Abstract
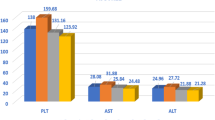
Oxidative stress (OS) and insulin resistance (IR) induced by hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection, are involved in the development of chronic hepatitis C (CHC) complications and progression to hepatocellular carcinoma. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of pegylated interferon alpha (IFNα) + ribavirin (PegIFNα+RVB) or sofosbuvir + NS5A inhibitor (SOF+InNS5A) on IR and the components of OS. HCV was genotyped in 20 CHC patients grouped by treatment with either PegIFNα+RVB (n = 10) or SOF+InNS5A (n = 10). The treatment’s effect on OS-induced damage to lipids (HNE-HDL), proteins (advanced glycation end products [AGEs]), and DNA (8-OHdG) as well as the concentrations of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-2, TNFα, IFNγ), ALT, AST, GSH and platelets was determined. Superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase activity as well as IR, determined by the HOMA1-IR index, was evaluated. The HCV genotypes (GT) found were GT1b (45%), GT1a (30%), GT2b (20%), and GT2a (5%). Viral RNA became undetectable by week 12 with SOF+InNS5A in 100% of the cases and with PegIFNα+RVB in 70% of the cases. After viral RNA became undetectable, regardless of treatment and GT, a significant increase in the platelet concentration and SOD activity was observed, whereas ALT, insulin, and IR decreased (p < 0.05). However, only for the SOF+InNS5A treated group was there an increase in oxidative damage to lipids (p < 0.017) and proteins (p < 0.05). None of the other parameters demonstrated any differences. These data confirm that OS persisted after treatment with either SOF+InNS5A or PegIFNα+RVB. IR could be considered a response biomarker to treatment with direct-acting antivirals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AASLD/IDSA (2019) HCV guidance panel. HCV guidance: recommendations for testing, managing, and treating hepatitis C. https://www.aasld.org. Accessed 19 Dec 2019
Blach S, Zeuzem S, Manns M, Altraif I, Duberg A-S, Muljono DH, Waked I, Alavian SM, Lee M-H, Negro F (2017) Global prevalence and genotype distribution of hepatitis C virus infection in 2015: a modelling study. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 2:161–176
Panduro A, Melendez GE, Fierro NA, Madrigal BR, Zepeda-Carrillo EA, Román S (2011) Epidemiología de las hepatitis virales en México. Salud publica de Mexico 53:S37–S45
WHO (2019) Hepatitis C, Fact sheet no. 164, World Health Organization Media Centre 2019. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs164/en/. Accessed 13 Dec 2019
Yang Z, Lu Y, Xu Q, Chen X (2016) Virologic responses and tolerance of peginterferon alfa plus ribavirin treatment for patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection in different age categories. Niger J Clin Pract 19:133–139
Vidali M, Tripodi M-F, Ivaldi A, Zampino R, Occhino G, Restivo L, Sutti S, Marrone A, Ruggiero G, Albano E (2008) Interplay between oxidative stress and hepatic steatosis in the progression of chronic hepatitis C. J Hepatol 48:399–406
Shin E-C, Sung PS, Park S-H (2016) Immune responses and immunopathology in acute and chronic viral hepatitis. Nat Rev Immunol 16:509
Reshi ML, Su Y-C, Hong J-R (2014) RNA viruses: ROS-mediated cell death. Int J Cell Biol 46:74–78
Simula MP, De Re V (2010) Hepatitis C virus-induced oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction: a focus on recent advances in proteomics. Proteom Clin Appl 4:782–793
Choi J, James Ou J-H (2006) Mechanisms of liver injury. III. Oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of hepatitis C virus. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 290:G847–G851
Vespasiani-Gentilucci U, Gallo P, De Vincentis A, Galati G, Picardi A (2014) Hepatitis C virus and metabolic disorder interactions towards liver damage and atherosclerosis. World J Gastroenterol 20:2825
Medvedev R, Ploen D, Hildt E (2016) HCV and oxidative stress: implications for HCV life cycle and HCV-associated pathogenesis. Oxidative Med Cell Longev
Ivanov AV, Bartosch B, Smirnova OA, Isaguliants MG, Kochetkov SN (2013) HCV and oxidative stress in the liver. Viruses 5:439–469
Ivanov AV, Valuev-Elliston VT, Tyurina DA, Ivanova ON, Kochetkov SN, Bartosch B, Isaguliants MG (2017) Oxidative stress, a trigger of hepatitis C and B virus-induced liver carcinogenesis. Oncotarget 8:3895
