Abstract
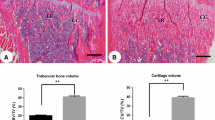
The cytoskeletal organization of osteoclasts is required for bone resorption. Binding of dynamin with guanosine triphosphate (GTP) was previously suggested to be required for the organization of the actin cytoskeleton. However, the role of the GTPase activity of dynamin in the organization of the actin cytoskeleton as well as in the bone-resorbing activity of osteoclasts remains unclear. This study investigated the effects of dynasore, an inhibitor of the GTPase activity of dynamin, on the bone-resorbing activity of and actin ring formation in mouse osteoclasts in vitro and in vivo. Dynasore inhibited the formation of resorption pits in osteoclast cultures by suppressing actin ring formation and rapidly disrupting actin rings in osteoclasts. A time-lapse image analysis showed that dynasore shrank actin rings in osteoclasts within 30 min. The intraperitoneal administration of dynasore inhibited receptor activator of nuclear factor κB ligand (RANKL)-induced trabecular bone loss in mouse femurs. These in vitro and in vivo results suggest that the GTPase activity of dynamin is critical for the bone-resorbing activity of osteoclasts and that dynasore is a seed for the development of novel anti-resorbing agents.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Suda T, Takahashi N, Udagawa N, Jimi E, Gillespie MT, Martin TJ (1999) Modulation of osteoclast differentiation and function by the new members of the tumor necrosis factor receptor and ligand families. Endocr Rev 20:345–357
Boyle WJ, Simonet WS, Lacey DL (2003) Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature 423:337–342
Takahashi N, Ejiri S, Yanagisawa S, Ozawa H (2007) Regulation of osteoclast polarization. Odontology 95:1–9
Teitelbaum SL (2011) The osteoclast and its unique cytoskeleton. Ann NY Acad Sci 1240:14–17
Vaananen HK, Zhao H, Mulari M, Halleen JM (2000) The cell biology of osteoclast function. J Cell Sci 113:377–381
Jurdic P, Saltel F, Chabadel A, Destaing O (2006) Podosome and sealing zone: specificity of the osteoclast model. Eur J Cell Biol 85:195–202
Nakayama T, Mizoguchi T, Uehara S, Yamashita T, Kawahara I, Kobayashi Y, Moriyama Y, Kurihara S, Sahara N, Ozawa H, Udagawa N, Takahashi N (2011) Polarized osteoclasts put marks of tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase on dentin slices–a simple method for identifying polarized osteoclasts. Bone 49:1331–1339
Urrutia R, Henley JR, Cook T, McNiven MA (1997) The dynamins: redundant or distinct functions for an expanding family of related GTPases? Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:377–384
Ungewickell EJ, Hinrichsen L (2007) Endocytosis: clathrin-mediated membrane budding. Curr Opin Cell Biol 19:417–425
Mettlen M, Pucadyil T, Ramachandran R, Schmid SL (2009) Dissecting dynamin’s role in clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Biochem Soc Trans 37:1022–1026
Schafer DA (2004) Regulating actin dynamics at membranes: a focus on dynamin. Traffic 5:463–469
Bruzzaniti A, Neff L, Sanjay A, Horne WC, De Camilli P, Baron R (2005) Dynamin forms a Src kinase-sensitive complex with Cbl and regulates podosomes and osteoclast activity. Mol Biol Cell 16:3301–3313
Horne WC, Sanjay A, Bruzzaniti A, Baron R (2005) The role(s) of Src kinase and Cbl proteins in the regulation of osteoclast differentiation and function. Immunol Rev 208:106–125
Bruzzaniti A, Neff L, Sandoval A, Du L, Horne WC, Baron R (2009) Dynamin reduces Pyk2 Y402 phosphorylation and SRC binding in osteoclasts. Mol Cell Biol 29:3644–3656
Eleniste PP, Du L, Shivanna M, Bruzzaniti A (2012) Dynamin and PTP-PEST cooperatively regulate Pyk2 dephosphorylation in osteoclasts. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 44:790–800
Gu C, Yaddanapudi S, Weins A, Osborn T, Reiser J, Pollak M, Hartwig J, Sever S (2010) Direct dynamin-actin interactions regulate the actin cytoskeleton. EMBO J 29:3593–3606
Shin NY, Choi H, Neff L, Wu Y, Saito H, Ferguson SM, De Camilli P, Baron R (2014) Dynamin and endocytosis are required for the fusion of osteoclasts and myoblasts. J Cell Biol 207:73–89
Macia E, Ehrlich M, Massol R, Boucrot E, Brunner C, Kirchhausen T (2006) Dynasore, a cell-permeable inhibitor of dynamin. Dev Cell 10:839–850
Newton AJ, Kirchhausen T, Murthy VN (2006) Inhibition of dynamin completely blocks compensatory synaptic vesicle endocytosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:17955–17960
