Abstract
Two-dimensional Mo2C/Mo2N composites were synthesized by high temperature ball milling and used as support materials for fabricating a chlorpyrifos (CPF) aptasensor. Gold nanoparticles (Au NPs) were electrodeposited on the surface of a Mo2C/Mo2N-modified electrode to connect with the ferrocene (Fc) probe via Au–S bonds. The Fc probe can hybridize with the aptamer probe to form a double-stranded structure. The addition of CPF made the double strands melt and the Fc probe approached the surface of the electrode, thereby resulting in amplification of the electrochemical response. The current response of the aptasensor for detecting CPF in solutions linearly varied from 0 to 400 ng mL−1 (with a maximum at 0.98 V vs. Ag/AgCl). The Au NPs/Mo2C/Mo2N composites exhibited satisfactory electrochemical behavior due to their excellent electrical conductivity and large surface area. This ultrasensitive aptasensor showed a low limit of detection of 0.036 ng mL−1. It was applied to determine CPF in real samples with acceptable recoveries from 94.7 to 116.7%, and the relative standard deviation was from 2.57 to 7.08%.
Graphical abstract

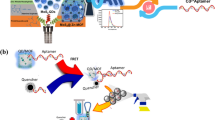
Schematic diagram of the manufacturing process of the aptasensor. Electrochemical aptasensor based on Mo2C/Mo2N/Au NP composites show excellent performance in detecting CPF.





