Abstract
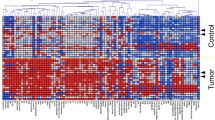
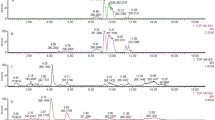
The aim of this study is to evaluate the effect of duration after meals for saliva collections for oral cancer detection using metabolomics. Saliva samples were collected from oral cancer patients (n = 22) and controls (n = 44). Saliva from cancer patients was collected 12 h after dinner, and 1.5 and 3.5 h after breakfast. Control subjects fasted >1.5 h prior to saliva collection. Hydrophilic metabolites were analyzed using capillary electrophoresis mass spectrometry. Levels of 51 metabolites differed significantly in controls vs. oral cancer patients at the 12-h fasting time point (P < 0.05). Fifteen and ten metabolites differed significantly at the 1.5- and 3.5-h time points, respectively. The area of under receiver operating characteristic curve for discriminating oral cancer patients from controls was greatest at the 12-h fasting time point. The collection time after meals affects levels of salivary metabolites for oral cancer screening. The 12-h fasting after dinner time point is optimal. This study contributes to design of saliva collection protocols for metabolomics-based biomarker discovery.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CE-TOFMS:
-
Capillary electrophoresis time-of-flight mass spectrometry
- FDR:
-
False discovery rate
- ROC:
-
Receiver operating characteristic
- AUC:
-
Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve
- SAM:
-
S-adenosylmethionine
References
Burton C, Shi H, Ma Y (2014) Normalization of urinary pteridines by urine specific gravity for early cancer detection. Clin Chim Acta 435:42–47. doi:10.1016/j.cca.2014.04.022
Dawes C (1974) Rhythms in salivary flow rate and composition. Int J Chronobiol 2(3):253–279
Dawes C, Pedersen AM, Villa A, Ekstrom J, Proctor GB, Vissink A, Wolff A (2015) The functions of human saliva: a review sponsored by the World Workshop on Oral Medicine VI. Arch Oral Biol 60(6):863–874. doi:10.1016/j.archoralbio.2015.03.004
de Almeida Pdel V, Gregio AM, Machado MA, de Lima AA, Azevedo LR (2008) Saliva composition and functions: a comprehensive review. J Contemp Dent Pract 9(3):72–80
Dodds MW, Johnson DA, Yeh CK (2005) Health benefits of saliva: a review. J Dent 33(3):223–233. doi:10.1016/j.jdent.2004.10.009
Gleber-Netto FO, Yakob M, Li F, Feng Z, Dai J, Kao HK, Wong DT (2016) Salivary biomarkers for detection of oral squamous cell carcinoma in a Taiwanese population. Clin Cancer Res. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-1761
Harthoorn LF, Dransfield E (2008) Periprandial changes of the sympathetic-parasympathetic balance related to perceived satiety in humans. Eur J Appl Physiol 102(5):601–608. doi:10.1007/s00421-007-0622-5
Hu S, Wang J, Meijer J, Ieong S, Xie Y, Yu T, Wong DT (2007) Salivary proteomic and genomic biomarkers for primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Arthritis Rheum 56(11):3588–3600. doi:10.1002/art.22954
Hu S, Gao K, Pollard R, Arellano-Garcia M, Zhou H, Zhang L, Wong DT (2010) Preclinical validation of salivary biomarkers for primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 62(11):1633–1638. doi:10.1002/acr.20289
Ishikawa S, Sugimoto M, Kitabatake K, Sugano A, Nakamura M, Kaneko M, Iino M (2016) Identification of salivary metabolomic biomarkers for oral cancer screening. Sci Rep 6:31520. doi:10.1038/srep31520
Kageyama G, Saegusa J, Irino Y, Tanaka S, Tsuda K, Takahashi S, Morinobu A (2015) Metabolomics analysis of saliva from patients with primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Clin Exp Immunol 182(2):149–153. doi:10.1111/cei.12683
Kawahara R, Bollinger JG, Rivera C, Ribeiro AC, Brandao TB, Paes Leme AF, MacCoss MJ (2016) A targeted proteomic strategy for the measurement of oral cancer candidate biomarkers in human saliva. Proteomics 16(1):159–173. doi:10.1002/pmic.201500224
Khurshid Z, Zohaib S, Najeeb S, Zafar MS, Slowey PD, Almas K (2016) Human saliva collection devices for proteomics: an update. Int J Mol Sci 17(6). doi:10.3390/ijms17060846
McNeil BK, Sorbellini M, Grubb RL 3rd, Apolo A, Cecchi F, Athauda G, Bottaro DP (2014) Preliminary evaluation of urinary soluble Met as a biomarker for urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. J Transl Med 12:199. doi:10.1186/1479-5876-12-199
Nishiyama A, Yokote Y, Sakagami H (2010) Changes in amino acid metabolism during activation of mouse macrophage-like cell lines. Vivo 24(6):857–860
Saeed AI, Bhagabati NK, Braisted JC, Liang W, Sharov V, Howe EA, Quackenbush J (2006) [9] TM4 microarray software suite. Methods Enzymol 411:134–193
Schneyer LH, Pigman W, Hanahan L, Gilmore RW (1956) Rate of flow of human parotid, sublingual, and submaxillary secretions during sleep. J Dent Res 35(1):109–114
Segal A, Wong DT (2008) Salivary diagnostics: enhancing disease detection and making medicine better. Eur J Dent Educ 12(Suppl 1):22–29. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0579.2007.00477.x
Sugimoto M, Wong DT, Hirayama A, Soga T, Tomita M (2010) Capillary electrophoresis mass spectrometry-based saliva metabolomics identified oral, breast and pancreatic cancer-specific profiles. Metabolomics 6(1):78–95. doi:10.1007/s11306-009-0178-y
Sugimoto M, Saruta J, Matsuki C, To M, Onuma H, Kaneko M, Tsukinoki K (2013) Physiological and environmental parameters associated with mass spectrometry-based salivary metabolomic profiles. Metabolomics 9(2):454–463
Toda M, Morimoto K, Nagasawa S, Kitamura K (2004) Effect of snack eating on sensitive salivary stress markers cortisol and chromogranin A. Environ Health Prev Med 9(1):27–29. doi:10.1265/ehpm.9.27
Wang Q, Gao P, Wang X, Duan Y (2014) The early diagnosis and monitoring of squamous cell carcinoma via saliva metabolomics. Sci Rep 4:6802. doi:10.1038/srep06802
Wei J, Xie G, Zhou Z, Shi P, Qiu Y, Zheng X, Jia W (2011) Salivary metabolite signatures of oral cancer and leukoplakia. Int J Cancer 129(9):2207–2217. doi:10.1002/ijc.25881
Yan X, Yang M, Liu J, Gao R, Hu J, Li J, Hu S (2015) Discovery and validation of potential bacterial biomarkers for lung cancer. Am J Cancer Res 5(10):3111–3122
Acknowledgements
We thank all sample providers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Grant support
This work was supported by grants from Yamagata prefecture, Tsuruoka city and the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) KAKENHI (16K11742).
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Handling Editor: J. M. Phang.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishikawa, S., Sugimoto, M., Kitabatake, K. et al. Effect of timing of collection of salivary metabolomic biomarkers on oral cancer detection. Amino Acids 49, 761–770 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-017-2378-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-017-2378-5