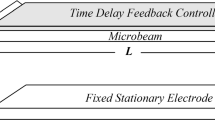
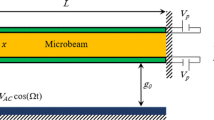
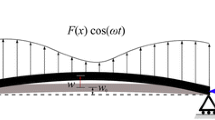
Abstract
In this paper, the nonlinear dynamics of an electostatically actuated microbeam with von kármán geometric nonlinearity and squeeze-film damping are studied. The governing equations and the boundary conditions are developed using the modified couple stress theory and Hamilton’s principle. The size-dependent responses are investigated for the primary, super-harmonic, sub-harmonic resonances, and static pull-in voltage. The effects of the thickness, width of the beam, and gap between electrodes on the frequency response of the resonance, the peak amplitude, nonlinearity of the system, and the pull-in voltage are investigated. Special attention is paid to the “softening” and “stiffening” effects of the linear stiffness. These results show that static behavior and forced vibration of the microbeam are highly size dependent. In addition, a delayed state feedback is introduced into the system. It shows appropriate control gain, and time delay can control the vibrational behavior of the microbeam.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Meng, G., Zhang, W.M.: Micro-Electro-Mechanical System Dynamics. Science Press, Beijing (2008)
Chen, S.H., Wang, T.: Micro-scale Plasticity Mechanics. University of Science and Technology of China Press, Anhui (2009)
Ding, N., Xu, X., Zheng, Z.Q.: A size-dependent nonlinear microbeam model based on the micropolar elasticity theory. Acta. Mech. 227, 3497–3515 (2016)
Rahaeifar, M., Kahrobaiyan, M.H., Ahmadian, M.T., et al.: Size-dependent pull-in phenomena in nonlinear microbridges. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 54, 306–310 (2012)
Zand, M.M., Ahmadian, M.T.: Characterization of coupled-domain multi-layer microplates in pull-in phenomenon, vibrations and dynamics. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 49, 1226–1237 (2007)
Nayfeh, A.H., Younis, M.I.: Dynamics of MEMS resonators under superharmonic and subharmonic excitations. J. Micromech. Microeng. 15, 1840–1847 (2005)
Fleck, N.A., Muller, G.M., Ashby, M.F., Hutchinson, J.W.: Strain gradient plasticity: theory and experiment. ACTA Metallurgica et Materialia 42, 475–487 (1994)
Stolken, J.S., Evans, A.G.: A microbend test method for measuring the plasticity length scale. Acta. Mater. 46, 5109–5115 (1998)
Yang, F., Chong, A.C.M., Lam, D.C.C., Tong, P.: Couple stress based strain gradient theory for elasticity. Int. J. Solids. Struct. 39, 2731–2743 (2002)
Xiao, Y., Wang, B.L., Zhou, S.J.: Pull-in voltage analysis of electrostatically actuated MEMS with piezoelectric layers: A size-dependent model. Mech. Res. Commun. 66, 7–14 (2015)
Wang, B.L., Zhou, S.J., Zhao, J.F.: Pull-in instability analysis of electrostatically actuated microplate with rectangular shape. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 12, 1085–1094 (2011)
Ghayesh, M.H., Farokhi, H., Alici, G.: Size-dependent electro-elasto-mechanics of MEMS with initially curved deformable electrodes. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 103, 247–264 (2015)
Askari, A.R., Tahani, M.: Size-dependent dynamic pull-in analysis of geometric non-linear micro-plates based on the modified couple stress theory. Phys. E-Low Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 86, 262–274 (2017)
Baghani, M.: Analytical study on size-dependent static pull-in voltage of microcantilevers using the modified couple stress theory. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 54, 99–105 (2012)
Zhao, J.F., Zhou, S.J., Wang, B.L., Wang, X.P.: Nonlinear microbeam modal based on strain gradient theory. Appl. Math. Model. 36, 267402686 (2012)
Askari, A.R., Tahani, M.: Size-dependent dynamic pull-in analysis of beam-type MEMS under mechanical shock based on the modified couple stress theory. Appl. Math. Model. 39, 934–946 (2015)
Ke, L.L., Wang, Y.S., Yang, J., Kitipornchai, S.: Nonlinear free vibration of size-dependent functionally graded microbeams. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 50, 256–267 (2012)
Askari, A.R., Tahani, M.: The influence of couple stress components and electrostatic actuation on free vibration characteristics of thin micro-plates. In: 7th International Conference on Mechanical, Industrial, and Manufacturing Technologies (MIMT), Cape Town, South Africa, Feb 01–03 (2016)
