Abstract
Objective
To describe the shedding profile of human herpesviruses in the saliva of renal transplant recipients.
Methods
This is a prospective case-control study of 50 renal transplant recipients and control group of 50 individuals (non-transplanted and immunocompetent). Mouthwash samples were collected via oral rinse and then submitted to screening for the presence of eight types of herpesviruses by using multiplex PCR. Fisher’s exact, chi-square, and Student t tests were used for statistical analysis, and the significance level was set at 5%.
Results
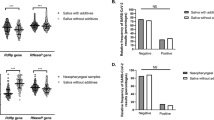
The mean age of the study group was 49.42 ± 12.94 years, 28/50 (56%) were female, and the time elapsed after transplantation was 68.20 ± 67.19 months. Herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) (P = 0.025) and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) (P = 0.024) were, statistically, more excreted in the saliva of renal transplant recipients compared to control group. Gender (P = 1.00) and age (P = 0.563) did not influence the salivary shedding of herpesviruses in renal transplant recipients. Individuals who excreted varicella-zoster virus in saliva had a shorter mean time of transplantation (22:00 + 2.82 months) (P < 0.001).
Conclusion
Renal transplant recipients excreted herpesviruses more often than controls, especially HSV-1 and EBV, with salivary shedding of herpesviruses being more frequent in patients with recent kidney transplantation.
Clinical relevance
The present findings support other longitudinal studies evaluating the relationship between oral shedding of human herpesviruses and clinical presence of active infection and renal transplant failure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gupta RK (2007) Opportunistic infections in renal allograft recipients. Transplant Proc 39:731–733
Meijers RW, Litjens NH, Hesselink DA, Langerak AW, Baan CC, Betjes MG (2015) Primary cytomegalovirus infection significantly impacts circulating T cells in kidney transplant recipients. Am J Transplant 15:3143–3156
Yalci A, Celebi ZK, Ozbas B, Sengezer OL, Unal H, Memikoğlu KO, Sengul S, Tuzuner A, Keven K (2015) Evaluation of infectious complications in the first year after kidney transplantation. Transplant Proc 47:1429–1432
Brazilian Association of Organ Transplantation (2016) Numerical data on donation of organs and transplants performed by state and institution in the period: Jan/Jun 2016. http://www.abto.org.br/abtov03/Upload/file/RBT/2016/1sem-RBT2016%20leitura.pdf. Accessed 26 jan 2017
Linares L, Cofán F, Cervera C, Ricart MJ, Oppenheimer F, Campistol JM, Moreno A (2007) Infection-related mortality in a large cohort of renal transplant recipients. Transplant Proc 39:2225–2227
Ak O, Yildirim M, Kucuk HF, Gencer S, Demir T (2013) Infections in renal transplant patients: risk factors and infectious agents. Transplant Proc 45:944–948
Gupta M, Diaz-Mitoma F, Feber J, Shaw L, Forget C, Filler G (2003) Tissue HHV6 and 7 determination in pediatric solid organ recipients—a pilot study. Pediatr Transplant 7:458–463
Al-Otaibi LM, Ngui SL, Scully CM, Porter SR, Teo CG (2007) Salivary human herpesvirus 8 shedding in renal allograft recipients with Kaposi’s sarcoma. J Med Virol 79:1357–1365
Al-Otaibi LM, Al-Sulaiman MH, Teo CG, Porter SR (2009) Extensive oral shedding of human herpesvirus 8 in a renal allograft recipient. Oral Microbiol Immunol 24:109–115
Le J, Gantt S (2013) Human herpesvirus 6, 7 and 8 in solid organ transplantation. Am J Transplant 13:128–137
Johnson G, Nelson S, Petric M, Tellier R (2000) Comprehensive PCR-based assay for detection and species identification of human herpesviruses. J Clin Microbiol 38:3274–3279
Nunes LA, Mussavira S, Bindhu OS (2015) Clinical and diagnostic utility of saliva as a non-invasive diagnostic fluid: a systematic review. Biochem Med (Zagreb) 25:177–192
Palmieri M, Martins VA, Sumita LM, Tozetto-Mendoza TR, Romano BB, Machado CM, Pannuti CS, Brandão TB, Ribeiro AC, Corrêa L, Braz-Silva PH (2016) Oral shedding of human herpesviruses in patients undergoing radiotherapy/chemotherapy treatment for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Oral Investig
