Abstract
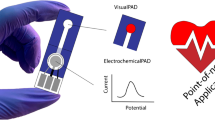
A dual-mode aptasensor using colorimetry and microfluidic chip (MC) together with stir bar sorptive extraction (SBSE) has been developed for firstly qualifying samples contaminated with Vibrio parahaemolyticus (V.P) and Salmonella typhimurium (S.T), then precisely determine both of them in positive samples. For this purpose, the aptamer-streptavidin encoded probes (Apt-SAEs) corresponding to different bacteria were prepared in advance. Then, a stir bar modified with 4-mercaptophenylboronic acid (MPBA) was made to extract bacteria together with Apt-SAE probes. The binding event of aptamer and target triggered the formation of two sandwich structures containing Apt-SAE, V.P or S.T. The concentration of bacteria could be enriched by 1000 times within 15 min to avoid long-time enrichment process. Finally, the stir bar was immersed in the 3,3′,5,5′-Tetramethylbenzidine (TMB)-H2O2 solution for color development. The color could be observed by naked eyes to judge whether the analytes were present. The colorless samples were judged to be negative. For the positive samples, the adsorbed encoded probes corresponding to different bacteria would be eluted from the stir bar and rapidly analyzed by the MC. Under the optimized conditions, 100 CFU/mL of V.P or S.T or both of them could be observed by colorimetry and 35 CFU/mL of them could be detected (S/N = 3) by the MC. The assay has significant application value for on-site screening and multiple detection of food-borne pathogenic bacteria.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang L, Shen X, Wang T, Chen P, Qi N, Yin BC, Ye BC (2020) A lateral flow strip combined with Cas9 nickase-triggered amplification reaction for dual food-borne pathogen detection. Biosens Bioelectron 165:112364
Paudyal N, Pan H, Liao X, Zhang X, Li X, Fang W, Yue M (2018) A meta-analysis of major foodborne pathogens in Chinese food commodities between 2006 and 2016. Foodborne Pathog Dis 15:187–197
Liu N, Zou D, Dong D, Yang Z, Ao D, Liu W, Huang L (2017) Development of a multiplex loop-mediated isothermal amplification method for the simultaneous detection of Salmonella spp. and Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Scientific Reports 7:45601
Yu N, Wu J (2019) Rapid and reagentless detection of thrombin in clinic samples via microfluidic aptasensors with multiple target-binding sites. Biosens Bioelectron 146:111726
Vinayaka AC, Ngo TA, Nguyen T, Bang DD, Wolff A (2020) Pathogen concentration combined solid-phase PCR on supercritical angle fluorescence microlens array for multiplexed detection of invasive nontyphoidal Salmonella serovars. Anal Chem 92:2706–2713
Yuan H, Chao Y, Li S, Tang MYH, Huang Y, Che Y, Wong AST, Zhang T, Shum HC (2018) Picoinjection-enabled multitarget loop-mediated isothermal amplification for detection of foodborne pathogens. Anal Chem 90:13173–13177
Yao L, Ye Y, Teng J, Xue F, Pan D, Li B, Chen W (2017) In vitro isothermal nucleic acid amplification assisted surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopic for ultrasensitive detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Anal Chem 89:9775–9780
Davis MA, Lim JY, Soyer Y, Harbottle H, Chang YF, New D, Orfe LH, Besser TE, Call DR (2010) Development and validation of a resistance and virulence gene microarray targeting Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica. J Microbiol Methods 82:36–41
Shahrokhian S, Ranjbar S (2019) Development of a sensitive diagnostic device based on Zeolitic Imidazolate Frameworks-8 using Ferrocene–Graphene oxide as electroactive indicator for Pseudomonas aeruginosa detection. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7:12760–12769
Shi H, Trinh Q, Xu W, Zhai B, Luo Y, Huang K (2012) A universal primer multiplex PCR method for typing of toxinogenic Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 95:1579–1587