Tahani, M., Askari, A.R., Mohandes, Y., et al.: Size-dependent free vibration analysis of electrostatically pre-deformed rectangular micro-plates based on the modified couple stress theory. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 94–95, 185–198 (2015)
Tahani, M., Batra, R.C., Askari, A.R.: Size-dependent free vibrations of electrostatically predeformed functionally graded micro-cantilevers. In: Global Conference on Polymer and Composite Materials (PCM), Beijing, P.R. China, May 16–19 (2015)
Ferezqi, H.Z., Masoud, T., Hamid, E.: Analytical approach to free vibrations of cracked Timoshenko beams made of functionally graded materials. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 17, 353–365 (2010)
Kong, S.L., Zhou, S.J., Nie, Z.F.: Static and dynamic analysis of micro beams based on strain gradient elasticity theory. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 47, 487–498 (2009)
Ma, H.M., Gao, X.L., Reddy, J.N.: A microstructure-dependent Timoshenko beam model based on a modified couple stress theory. J. Mech. Phys. Solids. 56, 3379–3391 (2008)
Kong, S., Zhou, S., Nie, Z., Wang, K.: The size-dependent natural frequency of Bernoulli–Euler micro-beams. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 46, 427–437 (2008)
Xia, W., Wang, L., Yin, L.: Nonlinear non-classical microscale beams: static bending, postbuckling and free vibration. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 48, 2044–2053 (2010)
Ke, L.L., Wang, Y.S.: Size effect on dynamic stability of functionally graded microbeam based on a modified coupled stress theory. Compos. Struct. 93, 342–350 (2011)
Farokhi, H., Ghayesh, M.H.: Nonlinear size-dependent dynamics of micro-arches with modal interactions. J. Vib. Control 22, 3679–3689 (2016)
Zhang, W.M., Meng, G.: Nonlinear dynamic analysis of electrostatically actuated resonant MEMS sensors under parametric excitation. J. IEEE Sens. J. 7, 370–380 (2007)
Farokhi, H., Ghayesh, M.H., Kosasih, B.: On the nonlinear resonant dynamics of Timoshenko microbeams: effects of axial load and geometric imperfection. Meccanica 51, 155–169 (2016)
Ghayesh, M.H., Farokhi, H.: Nonlinear dynamics of microplates. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 86, 60–73 (2015)
Ghayesh, M.H., Farokhi, H.: Coupled size-dependent behavior of shear deformable microplates. Acta. Mech. 227, 757–775 (2016)
Wang, B.L., Zhao, J.F., Zhou, S.J., et al.: Analysis of wave propagation in micro/nanobeam-like structures: a size-dependent model. Acta Mech. Sin. 28, 1659–1667 (2012)
Mohammad, H.K., Mohsen, A., Masoud, H., Mohammad, T.A.: Nonlinear size-dependent forced vibrational behavior of microbeams based on a non-classical continuum theory. J. Vib. Control 1, 1–16 (2011)
Nayfeh, A.H.: Introduction to Perturbation Techniques. Wiley, New York (1981)
Chong, A.C.M., Yang, F., Tong, P.: Torsion and bending of micron-scaled structures. J. Mater. Res. 16, 1052–1058 (2001)
Lam, D.C.C., Yang, F., Chong, A.C.M., Wang, J., Tong, P.: Experiments and theory in strain gradient elasticity. J. Mech. Phys. Solids. 51, 1477–1508 (2003)
Asghari, M., Kahrobaiyan, M.H., Ahmadian, M.T.: A nonlinear Timoshenko beam formulation based on the modified couple stress theory. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 48, 1749–1761 (2010)
Abdel-Rahman, E.M., Younis, M.I., Nayfeh, A.H.: Characterization of the mechanical behavior of an electrically actuated microbeam. J. Micromech. Microeng. 12, 759 (2002)
Timoshenko, S.P., Goodier, J.N.: Theory of Elasticity, 3rd edn. McGraw, New York (1970)
Shao, S., Masri, K.M., Younis, M.I.: The effects of time-delayed feedback controller on an electrically actuated resonator. Nonlinear Dyn. 74, 257–270 (2013)
Ramini, A.H., Younis, M.I., Sue, Q.: A low-gain electrostatically actuated resonant switch. Smart Mater. Struct. 22, 964–1726 (2013)
Hu, H.Y., Wang, Z.H.: Dynamics of Controlled Mechanical Systems with Delayed Feedback. Springer, Heidelberg (2002)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, N., Xu, X., Zheng, Z. et al. Size-dependent nonlinear dynamics of a microbeam based on the modified couple stress theory. Acta Mech 228, 3561–3579 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-017-1895-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-017-1895-3