Braz-Silva PH, Ortega KL, Rezende NP, Nunes FD, Magalhães MH (2006) Detection of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) in the oral mucosa of renal transplant patients. Diagn Cytopathol 34:24–28
Al-Otaibi LM, Moles DR, Porter SR, Teo CG (2012) Human herpesvirus 8 shedding in the mouth and blood of hemodialysis patients. J Med Virol 84:792–797
Baez CF, Guimarães MA, Martins RA, Zalona AC, Cossatis JJ, Zalis MG, Cavalcanti SM, Varella RB (2013) Detection of Merkel cell polyomavirus in oral samples of renal transplant recipients without Merkel cell carcinoma. J Med Virol 85:2016–2019
Yamamoto Y, Morooka M, Hashimoto S, Ihra M, Yoshikawa T (2014) Analysis of the shedding of three β-herpesviruses in urine and saliva of children with renal disease. J Med Virol 86:505–511
Carratalà J, Montejo M, Pérez-Romero P (2012) Infections caused by herpes viruses other than cytomegalovirus in solid organ transplant recipients. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin 30:63–69
Anastasopoulos NA, Duni A, Peschos D, Agnantis N, Dounousi E (2015) The Spectrum of infectious diseases in kidney transplantation: a review of the classification, pathogens and clinical manifestations. In Vivo 29:415–422
Neumann AB, Daxbacher EL, Chiaratti FC, Jeunon T (2016) Cutaneous involvement by cytomegalovirus in a renal transplant recipient as an indicator of severe systemic infection. An Bras Dermatol 91:80–83
Beyari MM, Hodgson TA, Cook RD, Kondowe W, Molyneux EM, Scully CM, Teo CG, Porter SR (2003) Multiple human herpesvirus-8 infection. J Infect Dis 188:678–689
Carraro E, Granato CF (2003 Jun) Single human cytomegalovirus gB genotype shed in multiple sites at the time of diagnosis in renal transplant recipients. J Med Virol 70(2):240–243
Kaufman HE, Azcuy AM, Varnell ED, Sloop GD, Thompson HW, Hill JM (2005) HSV-1 DNA in tears and saliva of normal adults. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 46:241–247
da Silva LM, Guimarães AL, Victória JM, Gomes CC, Gomez RS (2005) Herpes simplex virus type 1 shedding in the oral cavity of seropositive patients. Oral Dis 11:13–16
Lima RB, Santos PS, Malafronte P, Muller H, Caiaffa-Filho HH, Sens YA (2008) Oral manifestation of cytomegalovirus associated with herpes simplex virus in renal transplant recipient. Transplant Proc 40:1378–1381
López-Pintor RM, Hernández G, de Arriba L, Morales JM, Jiménez C, de Andrés A (2009) Oral ulcers during the course of cytomegalovirus infection in renal transplant recipients. Transplant Proc 41:2419–2421
Mustapic Z, Basic-Jukic N, Kes P, Lovcic V, Lj B-F, Mokos I, Kastelan Z, Zekan S (2011) Varicella zoster infection in renal transplant recipients: prevalence, complications and outcome. Kidney Blood Press Res 34:382–386
Netchiporouk E, Tchervenkov J, Paraskevas S, Sasseville D, Billick R (2013) Evaluation of herpes simplex virus infection morbidity and mortality in pancreas and kidney-pancreas transplant recipients. Transplant Proc 45:3343–3347
Schmidt-Westhausen A, Gelderblom HR, Neuhaus P, Reichart PA (1993) Epstein-Barr virus in lingual epithelium of liver transplant patients. J Oral Pathol Med 22:274–276
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Funding
This study was supported by the Government of Brazil through the National Council for Technological Development (CNPq) according to grant number # 443004/2014-5 and São Paulo State Research Support Foundation (FAPESP) according to grant numbers # 2015/03906-6, #2012/04223-1, and #2013/08242-3.
Ethical approval
All the procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards set by institutional and/or national research committees and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration, including its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee for Analysis of Research Project (CAPpesq) under protocol number 290/2011.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was individually obtained from all participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Santana Sarmento, D.J., Tozetto-Mendoza, T.R., Masami Sumita, L. et al. Oral shedding of human herpesviruses in renal transplant recipients. Clin Oral Invest 22, 885–891 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-017-2166-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-017-2166-3