Zhang X, Tang Q, Mi T, Zhao S, Wen K, Guo L, Mi J, Zhang S, Shi W, Shen J, Ke Y, Wang Z (2018) Dual-wavelength fluorescence polarization immunoassay to increase information content per screen: applications for simultaneous detection of total aflatoxins and family zearalenones in maize. Food Control 87:100–108
Di H, Ye L, Neogi SB, Meng H, Yan H, Yamasaki S, Shi L (2015) Development and evaluation of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay combined with enrichment culture for rapid detection of very low numbers of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in seafood samples. Biol Pharm Bull 38:82–87
Li N, Zong S, Zhang Y, Wang Z, Wang Y, Zhu K, Yang K, Wang Z, Chen B, Cui Y (2020) A SERS-colorimetric dual-mode aptasensor for the detection of cancer biomarker MUC1. Anal Bioanal Chem 412:5707–5718
Song C, Li J, Sun Y, Jiang X, Zhang J, Dong C, Wang L (2020) Colorimetric/SERS dual-mode detection of mercury ion via SERS-active peroxidase-like au@AgPt NPs. Sensors Actuators B Chem 310:127849
Wu Z (2019) A dual-mode (Fluorometric and colorimetric) Aptasensor for Vibrio parahaemolyticus detection using multifunctional nanoparticles. Food Anal Methods 12:1577–1584
Wang C, Gao X, Wang S, Liu Y (2020) A smartphone-integrated paper sensing system for fluorescent and colorimetric dual-channel detection of foodborne pathogenic bacteria. Anal Bioanal Chem 412:611–620
Ren R, Cai G, Yu Z, Zeng Y, Tang D (2018) Metal-polydopamine framework: an innovative signal-generation tag for colorimetric immunoassay. Anal Chem 90:11099–11105
Ren R, Cai G, Yu Z, Tang D (2018) Glucose-loaded liposomes for amplified colorimetric immunoassay of streptomycin based on enzyme-induced iron(II) chelation reaction with phenanthroline. Sensors Actuators B Chem 265:174–181
Lai W, Wei Q, Xu M, Zhuang J, Tang D (2017) Enzyme-controlled dissolution of MnO2 nanoflakes with enzyme cascade amplification for colorimetric immunoassay. Biosens Bioelectron 89:645–651
Zhang Y, Luo F, Zhang Y, Zhu L, Li Y, Zhao S, He P, Wang Q (2018) A sensitive assay based on specific aptamer binding for the detection of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium in milk samples by microchip capillary electrophoresis. J Chromatogr A 1534:188–194
Zhang Y, Hu X, Wang Q (2020) Sensitive and specific detection of E. coli, Listeria monocytogenes, and Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium in milk by microchip electrophoresis combined with multiplex PCR amplification. Microchemical Journal 157:104876
Luo F, Li Z, Dai G, Lu Y, He P, Wang Q (1615) Simultaneous detection of different bacteria by microchip electrophoresis combined with universal primer-duplex polymerase chain reaction. J Chromatogr A 2020:460734
David F, Sandra P (2007) Stir bar sorptive extraction for trace analysis. J Chromatogr A 1152:54–69
Cordes DB, Gamsey S, Singaram B (2006) Fluorescent quantum dots with Boronic acid substituted Viologens to sense glucose in aqueous solution. Angew Chem 118:3913–3916
Liang L, Liu Z (2011) A self-assembled molecular team of boronic acids at the gold surface for specific capture of cis-diol biomolecules at neutral pH. Chem Commun 47:2255–2257
Zeng R, Wang J, Wang Q, Tang D, Lin Y (2021) Horseradish peroxidase-encapsulated DNA nanoflowers: an innovative signal-generation tag for colorimetric biosensor. Talanta 221:121600
Gao Z, Lv S, Xu M, Tang D (2017) High-index {hk 0} faceted platinum concave nanocubes with enhanced peroxidase-like activity for an ultrasensitive colorimetric immunoassay of the human prostate-specific antigen. Analyst 142:911–917
Song K-M, Cho M, Jo H, Min K, Jeon SH, Kim T, Han MS, Ku JK, Ban C (2011) Gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric detection of kanamycin using a DNA aptamer. Anal Biochem 415:175–181
Zeng J, Gan N, Zhang K, He L, Lin J, Hu F, Cao Y (2019) Zero background and triple-signal amplified fluorescence aptasensor for antibiotics detection in foods. Talanta 199:491–498
