Abstract
Purpose
This study was conducted to evaluate the operative time, blood loss, hemoglobin drop, blood transfusion, and length of hospital stay in orthognathic surgery.
Methods
A 10-year retrospective analysis was performed on patients who underwent bilateral sagittal split osteotomy (with or without genioplasty), Le Fort I osteotomy (with or without genioplasty), or any combination of these procedures. A total of 271 patients were included.
Results
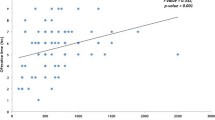
The age range was 17 to 49 years, with a mean age of 24.13 ± 4.51 years. Approximately 62% of patients underwent double-jaw surgery. The most common procedure was bilateral sagittal split with Le Fort I (37%). The average operative time was 3.96 ± 1.25 h. The mean estimated blood loss was 345.2 ± 149.74 mL. Approximately 9% of patients received intraoperative blood transfusion. The mean hemoglobin drop in the non-transfusion cases was 2.38 ± 0.89 g/dL. The mean postoperative hospital stay was 1.85 ± 0.83 days. Only one patient was admitted to the ICU for one night.
Conclusions
In orthognathic surgery, blood loss is relatively minor, blood transfusion is frequent, and ICU admission is unlikely. Operative time, blood loss, blood transfusion, and the complexity of the surgical procedure can significantly increase the length of hospital stay. Males may bleed more than females in orthognathic surgery. Hemoglobin drop can be overestimated due to hemodilution in orthognathic surgery, which may influence the decision to use blood transfusion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgereons (2015) AAOMS criteria for orthognatic surgery 1–6. Accessed 17 Feb 2017
Aziz SR (2004) Simon P. Hullihen and the origin of orthognathic surgery. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 62:1303–1307. doi:10.1016/j.joms.2003.08.044
Venugoplan SR, Nanda V, Turkistani K et al (2012) Discharge patterns of orthognathic surgeries in the United States. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 70:e77–e86. doi:10.1016/j.joms.2011.09.030
Kim SG, Park SS (2007) Incidence of complications and problems related to orthognathic surgery. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 65:2438–2444. doi:10.1016/j.joms.2007.05.030
Steel BJ, Cope MR (2012) Unusual and rare complications of orthognathic surgery: a literature review. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 70:1678–1691. doi:10.1016/j.joms.2011.05.010
Rummasak D, Apipan B, Kaewpradup P (2011) Factors that determine intraoperative blood loss in bimaxillary osteotomies and the need for preoperative blood preparation. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 69:e456–e460. doi:10.1016/j.joms.2011.02.085
Rodrigo C (1995) Induced hypotension during anesthesia with special reference to orthognathic surgery. Anesth Prog 42:41–58
Piñeiro-Aguilar A, Somoza-Martín M, Gandara-Rey JM, García-García A (2011) Blood loss in orthognathic surgery: a systematic review. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 69:885–892. doi:10.1016/j.joms.2010.07.019
Murphy MF, Wallington TB, Kelsey P et al (2001) Guidelines for the clinical use of red cell transfusions. Br J Haematol 113:24–31. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2141.2001.02701.x
Shetty V, Sriram G (2015) Effectiveness of intravenous haemocoagulase on haemorrhage control in bi-maxillary orthognathic surgery—a prospective, randomised, controlled, double-blind study. J Cranio-Maxillofacial Surg 43:2000–2003. doi:10.1016/j.jcms.2015.08.032
Schaberg SJ, Kelly JF, Terry BC et al (1976) Blood loss and hypotensive anesthesia in oral-facial corrective surgery. J Oral Surg 34:147–156
Posnick J (2014) Orthognatic surgery: principles & practice. Elsevier Saunders, p 309
Ervens J, Marks C, Hechler M et al (2010) Effect of induced hypotensive anaesthesia vs isovolaemic haemodilution on blood loss and transfusion requirements in orthognathic surgery: a prospective, single-blinded, randomized, controlled clinical study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 39:1168–1174. doi:10.1016/j.ijom.2010.09.003
Praveen K, Narayanan V, Muthusekhar MR, Baig MF (2001) Hypotensive anaesthesia and blood loss in orthognathic surgery: a clinical study. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 39:138–140. doi:10.1054/bjom.2000.0593
Choi WS, Samman N (2008) Risks and benefits of deliberate hypotension in anaesthesia: a systematic review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 37:687–703. doi:10.1016/j.ijom.2008.03.011
Choi WS, Irwin MG, Samman N (2009) The effect of tranexamic acid on blood loss during orthognathic surgery: a randomized controlled trial. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 67:125–133. doi:10.1016/j.joms.2008.08.015
Eftekharian H, Vahedi R, Karagah T, Tabrizi R (2015) Effect of tranexamic acid irrigation on perioperative blood loss during orthognathic surgery: a double-blind, randomized controlled clinical trial. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 73:129–133. doi:10.1016/j.joms.2014.07.033
Guyuron B, Vaughan C, Schlecter B (1996) The role of DDAVP (desmopressin) in orthognathic surgery. Ann Plast Surg 37:516–519. doi:10.1097/00000637-199611000-00010
de Lange J, Baas EM, Horsthuis RBG, Booij A (2008) The effect of nasal application of cocaine/adrenaline on blood loss in Le Fort I osteotomies. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 37:21–24. doi:10.1016/j.ijom.2007.07.017
