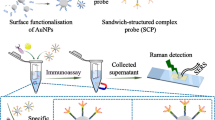
Abstract
A multifunctional surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) platform integrating sensitive detection and drug resistance analysis was developed for Gram-positive bacteria. The substrate was based on self-assembled Ti3C2Tx@Au NPs films and capture molecule phytic acid (IP6) to achieve specific capture of Gram-positive bacteria and different bacteria were analyzed by fingerprint signal. It had advantages of good stability and homogeneity (RSD = 8.88%). The detection limit (LOD) was 102 CFU/mL for Staphylococcus aureus and 103 CFU/mL for MRSA, respectively. A sandwich structure was formed on the capture substrate by signal labels prepared by antibiotics (penicillin G and vancomycin) and non-interference SERS probe molecules (4-mercaptobenzonitrile (2223 cm−1) and 2-amino-4-cyanopyridine (2240 cm−1)) to improve sensitivity. The LOD of Au NPs@4-MBN@PG to S. aureus and Au NPs@AMCP@Van to MRSA and S. aureus were all improved to 10 CFU/mL, with a wide dynamic linear range from 108 to 10 CFU/mL (R2 ≥ 0.992). The SERS platform can analyze the drug resistance of drug-resistant bacteria. Au NPs@4-MBN@PG was added to the substrate and captured MRSA to compare the SERS spectra of 4-MBN. The intensity inhomogeneity of 4-MBN at the same concentrations of MRSA and the nonlinearity at the different concentrations of MRSA revealed that MRSA was resistant to PG. Finally, the SERS platform achieved the determination of MRSA in blood. Therefore, this SERS platform has great significance for the determination and analysis of Gram-positive bacteria.
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
Shalaby M-AW, Dokla EM, Serya RA, Abouzid KA (2020) Penicillin binding protein 2a: an overview and a medicinal chemistry perspective. Eur J Med Chem 199:112312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112312
Campbell C, Fingleton C, Zeden MS, Bueno E, Gallagher LA, Shinde D et al (2021) Accumulation of succinyl coenzyme a perturbs the methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) succinylome and is associated with increased susceptibility to beta-lactam antibiotics. MBio 12:e00530-e621. https://doi.org/10.1128/mbio.00530-21
Ferrer-González E, Huh H, Al-Tameemi HM, Boyd JM, Lee S-H, Pilch DS (2021) Impact of FtsZ inhibition on the localization of the penicillin binding proteins in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol 203:e0020421. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.00204-21
Pang B, Zhao C, Li L, Song X et al (2018) Development of a low-cost paper-based ELISA method for rapid Escherichia coli O157:H7 detection. Anal Biochem 542:58–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2017.11.010
Zhou X, Hu Z, Chen L, Yang D, Xie S, Sun P, Zhou H et al (2020) Bacteria detection: from powerful SERS to its advanced compatible techniques. Biosens Adv Sci 7:2198–3844. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202001739
Tong Y-C, Li P-C, Yang Y, Lin Q-Y, Liu J-T, Gao Y-N, Zhang Y-N, Jin S, Qing S-Z, Xing F-S (2023) Detection of antibiotic resistance in feline-origin ESBL Escherichia coli from different areas of china and the resistance elimination of garlic oil to cefquinome on ESBL E. coli. Int J Mol Sci 24:9627. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119627
Akanny E, Bonhommé A, Bessueille F, Bourgeois S, Bordes C (2021) Surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy for bacteria analysis: a review. Appl Spectrosc Rev 56:380–422. https://doi.org/10.1080/05704928.2020.1796698
Wang J, Liang D, Feng J, Tang X (2019) Multicolor cocktail for breast cancer multiplex phenotype targeting and diagnosis using bioorthogonal surface-enhanced Raman scattering nanoprobes. Anal Chem 91:11045–11054. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b01382
Gao X, Yin Y, Wu H, Hao Z, Li J, Wang S, Liu Y (2020) Integrated SERS platform for reliable detection and photothermal elimination of bacteria in whole blood samples. Anal Chem 93:1569–1577. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.0c03981
Wu Z, Sun DW, Pu H, Wei Q, Lin X (2022) Ti3C2Tx MXenes loaded with Au nanoparticle dimers as a surface-enhanced Raman scattering aptasensor for AFB1 detection. Food Chem 372:131293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131293
Yu Z, Jiang L, Liu R, Zhao W, Yang Z, Zhang J, Jin S (2021) Versatile self-assembled MXene-Au nanocomposites for SERS detection of bacteria, antibacterial and photothermal sterilization. Chem Eng J 426:131914. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.131914
Mojtabavi M, VahidMohammadi A, Ganeshan K, Hejazi D, Shahbazmohamadi S, Kar S, Van Duin AC, Wanunu M (2021) Wafer-scale lateral self-assembly of mosaic Ti3C2Tx MXene monolayer films. ACS Nano 15:625–636. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.0c06393
Zhao X, Wang Z, Dong J, Huang T, Zhang Q, Zhang L (2020) Annealing modification of MXene films with mechanically strong structures and high electrochemical performance for supercapacitor applications. J Power Sources 470:228356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2020.228356
Zhuang Z, Chen H, Li C (2023) Robust pristine MXene films with superhigh electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness via spatially confined evaporation. ACS Nano 17:10628–10636. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.3c01697
Chen Y, Jiang C, Huang F, Yu Z, Jiang L (2023) Efficient interfacial self-assembled MXene/Ag NPs film nanocarriers for SERS-traceable drug delivery. Anal Bioanal Chem 415:5379–5389. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-023-04813-5
Kang Y, Liang Y, Sun H, Dan J, Zhang Q, Su Z, Wang J, Zhang W (2023) Selective enrichment of gram-positive bacteria from apple juice by magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles modified with phytic acid. Food Bioproc Tech 16:1280–1291. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-022-02984-0
