Abstract
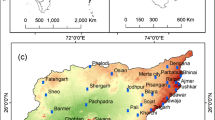
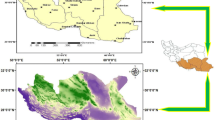
Drought monitoring is very important for water resource planning due to the impact of climate change on the frequency of drought events. The objective of this study was to evaluate the spatiotemporal characteristics of drought in Iran. Spatial and temporal distributions of drought severity were assessed using the well-accepted standardized reconnaissance drought index (RDIst) in seasonal and annual scales in 40 synoptic meteorological stations of Iran during the years 1967–2014. Parametric and nonparametric statistical tests were further used for trend assessments. According to the results of RDIst on an annual time scale, the trends of drought were positive in 87.5% of the stations. The results of seasonal RDIst also indicated that the trends of drought in winter (92.5%), spring (82.5%), summer (37.5%), and fall (67.5%) were upward. In sequence series of all seasons, 90% of all stations had a negative trend in the value of their calculated RDIst over time, which means an upward trend in drought over time. Our findings demonstrated an upward trend in drought over the study period. In 45% of the studied stations, winter had the most significant positive trend at all time scales. The results also showed that a moderate drought covered the highest portion of the study area. Generally, a positive trend was observed in coverage of extreme, severe, and moderate drought. However, a negative trend was evident in the coverage of extreme, severe, and moderate wet conditions during the time. It is suggested that the spatiotemporal distribution of the RDIst trend can be used to identify drought and mitigate its impacts in Iran.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used in this research will be available (by the corresponding author), upon reasonable request.
References
Ahani H, Kherad M, Kousari MR, Roosmalen LV, Aryanfar R, Hoseine SM (2012) Non-parametric trend analysis of the aridity index for three large arid and semi-arid basins in Iran. Theor Appl Climatol 112:553–564
Allen RG, Pereira LS, Raes D, Smith M (1998) Crop evapotranspiration. In: Guidelines for computing crop water requirements, FAO irrigation, and drainage paper 56. Roma, FAO
Asadi Zarch MA, Malekinezhad H, Mobin MH, Dastorani MT, Kousari MR (2011) Drought monitoring by reconnaissance drought index (RDI) in Iran. Water Resour Manag 25:3485–3504
Azadi S, Soltani Kopaei S, Faramarzi M, SoltaniTudeshki A, Pourmnafi S (2015) Evaluation of Palmer drought severity index central Iran. Water and Soil Sci (J Sci Technol Nat Resour) 19:305–318
Bahrami S, Zarei AR, Chakav S (2017) Analysis of drought transitions using log-linear models in Iran. Int J Water 11(3):266–278
Banimahd SA, Khalili D (2013) Factors influencing Markov chains predictability characteristics, utilizing SPI, RDI, EDI, and SPEI drought indices in different climatic zones. Water Resour Manag 27(11):3911–3928
Bari Abarghouei H, Asadi Zarch MM, Dastorani MT, Kousari MR, Safari Zarch M (2011) The survey of climatic drought trends in Iran. Stoch Env Res Risk A 25:851–863
Bazrafshan J, Khalili A (2013) Spatial analysis of meteorological drought in Iran from 1965 to 2003. Desert 18:63–71
Dinpashoh Y, Fakheri-Fard A, Moghaddam M, Jahanbakhsh S, Mirnia M (2004) Selection of variables for the purpose of regionalization of Iran’s precipitation climate using multivariate methods. J Hydrol 297:109–123
Dracup JA, Lee KS, Paulson EG (1980) On the definition of droughts. Water Resour Res 16:297–302
Farrel PJ, Stewart KR (2006) A comprehensive study of tests for normality and symmetry: extending the Spiegel halter test. J Stat Comput Simul 76(9):803–816
Ghabaei Sough M, Mosaedi A (2014) Modification of reconnaissance drought index (RDI) based on the best methods of evapotranspiration estimation and probability distribution function. J Range Watershed Manag (Iran J Nat Resour) 66(4):565–582 (In Persian)
Hao Z, AghaKouchak A (2013) Multivariate standardized drought index: a parametric multi-index model. Adv Water Resour 57:12–18
Keshin S (2006) Comparison of several univariate normality tests regarding type 1 error rate and power of the test in a simulation-based small sample. J Appl Sci 2(5):296–300
Khalili D, Farnoud T, Jamshidi J, Kamgar-Haghighi AA, Zand-Parsa S (2011) Comparability analyses of the SPI and RDI meteorological drought indices in different climatic zones. Water Resour Manag 25:1737–1757
Kwarteng F, Shwetha G, Rahul P (2017) Reconnaissance drought index as a potential drought monitoring tool in a Deccan plateau, hot semi-arid climatic zone. Int J Agric Sci 9(1):2183–2186
Mohammed R, Scholz M (2016) The reconnaissance drought index: a method for detecting regional arid climatic variability and potential drought risk. J Arid Environ 144:181–191
Nam WH, Hayes MJ, Svoboda MD, Tadesse T, Wilhite DA (2015) Drought hazard assessment in the context of climate change for South Korea. Agric Water Manag 160:106–117
Nazaripour H, Dostkamiyan M, Alizadeh S (2015) The spatial distribution patterns of temperature, precipitation, and humidity using geostatistical exploratory analysis (case study: Central Area of Iran). J Earth Space Phys 41(1):99–101
Razali M, Wah YB (2011) Power comparison of Shapiro-Wilk, Kolmogorov-Smirnov, Lilliefors, and Anderson-Darling tests. J Stat Mod Analy 2(1):21–33
Salhvand I, Montazeri M (2013) Zoning drought index (SPI, PNI, DI, CZI, ZSI) and test sequences in Khuzestan province in the GIS environment. Q Geogr J Chashmandaz-e-Zagros 5:35–52 (In Persian)
Tabari H, Abghari H, Hosseinzadeh Talaee P (2011) Temporal trends and spatial characteristics of drought and rainfall in arid and semiarid regions of Iran. Hydrol Process 26(22):3351–3361
Tajbakhsh S, Eisakhani N, Fazel Kazemi A (2015) Assessment of meteorological drought in Iran using standardized precipitation and evapotranspiration index (SPEI). J Earth Space Phys 40(2):313–321
Tallaksen LM, Van Lanen HAJ, (2004). Hydrological drought: processes and estimation methods for streamflow and groundwater. In: Developments in Water Science, vol. 48. Amsterdam, the Netherlands: Elsevier Science B.V.