Ma N, Ren X, Wang H, Kuang X, Fan D, Wu D, Wei Q (2020) Ultrasensitive controlled release Aptasensor using thymine-hg(2+)-thymine mismatch as a molecular switch for hg(2+) detection. Anal Chem 92:14069–14075
Zhang X, Yang Q, Lang Y, Jiang X, Wu P (2020) Rationale of 3,3′,5,5′-Tetramethylbenzidine as the chromogenic substrate in colorimetric analysis. Anal Chem 92:12400–12406
Zhang Y, Zhu L, He P, Zi F, Hu X, Wang Q (2019) Sensitive assay of Escherichia coli in food samples by microchip capillary electrophoresis based on specific aptamer binding strategy. Talanta 197:284–290
Wannapob R, Kanatharana P, Limbut W, Numnuam A, Asawatreratanakul P, Thammakhet C, Thavarungkul P (2010) Affinity sensor using 3-aminophenylboronic acid for bacteria detection. Biosens Bioelectron 26:357–364
McCluskey K, Boudreault J, St-Pierre P, Perez-Gonzalez C, Chauvier A, Rizzi A, Beauregard PB, Lafontaine DA, Penedo JC (2019) Unprecedented tunability of riboswitch structure and regulatory function by sub-millimolar variations in physiological Mg2. Nucleic Acids Res 47:6478–6487
Duan N, Wu S, Chen X, Huang Y, Xia Y, Ma X, Wang Z (2013) Selection and characterization of aptamers against Salmonella typhimurium using whole-bacterium systemic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment (SELEX). J Agric Food Chem 61:3229–3234
Yuan J, Tao Z, Yu Y, Ma X, Xia Y, Wang L, Wang Z (2014) A visual detection method for Salmonella Typhimurium based on aptamer recognition and nanogold labeling. Food Control 37:188–192
Jia F, Duan N, Wu S, Dai R, Wang Z, Li X (2015) Impedimetric Salmonella aptasensor using a glassy carbon electrode modified with an electrodeposited composite consisting of reduced graphene oxide and carbon nanotubes. Microchim Acta 183:337–344
Teng J, Ye Y, Yao L, Yan C, Cheng K, Xue F, Pan D, Li B, Chen W (2017) Rolling circle amplification based amperometric aptamer/immuno hybrid biosensor for ultrasensitive detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Microchim Acta 184:3477–3485
Duan N, Wu S, Ma X, Xia Y, Wang Z (2014) A universal fluorescent aptasensor based on AccuBlue dye for the detection of pathogenic bacteria. Anal Biochem 454:1–6
Duan N, Shen M, Wu S, Zhao C, Ma X, Wang Z (2017) Graphene oxide wrapped Fe3O4@au nanostructures as substrates for aptamer-based detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Microchim Acta 184:2653–2660
Duan N, Wu S, Yu Y, Ma X, Xia Y, Chen X, Huang Y, Wang Z (2013) A dual-color flow cytometry protocol for the simultaneous detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Salmonella typhimurium using aptamer conjugated quantum dots as labels. Anal Chim Acta 804:151–158
Duan N, Wu S, Dai S, Miao T, Chen J, Wang Z (2014) Simultaneous detection of pathogenic bacteria using an aptamer based biosensor and dual fluorescence resonance energy transfer from quantum dots to carbon nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 182:917–923
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21974074), Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (LY19B050001, LY20B050004), Natural Science Foundation of Ningbo (2019A610184, 2019A610197), Zhejiang Province Public Welfare Technology Application Research Project (LGN18H300001, LGC20B050006, LGC19B070003), Zhejiang Provincial Top Discipline of Biological Engineering(Level A) (KF2019001), Basic Research Project of Key Laboratory of Guangzhou (202102100001) and K. C. Wong Magna Fund in Ningbo University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing of interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(PDF 1424 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, M., Zeng, J., Wang, J. et al. Dual-mode aptasensor for simultaneous detection of multiple food-borne pathogenic bacteria based on colorimetry and microfluidic chip using stir bar sorptive extraction. Microchim Acta 188, 244 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04902-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04902-1