Habler O, Schwenzer K, Zimmer K et al (2004) Effects of standardized acute normovolemic hemodilution on intraoperative allogeneic blood transfusion in patients undergoing major maxillofacial surgery. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 33:467–475. doi:10.1016/j.ijom.2003.10.007
Tang ZL, Wang X, Yi B et al (2009) Effects of the preoperative administration of Yunnan Baiyao capsules on intraoperative blood loss in bimaxillary orthognathic surgery: a prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 38:261–266. doi:10.1016/j.ijom.2008.12.003
Stewart A, Newman L, Sneddon K, Harris M (2001) Aprotinin reduces blood loss and the need for transfusion in orthognathic surgery. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 39:365–370. doi:10.1054/bjom.2001.0664
Politano N, Jaskolka M, Blakey G et al (2012) The effect of preoperative recombinant erythropoietin on postoperative hematocrit level after orthognathic surgery. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 70:625–630. doi:10.1016/j.joms.2012.07.021
Landes CA, Stübinger S, Rieger J et al (2008) Critical evaluation of piezoelectric osteotomy in orthognathic surgery: operative technique, blood loss, time requirement, nerve and vessel integrity. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 66:657–674. doi:10.1016/j.joms.2007.06.633
Olsen JJ, Skov J, Ingerslev J et al (2016) Prevention of bleeding in orthognathic surgery—a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 74:139–150. doi:10.1016/j.joms.2015.05.031
Mangano DT, Tudor IC, Dietzel C (2006) The risk associated with aprotinin in cardiac surgery. N Engl J Med 354:353–365. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa051379
Schneeweiss S, Seeger JD, Landon J, Walker AM (2008) Aprotinin during coronary-artery bypass grafting and risk of death. New Engl J 358:771–783. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0707571
Huaman ET, Juvet LM, Nastri A et al (2008) Changing patterns of hospital length of stay after orthognathic surgery. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 66:492–497. doi:10.1016/j.joms.2007.08.025
Lupori JP, Van Sickels JE, Holmgreen WC (1997) Outpatient orthognathic surgery: review of 205 cases. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 55:558–563. doi:10.1016/S0278-2391(97)90483-3
Farrell BB, Tucker MR (2014) Orthognathic surgery in the office setting. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am 26:611–620. doi:10.1016/j.coms.2014.08.009
Varol A, Basa S, Ozturk S (2010) The role of controlled hypotension upon transfusion requirement during maxillary downfracture in double-jaw surgery. J Cranio-Maxillofacial Surg 38:345–349. doi:10.1016/j.jcms.2009.10.012
Yu CNF, Chow TK, Kwan ASK et al (2000) Intra-operative blood loss and operating time in orthognathic surgery using induced hypotensive general anaesthesia: prospective study. Hong Kong Med J 6:307–311
Posnick JC, Choi E, Chavda A (2016) Operative time, airway management, need for blood transfusions, and in-hospital stay for bimaxillary, intranasal, and osseous genioplasty surgery: current clinical practices. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 74:590–600. doi:10.1016/j.joms.2015.07.026
Devlin H, Horner K, Ledgerton D (1998) A comparison of maxillary and mandibular bone mineral densities. J Prosthet Dent 79:446–453
DeConde AS, Soler ZM (2016) Chronic rhinosinusitis: epidemiology and burden of disease. Am J Rhinol Allergy 30:134–139. doi:10.2500/ajra.2016.30.4297
Mayrovitz HN, Regan MB (1993) Gender differences in facial skin blood perfusion during basal and heated conditions determined by laser Doppler flowmetry. Microvasc Res 45:211–218. doi:10.1006/mvre.1993.1019
American Society of Plastic Surgeons Men and Plastic Surgery: Male-Specific Considerations. http://www.plasticsurgery.org/cosmetic-procedures/men-and-plastic-surgery?sub=The+surgery#section-title. Accessed 17 Feb 2017
Faverani LP, Ramalho-Ferreira G, Fabris ALS et al (2014) Intraoperative blood loss and blood transfusion requirements in patients undergoing orthognathic surgery. Oral Maxillofac Surg 18:305–310. doi:10.1007/s10006-013-0415-4
Chen C-M, Lai SS-T, Hsu K-J et al (2011) Assessment of the related factors of blood loss and blood ingredients among patients under hypotensive anesthesia in orthognathic surgery. J Craniofac Surg 22:1594–1597. doi:10.1097/SCS.0b013e31822e5edb
Billett H (1990) Hemoglobin and hematocrit. In: Clin. Methods Hist. Phys. Lab. Exam. 3rd edn. Butterworths, p 718–719
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr. Ashwin Shetty for his tremendous help with the statistical analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The study was approved by the Ethical Committee of the Research Center of Riyadh Colleges of Dentistry and Pharmacy, in accordance with the ethical standards of the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments.
Due to the retrospective nature of this study, informed consent is not required.
Sources of funds
Nil.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salma, R.G., Al-Shammari, F.M., Al-Garni, B.A. et al. Operative time, blood loss, hemoglobin drop, blood transfusion, and hospital stay in orthognathic surgery. Oral Maxillofac Surg 21, 259–266 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10006-017-0626-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10006-017-0626-1