Abstract
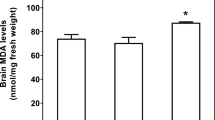
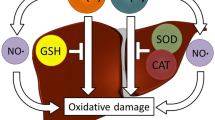
Iron [Fe(II)] and copper [Cu(II)] overloads in rat brain are associated with oxidative stress and damage. The purpose of this research is to study whether brain antioxidant enzymes are involved in the control of intracellular redox homeostasis in the brain of rats male Sprague–Dawley rats (80–90 g) that received drinking water supplemented with either 1.0 g/L of ferrous chloride (n = 24) or 0.5 g/L cupric sulfate (n = 24) for 42 days. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase, superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase, glutathione peroxidase (GPx) and glutathione transferase (GT) activities in brain were determined by spectrophotometric methods and NO production by the content of nitrite concentration in the organ. Chronic treatment with Fe(II) and Cu(II) led to a significant decrease of nitrite content and SOD activity in brain. Activity of NADPH oxidase increased with Cu(II) treatment. Concerning Fe(II), catalase and GT activities increased in brain after 28 and 4 days of treatment, respectively. In the case of Cu(II), catalase activity decreased whereas GT activity increased after 2 and 14 days, respectively. The regulation of redox homeostasis in brain involves changes of the activity of these enzymes to control the steady state of oxidant species related to redox signaling pathways upon Cu and Fe overload. NO may serve to detoxify cells from superoxide anion and hydrogen peroxide with the concomitant formation of peroxynitrite. However, the latest is a powerful oxidant which leads to oxidative modifications of biomolecules. These results suggest a common pathway to oxidative stress and damage in brain for Cu(II) and Fe(II).
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ATP7A:
-
ATPase copper exporter protein
- BBB:
-
Blood–brain barrier
- CDNB:
-
1 Chlorine-2,4 dinitro benzene
- C50 :
-
Metal content necessary to produce the half of the maximal effect
- Ctr1:
-
Copper transporter receptor 1
- Cu:
-
Copper
- Cu(II):
-
Divalent copper ion
- Fe:
-
Iron
- Fe(II):
-
Divalent iron ion
- GPx:
-
Glutathione peroxidase
- GS-DNB:
-
Glutathione-dinitrobenzene
- GSH:
-
Glutathione
- GT:
-
Glutathione transferase
- H2O2 :
-
Hydrogen peroxide
- HO• :
-
Hydroxyl radical
- NADPH:
-
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase
- NO− :
-
Nitroxyl anion
- NO+ :
-
Nitrosonium cation
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- N2O3 :
-
Dinitrogen trioxide
- O2 :
-
Oxygen
- ONNO− :
-
Peroxynitrite
- O2 − :
-
Superoxide anion
- 1O2 :
-
Singlet oxygen
- RNS:
-
Reactive nitrogen species
- ROOH:
-
Organic hydroperoxides
- ROO. :
-
Hydroperoxyl radical
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- RNS:
-
Reactive nitrogen species
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- t 1/2 :
-
Time necessary to produce the half of the maximal effect
- Tf:
-
Transferrin
- TfR:
-
Transferrin receptor
References
Jomova K, Valko M (2011) Advances in metal-induced oxidative stress and human disease. Toxicol 283:65–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2011.03.001
Zhao Y, Zhao B (2013) Oxidative stress and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2013:316–523. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/316523
Calabrese V, Lodi R, Tonon C, D’Agata V, Sapienza M, Scapagnini G, Mangiameli A, Pennisi G, Stella A, Butterfield D (2005) Oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction and cellular stress response in Friedreich’s ataxia. J Neurol Sci 233:145–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2005.03.012
Gutteridge JMC, Halliwell B (2018) Mini-review: oxidative stress, redox stress or redox success? Biochem Biophys Res Commun 502(2):183–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.05.045
Boveris A, Repetto MG, Bustamante J, Boveris AD, Valdez L (2008) The concept of oxidative stress in pathology. In: Alvarez S, Evelson P, Boveris A (eds) Free Radical Pathophysiology. Research Signpost, Kerala
Sies H (1991) Oxidative stress: from basic research to clinical application. Am J Med 91:31S-38S. https://doi.org/10.1016/0002-9343(91)90281-2
Sies H (2015) Oxidative stress: a concept in redox biology and medicine. Redox Biol 4:180–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2015.01.002
Sies H (2016) The concept of oxidative stress after 30 years. In: Gelpi RJ, Boveris A, Poderoso JJ (eds) Biochemistry of Oxidative Stress. Springer Internat, Publish, Switzerland. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-45865-6_1
Cornelius C, Koverech G, Crupi R, Di Paola R, Koverech A, Lodato F, Scuto M, Salinaro A, Cuzzocrea S, Calabrese E, Calabrese V (2014) Osteoporosis and Alzheimer pathology: role of cellular stress response and hormetic redox signaling in aging and bone remodeling. Front Pharmacol 5:120. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2014.00120