Similar content being viewed by others

References
Eddleston M, Buckley NA, Eyer P, Dawson AH (2008) Management of acute organophosphorus pesticide poisoning. Lancet 371(9612):597–607. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(07)61202-1
Carvalho FP (2017) Pesticides, environment, and food safety. Food and Energy Security 6(2):48–60. https://doi.org/10.1002/fes3.108
Lewis K, Tzilivakis J, Warner D, Green A (2016) An international database for pesticide risk assessments and management. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 22(4):1050–1064. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2015.1133242
Zhou J, Zou X, Song S, Chen G (2018) Quantum dots applied to methodology on detection of pesticide and veterinary drug residues. J Agric Food Chem 66(6):1307–1319. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b05119
Wang P, Dai W, Ge L, Yan M, Ge S, Yu J (2013) Visible light photoelectrochemical sensor based on au nanoparticles and molecularly imprinted poly(o-phenylenediamine)-modified TiO2 nanotubes for specific and sensitive detection chlorpyrifos. Analyst 138(3):939–945. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2an36266j
He L, Luo X, Xie H, Wang C, Jiang X, Lu K (2009) Ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction followed high-performance liquid chromatography for the determination of organophosphorus pesticides in water sample. Anal Chim Acta 655(1):52–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2009.09.044
Sinha SN, Pal RR, Dewan A, Mansuri MM, Saiyed HN (2006) Effect of dissociation energy on ion formation and sensitivity of an analytical method for determination of chlorpyrifos in human blood, using gas chromatography–mass spectrometer (GC–MS in MS/MS). Int J Mass Spectrom 253(1):48–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijms.2006.02.020
Jeanty G, Ghommidh C, Marty J (2001) Automated detection of chlorpyrifos and its metabolites by a continuous flow system-based enzyme sensor. Anal Chim Acta 436(1):119–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(01)00898-4
Li X, Zhang W, Wu X, Sun C, Chen M, Zeng Q (2012) Mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the lung: common findings and unusual appearances on CT. Clin Imaging 36(1):8–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinimag.2011.03.003
Li S, Liang W, Zheng F, Lin X, Cai J (2014) Ascorbic acid surface modified TiO2-thin layers as a fully integrated analysis system for visual simultaneous detection of organophosphorus pesticides. Nanoscale 6(23):14254–14261. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4NR04430D
Akyuz D, Keles T, Biyiklioglu Z, Koca A (2017) Electrochemical pesticide sensors based on electropolymerized metallophthalocyanines. J Electroanal Chem 804:53–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2017.09.044
Famulok M, Hartig JS, Mayer G (2007) Functional aptamers and aptazymes in biotechnology, diagnostics, and therapy. Chem Rev 107(9):3715–3743. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr0306743
Zhu L, Liu Y, Yang P, Liu B (2015) Label-free Aptasensor based on electrodeposition of gold nanoparticles on graphene and its application in the quantification of adenosine triphosphate. Electrochim Acta 172:88–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2015.04.100
Jiao Y, Jia H, Guo Y, Zhang H, Wang Z, Sun X, Zhao J (2016) An ultrasensitive aptasensor for chlorpyrifos based on ordered mesoporous carbon/ferrocene hybrid multiwalled carbon nanotubes. RSC Adv 6(63):58541–58548. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra07735h
Xu G, Huo D, Hou C, Zhao Y, Bao J, Yang M, Fa H (2018) A regenerative and selective electrochemical aptasensor based on copper oxide nanoflowers-single walled carbon nanotubes nanocomposite for chlorpyrifos detection. Talanta 178:1046–1052. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.08.086
Jiao Y, Hou W, Fu J, Guo Y, Sun X, Wang X, Zhao J (2017) A nanostructured electrochemical aptasensor for highly sensitive detection of chlorpyrifos. Sensors Actuators B Chem 243:1164–1170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.12.106
Roushani M, Nezhadali A, Jalilian Z (2018) An electrochemical chlorpyrifos aptasensor based on the use of a glassy carbon electrode modified with an electropolymerized aptamer-imprinted polymer and gold nanorods. Microchim Acta 185(12):551. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3083-0
Rohaizad N, Mayorga-Martinez CC, Sofer Z, Pumera M (2017) 1T-phase transition metal dichalcogenides (MoS2, MoSe2, WS2, and WSe2) with fast heterogeneous electron transfer: application on second-generation enzyme-based biosensor. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(46):40697–40706. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b13090
Arunbalaji S, Vasudevan R, Arivanandhan M, Alsalme A, Alghamdi A, Jayavel R (2020) CuO/MoS2 nanocomposites for rapid and high sensitive non-enzymatic glucose sensors. Ceram Int 46(10):16879–16885. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.03.265
Dong Y, Zhou M, Zhang L (2019) 3D multiporous Co,N co-doped MoO2/MoC nanorods hybrids as improved electrode materials for highly sensitive simultaneous determination of acetaminophen and 4-aminophenol. Electrochim Acta 302:56–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2019.02.006
Xiao T, Huang J, Wang D, Meng T, Yang X (2020) Au and Au-based nanomaterials: synthesis and recent progress in electrochemical sensor applications. Talanta 206:120210–120210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.120210
Vilian ATE, Dinesh B, Kang SM, Krishnan UM, Huh YS, Han YK (2019) Recent advances in molybdenum disulfide-based electrode materials for electroanalytical applications. Mikrochim Acta 186(3):203. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3287-y
Razavipanah I, Rounaghi GH, Deiminiat B, Damirchi S, Abnous K, Izadyar M, Khavani M (2019) A new electrochemical aptasensor based on MWCNT-SiO2@au core-shell nanocomposite for ultrasensitive detection of bisphenol a. Microchem J 146:1054–1063. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.02.018
Zhu C, Liu D, Chen Z, Li L, You T (2019) An ultra-sensitive aptasensor based on carbon nanohorns/gold nanoparticles composites for impedimetric detection of carbendazim at picogram levels. J Colloid Interface Sci 546:92–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2019.03.035
McGovern MS, Garnett EC, Rice C, Masel RI, Wieckowski A (2003) Effects of Nafion as a binding agent for unsupported nanoparticle catalysts. J Power Sources 115(1):35–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0378-7753(02)00623-7
Sun X, Zhu Y, Wang X (2012) Amperometric immunosensor based on deposited gold nanocrystals/4,4′-thiobisbenzenethiol for determination of carbofuran. Food Control 28(1):184–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2012.04.027
Desimoni E, Brunetti B (2013) Presenting analytical performances of electrochemical sensors. Some suggestions. Electroanalysis 25(7):1645–1651. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.201300150
Li Y, Gan Z, Li Y, Liu Q, Bao J, Dai Z, Han M (2010) Immobilization of acetylcholinesterase on one-dimensional gold nanoparticles for detection of organophosphorous insecticides. Science China Chem 53(4):820–825. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-010-0105-0
Manisankar P, Viswanathan S, Pusphalatha AM, Rani C (2005) Electrochemical studies and square wave stripping voltammetry of five common pesticides on poly 3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene modified wall-jet electrode. Anal Chim Acta 528(2):157–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2004.08.027
Uygun ZO, Dilgin Y (2013) A novel impedimetric sensor based on molecularly imprinted polypyrrole modified pencil graphite electrode for trace level determination of chlorpyrifos. Sensors Actuators B Chem 188:78–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2013.06.075
Wang K, Liu Q, Dai L, Yan J, Ju C, Qiu B, Wu X (2011) A highly sensitive and rapid organophosphate biosensor based on enhancement of CdS-decorated graphene nanocomposite. Anal Chim Acta 695(1–2):84–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2011.03.042
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Program for Key Research and Development Plan in Shaanxi Province (No. 2019SF-243), the Innovation Capability Support Program of Shaanxi Province (No. 2020TD-022), and the Strategic Priority Research Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDB40000000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOC 6334 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, Z., Liu, X., Li, Y. et al. Electrochemical aptasensor based on Mo2C/Mo2N and gold nanoparticles for determination of chlorpyrifos. Microchim Acta 188, 170 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04830-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04830-0