Thomas T, Jaiswal RV, Nayak TR (2016) Reconnaissance drought index-based evaluation of meteorological drought characteristics in Bundelkhand. Process Technol 24:23–30
Tigkas D, Vangelis H, Tsakiris G (2016) Introducing a modified reconnaissance drought index (RDIe) incorporating effective precipitation. Process Eng 162:332–339
Tsakiris G (2004) Meteorological drought assessment. Paper prepared for the needs of the European Research Program MEDROPLAN (Mediterranean Drought Preparedness and Mitigation Planning), Zaragoza. Spain
Tsakiris G, Vangelis H (2005) Establishing a drought index incorporating evapotranspiration. Eur Water 9(10):3–11
Tsakiris G, Rossi G, Iglesias A, Tsiourtis N, Garrote L, Cancelliere A, (2006). Drought indicators report. Report made for the needs of the European Research Program MEDROPLAN (Mediterranean Drought Preparedness and Mitigation Planning)
Tsakiris G, Pangalou D, Tigkas D, Vangelis H (2007) Assessing the areal extent of drought. Water resources management: new approaches and technologies European water resources association, Chania, Crete Greece, 14–16 June
Tsakiris G, Nalbantis I, Cavadias G (2011) Regionalization of low flows based on canonical correlation analysis. Adv Water Resour 34:865–872
Tsakiris G, Nalbantis I, Vangelis H, Verbeiren B, Huysmans M, Tychon B, Jacquemin I, Canters F, Vanderhaegen S, Engelen G, Poelmans L, Becker P, Batelaan O (2013) A system-based paradigm of drought analysis for operational management. Water Resour Manag 27:5281–5297
United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) (1992) World Atlas of Desertification. Edward Arnold, London, UK
Wilhite DA, Glantz MH (1985) Understanding the drought phenomenon: the role of definitions. Water Int 10(3):111–120
Yue S, Pilon P (2004) A comparison of the power of the t-test, Mann-Kendall, and bootstrap tests for trend detection. Hydrol Sci 49(1):21–37
Yue S, Pilon P, Cavadias G (2002) Power of the Mann-Kendall and Spearman’s rho tests for detecting monotonic trends in hydrological series. J Hydrol 259:254–271
Zandi Lak H, Fooladmand HR, Boustani F (2014) Evaluation of the wheat agricultural drought return period in the province of Fars using the RDI index. Water Eng 7:1–10 (In Persian)
Zarei AR, Mahmoudi MR (2017) Evaluation of changes in the RDIst index affected by different potential evapotranspiration calculation methods. Water Resour Manag 31:4981–4999
Zarei AR, Moghimi MM (2019) Environmental assessment of semi-humid and humid regions based on modeling and forecasting of changes in monthly temperature. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16(3):1457–1470
Zarei AR, Moghimi MM, Mahmoudi MR (2016a) Modeling and prediction of seasonal drought, using RDI index and time series models (case study: Tehran synoptic station). Desert Ecosyst Eng J 11(5):105–116 (In Persian)
Zarei AR, Moghimi MM, Mahmoudi MR (2016b) Parametric and non-parametric trend of drought in arid and semi-arid regions using the RDI index. Water Resour Manag 30(14):5479–5500
Zarei AR, Moghimi MM, Bahrami B (2019) Comparison of reconnaissance drought index (RDI) and effective reconnaissance drought index (eRDI) to evaluate drought severity. Sust Water Resour Manag 5:1345–1356
Acknowledgments
Thanks to the Meteorological Organization of Iran for providing the data needed in this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The participation of Samira Bazrkar and Abdol Rassoul Zarei includes the data collection, analyzing the results and writing the article, and the participation of Mehdi Bahrami includes writing the article and help to analyzing the results.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The authors confirm that this article is original research and has not been published or presented previously in any journal or conference in any language (in whole or in part).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Consent to participate and consent to publish
The authors declare that they have consent to participate and consent to publish.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bahrami, M., Bazrkar, S. & Zarei, A.R. Spatiotemporal investigation of drought pattern in Iran via statistical analysis and GIS technique. Theor Appl Climatol 143, 1113–1128 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-020-03480-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-020-03480-1