Calabrese V, Cornelius C, Dinkova-Kostova AT, Calabrese EJ, Mattson MP (2010) Cellular stress responses, the hormesis paradigm, and vitagenes: novel targets for therapeutic intervention in neurodegenerative disorders. Antioxid Redox Signal 13:1763–1811. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2009.3074
Calabrese V, Mancuso C, Cornelius C, Calafato M, Ventimiglia B, Butterfield D, Dinkova-Kostova AT, Rizzarelli E (2008) Reactive nitrogen species and cellular stress tolerance in aging and neurodegeneration: Role of vitagenes. In: Alvarez S, Evelson P, Boveris A (eds) Free Radical Pathophysiology. Research Signpost, Kerala
Sies H (2007) Biological redox systems and oxidative stress. Cell Mol Life Sci 64:2181–2188. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-007-7230-8
Boveris A, Musacco Sebio R, Ferrarotti N, Saporito Magriñá C, Torti H, Massot F, Repetto MG (2012) The acute toxicity of iron and copper: biomolecule oxidation and oxidative damage in rat liver. J Inorg Biochem 116:63–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2012.07.004
Musacco-Sebio R, Ferrarotti N, Saporito- Magriñá C, Semprine J, Fuda J, Torti H, Boveris A, Repetto MG (2014) Oxidative damage to rat brain in iron and copper overloads. Metallomics 6:1410–1416. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3mt00378g
Musacco-Sebio R, Saporito-Magriñá C, Semprine J, Torti H, Ferrarotti N, Castro-Parodi M, Damiano A, Boveris A, Repetto MG (2014) Rat liver antioxidant response to iron and copper overloads. J Inorg Biochem 137:94–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2014.04.014
Semprine J, Ferrarotti N, Musacco Sebio R, Saporito Magriñá C, Fuda J, Torti H, Castro Parodi M, Damiano A, Boveris A, Repetto MG (2014) Brain antioxidant responses to acute iron and copper intoxications in rats. Metallomics 6:2083–2089. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4mt00159a
Musacco-Sebio R, Ferrarotti N, Saporito-Magriñá C, Fuda J, Torti H, Lairión F, Boveris A, Repetto MG (2019) Redox dyshomeostasis in the experimental chronic hepatic overloads with iron or copper. J Inorg Biochem 191:119–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2018.11.014
Musacco-Sebio R, Ferrarotti N, Lairion F, Saporito-Magriñá C, Fuda J, Torti H, Boveris A, Repetto MG (2019) Brain oxidative stress in rat with chronic iron and copper overload. J Inorg Biochem 199:110799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2019.110799
Wiegand HL, Orths CT, Kerpen K, Lutze HV, Schmidt TC (2017) Investigation of the iron-peroxo complex in the fenton reaction: kinetic indication, decay kinetics, and hydroxyl radical yields. Environ Sci Technol 51:14321–14329. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b03706
Lairion F, Saporito-Magriñá C, Musacco-Sebio R, Fuda J, Torti H, Repetto MG (2021) Nitric oxide, chronic iron and copper overloads and regulation of redox homeostasis in rat liver. J Biol Inorg Chem. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00775-021-01908-1
Freitas Ferreira MC, Zucki F, Duarte J, Godoy Iano F, Farias Ximenes V, Rabelo Buzalaf M, Cardoso de Oliveira R (2017) Influence of iron on modulation of the antioxidant system in rat brains exposed to lead. Environ Toxicol 32:813–822. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.22281
Ala A, Walker AP, Ashkan K, Dooley JS, Schilsky ML (2007) Wilson`s Disease. Lancet 369:397–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60196-2
Rodriguez-Castro KI, Hevia-Urrutia FJ, Sturniolo G (2015) Wilson’s disease: a review of what we have learned. World J Hepatol 7:2859–2870. https://doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v7.i29.2859
Sengupta P (2013) The laboratory rat: relating its age with human’s. Int J Prev Med 4(6):624–630
AVMA Guidelines for the Euthanasia of Animals (2013). 2:38
Skoog D, West D, Holler F (2014) Fundamentos de Química Analítica. McGraw-Hill, México
González Flecha B, Llesuy S, Boveris A (1991) Hydroperoxide-initiated chemiluminescence: an assay for oxidative stress in biopsies of heart, liver, and muscle. Free Radic Biol Med 10:93–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/0891-5849(91)90002-k
Boveris A, Oshino N, Chance B (1972) The cellular production of hydrogen peroxide. Biochem J 128:617–627. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj1280617
Ding AH, Nathan CF, Stuehr DJ (1998) Release of reactive nitrogen intermediates and reactive oxygen intermediates from mouse peritoneal macrophages. Comparison of activating cytokines and evidence for independent production. J Immunol 141:2407–2412. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.15-16864