Chung C, Barylko B, Leitz J, Liu X, Kavalali ET (2010) Acute dynamin inhibition dissects synaptic vesicle recycling pathways that drive spontaneous and evoked neurotransmission. J Neurosci 30:1363–1376
Otsuka A, Abe T, Watanabe M, Yagisawa H, Takei K, Yamada H (2009) Dynamin 2 is required for actin assembly in phagocytosis in Sertoli cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 378:478–482
Takahashi N, Udagawa N, Kobayashi Y, Suda T (2007) Generation of osteoclasts in vitro, and assay of osteoclast activity. Methods Mol Med 135:285–301
Okamoto M, Udagawa N, Uehara S, Maeda K, Yamashita T, Nakamichi Y, Kato H, Saito N, Minami Y, Takahashi N, Kobayashi Y (2014) Noncanonical Wnt5a enhances Wnt/beta-catenin signaling during osteoblastogenesis. Sci Rep 4:4493
Kuroda H, Nakamura M, Kamiyama K (1996) Effects of calcitonin and parathyroid hormone on the distribution of F-actin in the clear zone of osteoclasts in vivo. Bone 19:115–120
Tomimori Y, Mori K, Koide M, Nakamichi Y, Ninomiya T, Udagawa N, Yasuda H (2009) Evaluation of pharmaceuticals with a novel 50-h animal model of bone loss. J Bone Miner Res 24:1194–1205
Maeda K, Kobayashi Y, Udagawa N, Uehara S, Ishihara A, Mizoguchi T, Kikuchi Y, Takada I, Kato S, Kani S, Nishita M, Marumo K, Martin TJ, Minami Y, Takahashi N (2012) Wnt5a-Ror2 signaling between osteoblast-lineage cells and osteoclast precursors enhances osteoclastogenesis. Nat Med 18:405–412
Morimoto R, Uehara S, Yatsushiro S, Juge N, Hua Z, Senoh S, Echigo N, Hayashi M, Mizoguchi T, Ninomiya T, Udagawa N, Omote H, Yamamoto A, Edwards RH, Moriyama Y (2006) Secretion of l-glutamate from osteoclasts through transcytosis. EMBO J 25:4175–4186
Ochoa GC, Slepnev VI, Neff L, Ringstad N, Takei K, Daniell L, Kim W, Cao H, McNiven M, Baron R, De Camilli P (2000) A functional link between dynamin and the actin cytoskeleton at podosomes. J Cell Biol 150:377–389
Destaing O, Saltel F, Geminard JC, Jurdic P, Bard F (2003) Podosomes display actin turnover and dynamic self-organization in osteoclasts expressing actin-green fluorescent protein. Mol Biol Cell 14:407–416
Lee A, Frank DW, Marks MS, Lemmon MA (1999) Dominant-negative inhibition of receptor-mediated endocytosis by a dynamin-1 mutant with a defective pleckstrin homology domain. Curr Biol 9:261–264
Palokangas H, Mulari M, Vaananen HK (1997) Endocytic pathway from the basal plasma membrane to the ruffled border membrane in bone-resorbing osteoclasts. J Cell Sci 110:1767–1780
Stenbeck G, Horton MA (2004) Endocytic trafficking in actively resorbing osteoclasts. J Cell Sci 117:827–836
Ishii KA, Fumoto T, Iwai K, Takeshita S, Ito M, Shimohata N, Aburatani H, Taketani S, Lelliott CJ, Vidal-Puig A, Ikeda K (2009) Coordination of PGC-1beta and iron uptake in mitochondrial biogenesis and osteoclast activation. Nat Med 15:259–266
Yu T, Robotham JL, Yoon Y (2006) Increased production of reactive oxygen species in hyperglycemic conditions requires dynamic change of mitochondrial morphology. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:2653–2658
Roth D, Krammer PH, Gulow K (2014) Dynamin related protein 1-dependent mitochondrial fission regulates oxidative signalling in T cells. FEBS Lett 588:1749–1754
Masaike Y, Takagi T, Hirota M, Yamada J, Ishihara S, Yung TM, Inoue T, Sawa C, Sagara H, Sakamoto S, Kabe Y, Takahashi Y, Yamaguchi Y, Handa H (2010) Identification of dynamin-2-mediated endocytosis as a new target of osteoporosis drugs, bisphosphonates. Mol Pharmacol 77:262–269
Takito J, Otsuka H, Yanagisawa N, Arai H, Shiga M, Inoue M, Nonaka N, Nakamura M (2014) Regulation of osteoclast multinucleation by the actin cytoskeleton signaling network. J Cell Physiol 230:395–405
Nakamura M, Udagawa N, Matsuura S, Mogi M, Nakamura H, Horiuchi H, Saito N, Hiraoka BY, Kobayashi Y, Takaoka K, Ozawa H, Miyazawa H, Takahashi N (2003) Osteoprotegerin regulates bone formation through a coupling mechanism with bone resorption. Endocrinology 144:5441–5449
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research, Kakenhi [Grant number: 25221310 (N.T.), 24390417(N.U.), 25293423 (Y.K.), 25462904 (S.U.)].
Conflict of interest
None of the authors have any conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
G. J. Thirukonda and S. Uehara contributed equally to this work.
About this article
Cite this article
Thirukonda, G.J., Uehara, S., Nakayama, T. et al. The dynamin inhibitor dynasore inhibits bone resorption by rapidly disrupting actin rings of osteoclasts. J Bone Miner Metab 34, 395–405 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-015-0683-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-015-0683-1