Bernsmeier C, Duong FH, Christen V, Pugnale P, Negro F, Terracciano L, Heim MH (2008) Virus-induced over-expression of protein phosphatase 2A inhibits insulin signalling in chronic hepatitis C. J Hepatol 49:429–440
Miyamoto H, Moriishi K, Moriya K, Murata S, Tanaka K, Suzuki T, Miyamura T, Koike K, Matsuura Y (2007) Involvement of the PA28γ-dependent pathway in insulin resistance induced by hepatitis C virus core protein. J Virol 81:1727–1735
Parvaiz F, Manzoor S, Iqbal J, McRae S, Javed F, Ahmed QL, Waris G (2014) Hepatitis C virus nonstructural protein 5A favors upregulation of gluconeogenic and lipogenic gene expression leading towards insulin resistance: a metabolic syndrome. Arch Virol 159:1017–1025
Ansari MHK, Omrani M-D, Kheradmand F (2015) Oxidative stress response in patients infected by diverse hepatitis C virus genotypes. Hepat Mon 15(2):e22069. https://doi.org/10.5812/hepatmon.22069
Panduro A, Roman S (2016) Need of righteous attitudes towards eradication of hepatitis C virus infection in Latin America. World J Gastroenterol 22:5137
Ting AT, Bertrand MJ (2016) More to life than NF-κB in TNFR1 signaling. Trends Immunol 37:535–545
Roche B, Coilly A, Duclos-Vallee JC, Samuel D (2018) The impact of treatment of hepatitis C with DAA s on the occurrence of HCC. Liver Int 38:139–145
Neuman MG, Benhamou J-P, Bourliere M, Ibrahim A, Malkiewicz I, Asselah T, Martinot-Peignoux M, Shear NH, Katz GG, Akremi R (2002) Serum tumour necrosis factor-α and transforming growth factor-β levels in chronic hepatitis C patients are immunomodulated by therapy. Cytokine 17:108–117
Vendemiale G, Grattagliano I, Portincasa P, Serviddio G, Palasciamo G, Altomare E (2001) Oxidative stress in symptom-free HCV carriers: relation with ALT flare-up. Eur J Clin Investig 31:54–63
Tanahashi N (2006) Antiplatelet therapy for acute ischemic stroke. Nihon Rinsho Jpn J Clin Med 64(Suppl 8):49–53
Iwane S, Mizuta T, Kawaguchi Y, Takahashi H, Oza N, Oeda S, Nakashita S, Kuwashiro T, Otsuka T, Kawazoe S, Eguchi Y, Anzai K, Ozaki I, Fujimoto K (2015) Impact of body weight reduction via diet and exercise on the anti-viral effects of pegylated interferon plus ribavirin in chronic hepatitis C patients with insulin resistance: a randomized controlled pilot trial. Intern Med (Tokyo, Jpn) 54:3113–3119
Khattab M, Emad M, Abdelaleem A, Eslam M, Atef R, Shaker Y, Hamdy L (2010) Pioglitazone improves virological response to peginterferon alpha-2b/ribavirin combination therapy in hepatitis C genotype 4 patients with insulin resistance. Liver Int Off J Int Assoc Study Liver 30:447–454
Huang JF, Huang CF, Yeh ML, Dai CY, Hsieh MH, Yang JF, Huang CI, Lin YH, Liang PC, Lin ZY, Chen SC, Yu ML, Chuang WL (2017) The outcomes of glucose abnormalities in chronic hepatitis C patients receiving interferon-free direct antiviral agents. Kaohsiung J Med Sci 33:567–571
Lévy PL, Duponchel S, Eischeid H, Molle J, Michelet M, Diserens G, Vermathen M, Vermathen P, Dufour JF, Dienes HP (2017) Hepatitis C virus infection triggers a tumor-like glutamine metabolism. Hepatology 65:789–803
Uribe-Noguez LA, Ocaña-Mondragón A, Mata-Marín JA, Gómez-Torres ME, Ribas-Aparicio RM, de la Luz Martínez-Rodríguez M (2018) Presence of rare hepatitis C virus subtypes, 2j, 2k, and 2r in Mexico City as identified by sequencing. J Med Virol 90:1277–1282
Lin ZH, Xin YN, Dong QJ, Wang Q, Jiang XJ, Zhan SH, Sun Y, Xuan SY (2011) Performance of the aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index for the staging of hepatitis C-related fibrosis: an updated meta-analysis. Hepatology 53:726–736
Ahmed MM, Abdel-Salam OM, Mohammed NA, Habib DF, Gomaa HE-E (2013) Oxidative status and the response to pegylated-interferon alpha2a plus ribavirin in chronic genotype 4 HCV hepatitis. EXCLI J 12:605
El-Kannishy G, Arafa M, Abdelaal I, Elarman M, El-Mahdy R (2012) Persistent oxidative stress in patients with chronic active hepatitis-C infection after antiviral therapy failure. Saudi J Gastroenterol Off J Saudi Gastroenterol Assoc 18:375
Beig J, Orr D, Harrison B, Gane E (2018) Hepatitis C virus eradication with new interferon-free treatment improves metabolic profile in hepatitis C virus-related liver transplant recipients. Liver Transplant 24:1031–1039
Forment GR, Gómez EV, Sollet ZC, Pérez YM, Sieres NP, Bonne OM, Ramos LV (2011) Marcadores de daño oxidativo y defensa antioxidante en pacientes con hepatitis crónica C no respondedores al tratamiento con INF-a-PEG mas ribavirina. Revista Biomédica 22:11
