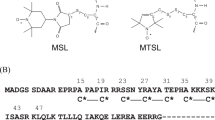
Abstract
Troponin (Tn) is a protein that consists of three subunits, troponin C (TnC), troponin I (TnI), and troponin T (TnT), and Tn controls cardiac muscle contraction by calcium ion binding and phosphorylation. The Ca2+-binding site is the E–F hand motif (C helix–loop–D helix) in the N-terminal domain of TnC, and the structural transition induced by Ca2+ is the opening of these helices and the interaction with TnI, probably at the A and B helices. In this paper, we studied structural changes in the TnC–TnI binary complex on Ca2+ binding by double quantum coherence (DQC) distance measurements. We used a binary complex of the cardiac troponin C and I (cTnC and cTnI) complexes, chose four positions of nitroxide spin label at helices A, B, C, and D in the N-terminal domain and chose the E helix in the C-terminal domain as the reference position to study the structural changes on Ca2+ addition. The label positions were (A22C/S98C), (M47C/S98C), (Q58C/S98C), and (C84/S98C) for the A, B, C, and D helices, respectively. The effects of phosphorylation of the cardiac-specific N-terminal region of cTnI were studied using a phosphomimetic cTnI mutant. Analysis of the modulation of the DQC echo signals provided the distribution of the spin–spin distance. The distances averaged over the distribution showed that the labels on the A, B, and C helices decreased, i.e., moved to the E helix, on Ca2+ binding, while the distance of the label on the D helix showed almost no change. Shoulders and/or small separate peaks were observed in the shape of the distribution and were analyzed as the sum of a few Gaussian functions. The Gaussian functions were grouped into two components, components 1 and 2, at the longer and shorter distances, respectively, separated by 0.7–1.5 nm. The fractions of component 2 were ca. 0.1–0.2 in the Ca2+-free state and increased by 0.2–0.3 on Ca2+ addition, suggesting that the increase in component 2 is related to physiological control of cardiac muscle contraction. The phosphomimetic-modification effects on the Ca2+-induced changes of the fraction of components and the distances of the C- and D-helix labels are small. On the other hand, in the A and B helices, there are significant effects on the Ca2+-induced changes in the distances of the components. The different behaviors of A/B and C/D helices support the current model of the phosphorylation effects in which both N-terminal region and regulatory domain of cTnI interact with the A and B helices of cTnC.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.S. Zot, J.D. Potter, Ann. Rev. Biophys. Biophys. Chem. 16, 535–559 (1987)
S. Takeda, A. Yamashita, K. Maeda, Y. Maeda, Nature 424, 35–41 (2003)
M.V. Vinogradova, D.B. Stone, G.G. Malanina, C. Karatzaferi, R. Cooke, R.A. Mendelson, R.J. Fletterick, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 5038–5043 (2005)
J.J. Jayasundar, J. Xing, J.M. Robinson, H.C. Cheung, W.-J. Dong, PLoS One 9, e87135 (2014)
P.R. Potluri, J. Chamoun, J.A. Cooke, M. Badr, J.A. Guse, R. Rayes, N.M. Cordina, D. McCamey, P.G. Fajer, L.J. Brown, J. Struct. Biol. 200, 376–387 (2017)
N.M. Cordina, C.K. Liew, P.R. Potluri, P.M. Curmi, P.G. Fajer, T.M. Logan, J.P. Mackay, L.J. Brown, PLoS One 9, e112976 (2014)
P.M. Hwang, F. Cai, S.E. Pineda-Sanabria, D.C. Corson, B.D. Sykes, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 111, 14412–14417 (2014)
D.G. Ward, M.P. Cornes, I.P. Trayer, J. Biol. Chem. 277, 41795–41801 (2002)
C. Dohet, E. Al-Hillawi, I.P. Trayer, J.C. Rüegg, FEBS Lett. 377, 131–134 (1995)
R. Zhang, J. Zhao, A. Mandveno, J.D. Potter, Circ. Res. 76, 1028–1035 (1995)
J.C. Kentish, D.T. McCloskey, J. Layland, S. Palmer, J.M. Leiden, A.F. Martin, R.J. Solaro, Circ. Res. 88, 1059–1065 (2001)
J. Layland, R.J. Solaro, A.M. Shah, Cardiovasc. Res. 66, 12–21 (2005)
W.-J. Dong, J. Xing, M. Villain, M. Hellinger, J.M. Robinson, M. Chandra, R.J. Solaro, P.K. Umeda, H.C. Cheung, J. Biol. Chem. 274, 31382–31390 (1999)
