Abstract
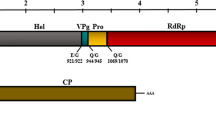
A new macluravirus infecting Pinellia ternata in China was identified by high-throughput sequencing (HTS) and tentatively named “crow-dipper mosaic-associated virus” (CrdMV). The complete genome sequence of CrdMV was determined by reverse transcription (RT) PCR and rapid amplification of cDNA ends (RACE) PCR. The genomic RNA of CrdMV consists of 8,454 nucleotides (nt), excluding the poly(A) tail at the 3′ end. CrdMV has a genomic structure typical of macluraviruses, with large open reading frame encoding a polyprotein of 2,696 amino acids (aa). CrdMV shares 54.40%–59.37% nt sequence identity at the genome sequence level, 48.00%–58.58% aa sequence identity, at the polyprotein sequence level and 37.27%–49.22% aa sequence identity at the CP sequence level with other members of the genus Macluravirus. These values are well below the species demarcation threshold for the family Potyviridae. Phylogenetic analysis based on the amino acid sequences of polyproteins confirmed that CrdMV clusters closely with broad-leafed dock virus A (BDVA, GenBank accession no. KU053507). These results suggest that CrdMV should be considered a distinct member of the genus Macluravirus.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams MJ, Zerbini FM, French R et al (2012) Potyviridae. In: King AMQ, Adams MJ, Carstens EB et al (eds) Virus taxonomy: ninth report of the international committee on taxonomy of viruses. Elsevier, San Diego, pp 1069–1089
Elangovan S, Srikakulam N, Pandi G et al (2019) The first complete genomic sequence of cardamom mosaic virus, a member of the genus Macluravirus (family Potyviridae). Arch Virol 164:1723–1726
Lan P, Meng Y, Shen P et al (2018) Complete genome sequence of yam chlorotic necrosis virus, a novel macluravirus infecting yam. Arch Virol 163:2275–2278
Zhang P, Peng J, Guo H et al (2016) Complete genome sequence of yam chlorotic necrotic mosaic virus from Dioscorea parviflora. Arch Virol 161:1715–1717
Chen J, Li D (1994) Separating and partial characterization of two viruses from natural-infected Pinellia ternata. Biotechnology 4(4):24–28
Chen J, Zheng HY, Lin L et al (2004) A virus related to Soybean mosaic virus from Pinellia ternata in China and its comparison with local soybean SMV isolates. Arch Virol 149(2):349–363
Cui LY, Pang XJ, Qi YH et al (2018) Identification of the pathogens of Pinellia ternata virus by small RNA deep sequencing. Chin J Biochem Mol Biol 34(12):1334–1341
Zerbino DR, Birney E (2008) Velvet: algorithms for de novo short read assembly using de Bruijn graphs. Genome Res 18:821–829
Scotto-Lavino E, Du G, Frohman MA (2006) 3’ end cDNA amplification using classic RACE. Nat Protoc 1(6):2742–2745
Scotto-Lavino E, Du G, Frohman MA (2006) 5’ end cDNA amplification using classic RACE. Nat Protoc 1(6):2555–2562
Urcuqui-Inchima S, Haenni AL, Bernardi F (2001) Potyvirus proteins: a wealth of functions. Virus Res 74:157–175
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N et al (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Martin DP, Murrell B, Golden M et al (2015) RDP4: detection and analysis of recombination patterns in virus genomes. Virus Evol. https://doi.org/10.1093/ve/vev003
Funding
This work was supported by the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences (Grant number 2016-I2M-3-017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and animal rights
This study did not include experiments with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Stephen John Wylie.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, R., Chen, B., Li, Y. et al. Complete genomic sequence of crow-dipper mosaic-associated virus, a novel macluravirus infecting Pinellia ternata. Arch Virol 165, 491–494 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-019-04471-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-019-04471-y