Sarrasague MM, Barrado DA, Zubillaga M, Hager A, De Paoli T, Boccio J (2006) Conceptos actuales del metabolismo del glutatión Utilización de los isótopos estables para la evaluación de su homeostasis. Acta bioquímica clínica latinoamericana 40:45–54
Gottschall C, Pereira TG, Rabito EI, Álvares-Da-Silva MR (2015) Nutritional status and dietary intake in non-cirrhotic adult chronic hepatitis C patients. Arquivos de Gastroenterologia 52:204–209
Duarte-Rojo A, Altamirano JT, Feld JJ (2012) Noninvasive markers of fibrosis: key concepts for improving accuracy in daily clinical practice. Ann Hepatol 11:426–439
Kleiner G, Marcuzzi A, Zanin V, Monasta L, Zauli G (2013) Cytokine levels in the serum of healthy subjects. Mediat Inflamm
Lecube A, Hernández C, Genescà J, Simó R (2006) Proinflammatory cytokines, insulin resistance, and insulin secretion in chronic hepatitis C patients: a case–control study. Diabetes Care 29:1096–1101
Patel K, Remlinger KS, Walker TG, Leitner P, Lucas JE, Gardner SD, McHutchison JG, Irving W, Guha IN (2014) Multiplex protein analysis to determine fibrosis stage and progression in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 12(2113–2120):e2113
Marti L, Moreno A, Filella X, Marín J, Almela M, Benito N, Sánchez M, Gatell J (2003) Cytokines value as a sepsis and mortality predictor in elderly patients with fever. Med Clin 121:361–366
Yoshioka K, Kakumu S, Arao M, Tsutsumi Y, Inoue M (1989) Tumor necrosis factor α production by peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with chronic liver disease. Hepatology 10:769–773
Winczura A, Czubaty A, Winczura K, Masłowska K, Nałęcz M, Dudzińska DA, Saparbaev M, Staroń K, Tudek B (2014) Lipid peroxidation product 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal modulates base excision repair in human cells. DNA Repair 22:1–11
Radak Z, Zhao Z, Goto S, Koltai E (2011) Age-associated neurodegeneration and oxidative damage to lipids, proteins and DNA. Mol Asp Med 32:305–315
Farinati F, Cardin R, Degan P, De Maria N, Floyd RA, Van Thiel DH, Naccarato R (1999) Oxidative DNA damage in circulating leukocytes occurs as an early event in chronic HCV infection. Free Radic Biol Med 27:1284–1291
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge all the patients who kindly gave their consent to participate in this study. The authors would also like to thank the staff of the Infectious Diseases Department and of the Medical Research Unit, and to Dr. Leonardo M. Porchia for his input with respect to the manuscript content and grammar.
Funding
This work was funded by the Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (CONACYT)-[SALUD-2015-1-261113] and the Fondo en Investigación en Salud (FIS) of the Instituto Mexicano del Seguro Social [FIS/IMSS/PROT/G15/1411] and [FIS/IMSS/PROT/G11/952].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Alicia Ocaña-Mondragón, Luis A. Uribe-Noguez, José Antonio Mata-Marin, Jesús Gaytán-Martínez, and Stefan Mauss designed and conducted the study, interpreted the results, participated in the writing of the report, and agreed to its content. Allison Cázares-Cortáazar, María de la Luz Martínez-Rodríguez, Alberto Chapararro-Saánchez, and Stefan Mauss collaborated on the revision of the paper. Allison Cázares-Cortáazar, Luis A. Uribe-Noguez, and Pedro Esteban Villavicencio-Ferrel collaborated on the assays.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The research protocol was approved by the local ethics committee (register no. R 2017-1302-101).
Consent to participate
In accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, written, informed consent was collected from each patient.
Availability of data and material
The datasets generated and/or analyzed in the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Michael A. Purdy.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cázares-Cortazar, A., Uribe-Noguez, L.A., Mata-Marín, J.A. et al. A decrease in hepatitis C virus RNA to undetectable levels in chronic hepatitis C patients after PegIFNα + RVB or sofosbuvir + NS5A inhibitor treatment is associated with decreased insulin resistance and persistent oxidative stress. Arch Virol 165, 2759–2766 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-020-04797-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-020-04797-y