrogen Energy 37:8408–8417
Davids MW, Lototskyy M, Nechaev A, Naidoo Q, Williams M, Klochko Y (2011) Surface modification of TiFe hydrogen storage alloy by metal-organic chemical vapour deposition of palladium. Inter J Hydrogen Energy 36:9743–9750
Abrashev B, Spassov T, Bliznakov S, Popov A (2010) Microstructure and electrochemical hydriding/dehydriding properties of ball-milled TiFe-based alloys. Int J Hydrog Energy 35:6332–6337
Kumar S, Tiwari GP, Sonak S, Jain U, Krishnamurthy N (2014) High performance FeTi-3.1 mass % V alloy for on board hydrogen storage solution. Energy 75:520–524
Jankowska E, Jurczyk M (2004) Electrochemical properties of sealed Ni–MH batteries using nanocrystalline TiFe-type anodes. J Alloys Compd 372:L9–L12
Jankowska E, Jurczyk M (2002) Electrochemical behaviour of high-energy ball-milled TiFe alloy. J Alloys Compd 346:L1–L3
Szajek A, Jurczyk M, Jankoowska E (2003) The electronic and electrochemical properties of the TiFe-based alloys. J Alloys Compd 348:285–292
Lv P, Huot J (2016) Hydrogen storage properties of Ti0.95FeZr0.05, TiFe0.95Zr0.05 and TiFeZr0.05 alloys. Int J Hydrog Energy 41:22128–22133
Jain P, Gosselin C, Skryabina N, Fruchart D, Huot J (2015) Hydrogenation properties of TiFe with Zr7Ni10 alloy as additive. J Alloys Compd 636:375–380
Zadorozhnyy VY, Klyamkin SN, Zadorozhnyy MY, Gorshenkov MV, Kaloshkin SD (2014) Mechanical alloying of nanocrystalline intermetallic compound TiFe doped with sulfur and magnesium. J Alloys Compd 615:S569–S572
Jurczyk M (2004) Nanostructured electrode materials for Ni-MHx batteries prepared by mechanical alloying. J Mater Sci 39:5271–5274
Percheron-Guégan A, Latroche M (2011) Influence of the addition of vanadium on the hydrogenation properties of the compounds TiFe0.9Vx and TiFe0.8Mn0.1Vx (x=0, 0.05 and 0.1). J Alloys Compd 509:5562–5566
Miyamura H, Takada M, Kikuchi S (2005) Characteristics of hydride electrodes using Ti–Fe–Pd–X alloys. J Alloys Compd 404-406:675–678
Zaluski L, Zaluska A, Tessier P, Strom-Olsen JO, Schulz R (1995) Catalytic effect of Pd on hydrogen absorption in mechanically alloyed Mg2Ni, LaNi5 and FeTi. J Alloys Compd 217:295–300
Hou X, Hu R, Zhang T, Kou H, Li J (2013) Hydrogenation behavior of high-energy ball milled amorphous Mg2Ni catalyzed by multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Int J Hydrog Energy 38:16168–16176
Yao X, Wu C, Du A, Zou J, Zhu Z, Wang P, Cheng H, Smith S, Lu G (2007) Metallic and carbon nanotube-catalyzed coupling of hydrogenation in magnesium. J Am Chem Soc 129:15650–15654
Gattia DM, Gizer G, Montone A (2014) Effects of the compaction pressure and of the cycling process on kinetics and microstructure of compacted MgH2-based mixtures. Int J Hydrog Energy 39:9924–9930
Jung CB, Lee KS (1997) Electrode characteristics of metal hydride electrodes prepared by mechanical alloying. J Alloys Compd 253-254:605–608
Aoyagi H, Aoki K, Masumoto T (1995) Effect of ball milling on hydrogen absorption properties of FeTi, Mg2Ni and LaNi5. J Alloys Compd 231:804–809
Hosni B, Khaldi C, Elkedim O, Fenineche N, Lamloumi J (2017) Electrochemical properties of Ti2Ni hydrogen storage alloy. Int J Hydrog Energy 42:1420–1428
Khaldi C, Mathlouthi H, Lamloumi J, Percheron-Guégan A (2006) Electrochemical studies on the effect of cobalt substitution by iron in LaNi3.55Mn0.4Al0.3Co0.75 alloys. Phys Chem News 29:76–80
Kaabi A, Khaldi C, Lamloumi J (2016) Thermodynamic and kinetic parameters and high rate discharge-ability of the AB5-type metal hydride anode. Int J Hydrog Energy 41:9914–9923
Huang LW, Elkedim O, Jarzebski M, Hamzaoui R, Jurczyk M (2010) Structural characterization and electrochemical hydrogen storage properties of Mg2Ni1−xMnx(x = 0, 0.125, 0.25, 0.375) alloys prepared by mechanical alloying. Int J Hydrog Energy 35:6794–6803
Zadorozhnyy V, Klyamkin S, Zadorozhnyy M, Bermesheva O, Kaloshkin S (2012) Hydrogen storage nanocrystalline TiFe intermetallic compound: synthesis by mechanical alloying and compacting. Int J Hydrog Energy 37:17131–17136
Abrashev B, Bliznakov S, Spassov T, Popov A (2007) Electrochemical hydriding of nanocrystalline TiFe alloys. J Appl Electrochem 37:871–875
Hosni B, Li X, Khaldi C, Elkedim O, Lamloumi J (2014) Structure and electrochemical hydrogen storage properties of Ti2Ni alloy synthesized by ball milling. J Alloys Compd 615:119–125
Li XD, Elkedim O, Nowak M, Jurczyk M, Chassagnon R (2013) Structural characterization and electrochemical hydrogen storage properties of Ti2-xZrxNi(x=0; 0.1; 0.2) alloys prepared by mechanical alloying. Int J Hydrog Energy 38:12126–12132
Balcerzak M, Jakubowicz J, Kachlicki T, Jurczyk M (2015) Hydrogenation properties of nanostructured Ti2Ni-based alloys and nanocomposites. J Power Sources 280:435–445
Nishina T, Ura H, Uchida I (1997) Determination of chemical diffusion coefficients in metal hydride particles with a microelectrode technique. J Electrochem Soc 144:1273–1277
Zheng G, Popov BN, White RE (1995) Electrochemical determination of the diffusion coefficient of hydrogen through an LaNi4.25Al0.75 electrode in alkaline aqueous solution. J Electrochem Soc 142:2695–2698
Kaabi A, Tliha M, Dhahri A, Khaldi C, Lamloumi J (2016) Study of electrochemical performances of perovskite-type oxide LaGaO3 for application as a novel anode material for Ni-MH secondary batteries. Ceram Int 42:11682–11686
Ben Belgacem Y, Khaldi C, Lamloumi J (2016) The effect of the discharge rate on the electrochemical properties of AB3-type hydrogen storage alloy as anode in nickel–metal hydride batteries. Int J Hydrog Energy. doi:10.1016/j.ijhedrne.2016.12.143
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the Conseil Regional de Franche-Comté.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hosni, B., Fenineche, N., ElKedim, O. et al. Structural and electrochemical properties of TiFe alloys synthesized by ball milling for hydrogen storage. J Solid State Electrochem 22, 17–29 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-017-3718-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-017-3718-9