Wei Y, Sowers J, Nistala R, Gong H, Uptergrove G, Clark S, Morris M, Szary N, Manrique C, Stump C (2006) Angiotensin II-induced NADPH oxidase activation impairs insulin signaling in skeletal muscle cells. J Biol Chem 281:35137–35146. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m601320200
McCord J, Fridovich I (1969) Superoxide dismutase. an enzymatic function for erythrocuprein hemocuprein. J Biol Chem 244:049–6055
Misra HP, Fridovich I (1972) The role of superoxide anion in the autoxidation of epinephrine and a simple assay for superoxide dismutase. J Biol Chem 247:3170–3175
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Meth Enzymol 10:121–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(84)05016-3
Chance B (1954) Determination of Catalase Activity. In: Glick J (ed) Methods of biochemical analysis. Interscience Publishers, New York
Wendel A (1981) Glutathione peroxidase. Meth Enzymol 77:325–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0076-6879(81)77046-0
Habig W, Pabts M, Jakoby W (1974) Glutathione S-transferases. The first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem 249:7130–7139
Valko M, Rhodes C, Moncol J, Izakovic M, Mazur M (2006) Free radicals, metals and antioxidants in oxidative stress-induced cancer. Chem Biol Interact 160:1–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2005.12.009
Przbylkowski A, Gromadzka G, Wawer A, Grygorowicz T, Cybulska A, Czlonkowka A (2013) Intestinal expression of metal transporters in Wilson’s disease. Biometals 26:925–934. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-013-9668-5
Saporito Magriñá CM, Musacco Sebio RN, Andrieux G, Kook L, Orrego MT, Tuttolomondo MV, Desimone MF, Boerries M, Borner C, Repetto MG (2018) Copper-induced cell death and the protective role of glutathione: the implication of impaired protein folding rather than oxidative stress. Metallomics 10(12):1743–1754. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8mt00182k
Rao P, Hayon E (1973) Experimental determination of the redox potential of the superoxide radical O2−. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 51:468–473. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-291X(73)91280-1
Finkel T (2000) Redox dependent signal transduction. FEBS Lett 476:52–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-5793(00)01669-0
Ansari H, Roberts K, Scheff S (2014) A time course of NADPH-oxidase upregulation and endothelial nitric oxide synthase activation in the hippocampus following neurotrauma. Free Radic Biol Med 77:21–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.freeradbiomed.2014.08.025
Huie RE, Padmaja S (1993) The reaction of no with superoxide. Free Radic Res Commun 18:195–199. https://doi.org/10.3109/10715769309145868
Ma MW, Wang J, Zhang Q, Wang R, Dhandapani KM, Vadlamudi RK, Brann DW (2017) NADPH oxidase in brain injury and neurodegenerative disorders. Mol Neurodegener 12:7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13024-017-0150-7
Goldsteins G, Hakosalo V, Jaronen M, Keuters MH, Lehtonen Š, Koistinaho J (2022) CNS redox homeostasis and dysfunction in neurodegenerative diseases. Antioxidants 11:405. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11020405
Cvetko F, Caldwell S, Higgin M, Suzuki T, Yamamoto M, Prag H, Hartley R, Dinkova-Kostova A, Murphy M (2021) Nrf2 is activated by disruption of mitochondrial thiol homeostasis but not by enhanced mitochondrial superoxide production. Biol Chem 296:100169. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA120.016551
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Professor Alberto Boveris for his teachings and scientific contributions at the beginning of this research work, guiding the development of this experimental line.
Funding
This study was supported by grants from the University of Buenos Aires (UBACyT 20020170100197BA); the National Research Council of Argentina (CONICET) and the National Agency of Science and Technology of Argentina (ANPCYT) (PICT-2016–002077).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CS-M: methodology, validation, investigation, visualization, FL: validation, formal analysis, methodology, investigation, writing-original-draft, RM-S: methodology, investigation, JF: investigation, HT: investigation, resources, MGR: conceptualization, formal analysis, writing-original-draft, writing, review and editing, project administration, funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Saporito-Magriñá, C., Lairion, F., Musacco-Sebio, R. et al. Biochemical regulatory processes in the control of oxidants and antioxidants production in the brain of rats with iron and copper chronic overloads. J Biol Inorg Chem 27, 665–677 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00775-022-01960-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00775-022-01960-5