Lu X, Zhang Y, Cheng W, Liu Y, Wu X, Li X, Dong F, Li J, Nie X (2022) Experimental and computational study on the inhibitory effect of phytic acid on U (VI) biomineralization by Shewanella putrefaciens. Chem Eng J 450:138364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.138364
Miao L, Liu W, Qiao Q, Li X, Xu Z (2020) Fluorescent antibiotics for real-time tracking of pathogenic bacteria. J Pharm Anal 10:444–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpha.2020.09.003
Pang Y, Wan N, Shi L, Wang C, Sun Z, Xiao R, Wang S (2019) Dual-recognition surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) biosensor for pathogenic bacteria detection by using vancomycin-SERS tags and aptamer-Fe3O4@ Au. Anal Chim Acta 1077:288–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2019.05.059
Pinheiro PC, Fateixa S, Trindade T (2017) SERS detection of penicillin G using magnetite decorated with gold nanoparticles. Magnetochemistry 3:32. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry3040032
Zhuang H, Zhu F, Lan P, Ji S, Sun L, Chen Y, Wang Z, Jiang S, Zhang L, Zhu Y (2021) A random forest model based on core genome allelic profiles of MRSA for penicillin plus potassium clavulanate susceptibility prediction. Microb Genom 7:000610. https://doi.org/10.1099/mgen.0.000610
Tran K-N, Rybak MJ (2017) Vancomycin (VAN) Combinations with Β-lactams (BLs) against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), heterogeneous intermediate-level resistance to vancomycin (hVISA) and vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus (VISA). Open Forum Infect Di suppl_1:S471–S471. https://doi.org/10.1093/ofid/ofx163.1203
Liu R, Jiang L, Lu C, Yu Z, Li F, Jing X, Xu R, Zhou W, Jin S (2020) Large-scale two-dimensional titanium carbide MXene as SERS-active substrate for reliable and sensitive detection of organic pollutants. Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 236:118336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2020.118336
Zhang Q, He L, Rani KK, Wu D, Han J, Chen Y, Su W (2021) Colorimetric detection of neomycin sulfate in tilapia based on plasmonic core-shell Au@ PVP nanoparticles. Food Chem 356:129612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129612
Ding Z, Wong TN (2017) Three-dimensional dynamics of thin liquid films on vertical cylinders with Marangoni effect. Phys Fluids 29:011701. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4974076
Kim TH, Kim H, Choi KI, Yoo J, Seo YS, Lee JS, Koo J (2016) Graphene oxide monolayer as a compatibilizer at the polymer–polymer interface for stabilizing polymer bilayer films against dewetting. Langmuir 32:12741–12748. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.6b03095
Wang H, Zhou Y, Jiang X, Sun B, He Y (2015) Simultaneous capture, detection, and inactivation of bacteria as enabled by a surface-enhanced raman scattering multifunctional chip. Angew Chem 54:5132–5136. https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.201412294
Yang D, Zhou H, Haisch C, Niessner R, Ying Y (2016) Reproducible E. coli detection based on label-free SERS and mapping. Talanta 146:457–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2015.09.006
Qiu M, Zheng M, Zhang J, Yang X, Zhang Y, Zhang W, Man C et al (2023) Recent advances on emerging biosensing technologies and on-site analytical devices for detection of drug-resistant foodborne pathogens. Trends Analyt Chem 167:117258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2023.117258
Chen X, Meiqiong L, Yu H et al (2019) Surface-enhanced Raman scattering method for the identification of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus using positively charged silver nanoparticles. Microchimica Acta 186:102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3150-6
Arjomandi OK, Kavoosi M, Adibi H (2019) Synthesis and enzyme-based evaluation of analogues L-tyrosine thiol carboxylic acid inhibitor of metallo-β-lactamase IMP-1. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 34:1414–1425. https://doi.org/10.1080/14756366.2019.1651314
Pidgeon SE, Pire MM (2017) Vancomycin-dependent response in live drug-resistant bacteria by metabolic labeling. Angew Chem 56:8839–8843. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201704851
Shen Y, Liang L, Zhang J, Li Z, Yue J, Wang J, Xu W, Shi W, Xu S (2019) Interference-free surface-enhanced Raman scattering nanosensor for imaging and dynamic monitoring of reactive oxygen species in mitochondria during photothermal therapy. Sens Actuators B Chem 285:84–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.01.036
Funding
This work was supported by Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (grant numbers LZ22F050004, LY20F050008) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 52271139, 62075202).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xiangwen Qu: conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, investigation, data curation, writing—original draft. Pengwei Zhou: conceptualization, funding acquisition, project administration, supervision. Boya Shi: data curation. Yekai Zheng: data curation. Lian Kan: resources, investigation. Li Jiang: funding acquisition, project administration, writing—review and editing, supervision.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This research did not involve human or animal samples.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, X., Zhou, P., Shi, B. et al. A sandwich-structured multifunctional platform based on self-assembled Ti3C2Tx@Au NPs films, antibiotics, and silent region SERS probe for the capture, determination, and drug resistance analysis of Gram-positive bacteria. Microchim Acta 191, 305 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-024-06387-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-024-06387-0