P.P. Borbat, J.H. Freed, in Biological Magnetic Resonance 19, ed. by L.J. Berliner, S.S. Eaton, G.R. Eaton (Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, 2000), pp. 383–459
P.P. Borbat, H.S. Mchaourab, J.H. Freed, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124, 5304–5314 (2002)
J. Abe, S. Ueki, T. Arata, S. Yamauchi, Y. Ohba, Appl. Magn. Reson. 42, 473–485 (2012)
G. Jeschke, Y. Polyhach, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 9, 1895–1910 (2007)
P.G. Fajer, J. Phys. Condens. Matter 17, S1459–S1469 (2005)
S. Ueki, M. Nakamura, T. Komori, T. Arata, Biochemistry 44, 411–416 (2005)
M. Nakamura, S. Ueki, H. Hara, T. Arata, J. Mol. Biol. 348, 127–137 (2005)
W.-J. Dong, C.-K. Wang, A.M. Gordon, H.C. Cheung, Biophys. J. 72, 850–857 (1997)
C.S. Farah, C.A. Miyamoto, C.H.I. Ramos, A.C.R. Da Silva, R.B. Quaggio, K. Fujimori, L.B. Smillie, F.C. Reinach, J. Biol. Chem. 269, 5230–5240 (1994)
W.-J. Dong, S.S. Rosenfeld, C.-K. Wang, A.M. Gordon, H.C. Cheung, J. Biol. Chem. 271, 688–694 (1996)
T.E. Gillis, C.R. Marshall, X.-H. Xue, T.J. Borgford, G.F. Tibbits, Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 279, R1707–R1715 (2000)
Y. Mizuta, S. Kazama, Y. Ohba, N. Sakai, Y. Yamamoto, Y. Shimoyama, Rev. Sci. Inst. 79, 044705 (2008)
G. Jeschke, G. Panek, A. Godt, A. Bender, H. Paulsen, Appl. Magn. Reson. 26, 223–244 (2004)
G. Jeschke, V. Chechik, P. Ionita, A. Godt, H. Zimmermann, J. Banham, C.R. Timmel, D. Hilger, H. Jung, Appl. Magn. Reson. 30, 473–498 (2006)
Y.-W. Chiang, P.P. Borbat, J.H. Freed, J. Magn. Reson. 172, 279–295 (2005)
S.K. Sia, M.X. Li, L. Spyracopoulos, S.M. Gagne, W. Liu, J.A. Putkey, B.D. Sykes, J. Biol. Chem. 272, 18216–18221 (1997)
L. Spyracopoulos, M.X. Li, S.K. Sia, S.M. Gagne, M. Chandra, R.J. Solaro, B.D. Sykes, Biochemistry 36, 12138–12146 (1997)
W.T. Heller, N.L. Finley, W.-J. Dong, P. Timmins, H.C. Cheung, P.R. Rosevear, J. Trewhella, Biochemistry 42, 7790–7800 (2003)
D.G. Ward, S.M. Brewer, M.P. Cornes, I.P. Trayer, Biochemistry 42, 10324–10332 (2003)
M.X. Li, L. Spyracopoulos, B.D. Sykes, Biochemistry 38, 8289–8298 (1999)
V. Gaponenko, E. Abusamhadneh, M.B. Abbott, N. Finley, G. Gasmi-Seabrook, R.J. Solaro, M. Rance, P.R. Rosevear, J. Biol. Chem. 274, 16681–16684 (1999)
M.B. Abbott, V. Gaponenko, E. Abusamhadneh, N. Finley, G. Li, A. Dvoretsky, M. Rance, R.J. Solaro, P.R. Rosevear, J. Biol. Chem. 275, 20610–20617 (2000)
J.W. Howarth, J. Meller, R.J. Solaro, J. Trewhella, P.R. Rosevear, J. Mol. Biol. 373, 706–722 (2007)
T. Aihara, M. Nakamura, S. Ueki, H. Hara, M. Miki, T. Arata, J. Biol. Chem. 285, 10671–10677 (2010)
C. Risi, J. Eisner, B. Belknap, D. H. Heeley, H. D. White, G. F. Schröder, V. E. Galkin, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 114, 6782-6787
Y. Cheng, S. Lindert, P. Kekenes-Huskey, V.S. Rao, R.J. Solaro, P.R. Rosevear, R. Amaro, A.D. McCulloch, J.A. McCammon, M. Regnier, Biophys. J 107, 1675–1685 (2014)
Acknowledgements
This work was performed under the auspices of the CREST project of the Japan Science and Technology Agency and was supported in part by cooperative research program no. 2015217 and 20161096 of Institute of Multidisciplinary Research for Advanced Materials, Tohoku University. T.A. was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on the Innovative Area (no. 25117512) from MEXT of Japan. T.A. is grateful to the Collaborative Research Program of Institute for Protein Research, Osaka University, CR -17- 02.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abe, J., Ueki, S., Yamauchi, S. et al. Double Quantum Coherence EPR Reveals the Structure–Function Relationships of the Cardiac Troponin C–Troponin I Complex Regulated by Ca2+ Ions and a Phosphomimetic. Appl Magn Reson 49, 893–910 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00723-018-1031-0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00723-018-1031-0