Abstract
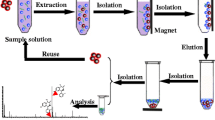
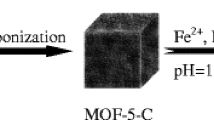
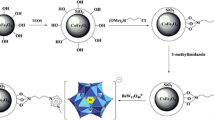
A novel magnetic porous carbon with a high specific surface and magnetization saturation, derived from a Zn/Co-MOF-5, was fabricated by direct carbonization of Zn/Co-MOF-5 without the need of additional carbon precursors under optimum pyrolysis temperature. The material was employed as an adsorbent for magnetic solid-phase extraction of four carbamates from water and tomato samples prior to high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem quadrupole mass spectrometry analysis. Under optimum conditions, the method displayed good linearity (r > 0.9987) within the concentration range 0.05–20 ng mL−1 for water samples and 0.1–40 ng g−1 for tomato samples. The limits of detection (S/N = 3) for the four carbamate pesticides were in the range 0.0006–0.013 ng mL−1 for water samples and 0.001–0.01 ng g−1 for tomato samples and satisfactory spiked recoveries in the range 86.1 to 109.1% were obtained with the relative standard deviation values from 2.1 to 14.0%.

Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nantia EA, Moreno-González D, Manfo FPT, Gámiz-Gracia L, García-Campaña AM (2017) QuEChERS-based method for the determination of carbamate residues in aromatic herbs by UHPLC-MS/MS. Food Chem 216:334–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.08.038
Wu Q, Zhou X, Li Y, Zang X, Wang C, Wang Z (2009) Application of dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction combined with high-performance liquid chromatography to the determination of carbamate pesticides in water samples. Anal Bioanal Chem 393:1755–1761. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-009-2625-z
Council E (1998) EU Council directive on the quality of water intended for human consumption, 98/83/CE
Tang S, Zhang H, Lee HK Advances in sample extraction. Anal Chem 88:acs.analchem.5b04040. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5b04040
Augusto F, Hantao LW, Mogollón NG, Braga SC (2013) New materials and trends in sorbents for solid-phase extraction. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 43:14–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2012.08.012
Andrade-Eiroa A, Canle M, Leroy-Cancellieri V, Cerdà V (2015) Solid phase extraction of organic compounds: a critical review: part I. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 80:655–667. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2015.08.015
Wu J, Liang X, Hao L, Wang C, Wu Q, Wang Z (2017) Graphene oxide cross-linked with phytic acid: an efficient adsorbent for the extraction of carbamates. Microchim Acta 184:3773–3779. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2413-y
Khezeli T, Daneshfar A (2017) Development of dispersive micro-solid phase extraction based on micro and nano sorbents. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 89:99–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2017.01.004
Herrero-Latorre C, Barciela-García J, García-Martín S, Peña-Crecente R, Otárola-Jiménez J (2015) Magnetic solid-phase extraction using carbon nanotubes as sorbents: a review. Anal Chim Acta 892:10–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2015.07.046
Maya F, Cabello CP, Frizzarin RM, Estela JM, Palomino GT, Cerda V (2017) Magnetic solid-phase extraction using metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) and their derived carbons. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 90:142–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2017.03.004
Kitagawa S (2014) Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs). Chem Soc Rev 43:5415–5418. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CS90059F
Chaikittisilp W, Ariga K, Yamauchi Y (2013) A new family of carbon materials: synthesis of MOF-derived nanoporous carbons and their promising applications. J Mater Chem A 1:14–19. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2TA00278G
Tang J, Yamauchi Y (2016) MOF morphologies in control. Nat Chem 8:638–639. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchem.2548
Yang W, Li X, Li Y, Zhu R, Pang H (2019) Applications of metal–organic-framework-derived carbon materials. Adv Mater 31:1804740. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201804740
Yu M, Wang L, Hu L, Li Y, Luo D, Mei S (2019) Recent applications of magnetic composites as extraction adsorbents for determination of environmental pollutants. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 119:115611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2019.07.022
Jin L, Zhao X, Qian X, Dong M (2018) Nickel nanoparticles encapsulated in porous carbon and carbon nanotube hybrids from bimetallic metal-organic-frameworks for highly efficient adsorption of dyes. J Colloid Interface Sci 509:245–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.09.002
Li D, He M, Chen B, Hu B (2019) Metal organic frameworks-derived magnetic nanoporous carbon for preconcentration of organophosphorus pesticides from fruit samples followed by gas chromatography-flame photometric detection. J Chromatogr A 1583:19–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.11.012
Liu Y, Gao Z, Wu R, Wang Z, Chen X, Chan TD (2017) Magnetic porous carbon derived from a bimetallic metal-organic framework for magnetic solid-phase extraction of organochlorine pesticides from drinking and environmental water samples. J Chromatogr A 1479:55–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2016.12.014
Liu B, Shioyama H, Akita T, Xu Q (2008) Metal-organic framework as a template for porous carbon synthesis. J Am Chem Soc 130:5390–5391. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja7106146
Rocío-Bautista P, González-Hernández P, Pino V, Pasán J, Afonso AM (2017) Metal-organic frameworks as novel sorbents in dispersive-based microextraction approaches. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 90:114–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2017.03.002
Liu X, Wang C, Wu Q, Wang Z (2016) Magnetic porous carbon-based solid-phase extraction of carbamates prior to HPLC analysis. Microchim Acta 183:415–421. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1664-8
Hao L, Liu X-L, Wang J-T, Wang C, Wu Q-H, Wang Z (2016) Metal-organic framework derived magnetic nanoporous carbon as an adsorbent for the magnetic solid-phase extraction of chlorophenols from mushroom sample. Chin Chem Lett 27:783–788. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2016.01.021
Liu Y, Zeng G, Tang L, Cai Y, Pang Y, Zhang Y, Yang G, Zhou Y, He X, He Y (2015) Highly effective adsorption of cationic and anionic dyes on magnetic Fe/Ni nanoparticles doped bimodal mesoporous carbon. J Colloid Interface Sci 448:451–459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2015.02.037
Cazetta AL, Pezoti O, Bedin KC, Silva TL, Paesano Junior A, Asefa T, Almeida VC (2016) Magnetic activated carbon derived from biomass waste by concurrent synthesis: efficient adsorbent for toxic dyes. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 4:1058–1068. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.5b01141
MãNguez EG, Coronado E (2018) Magnetic functionalities in MOFs: from the framework to the pore. Chem Soc Rev 47:533–557. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CS00653E
Hao L, Wang C, Wu Q, Li Z, Zang X, Wang Z (2014) Metal–organic framework derived magnetic nanoporous carbon: novel adsorbent for magnetic solid-phase extraction. Anal Chem 86:12199–12205. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac5031896
Li M, Wang J, Jiao C, Wang C, Wu Q, Wang Z (2016) Magnetic porous carbon derived from a Zn/Co bimetallic metal–organic framework as an adsorbent for the extraction of chlorophenols from water and honey tea samples. J Sep Sci 39:1884–1891. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201600097
Wu Q, Cheng S, Wang C, Li X, Li Z, Hao C (2016) Magnetic porous carbon derived from a zinc-cobalt metal-organic framework: a adsorbent for magnetic solid phase extraction of flunitrazepam. Microchim Acta 183:3009–3017. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1948-7
Lim S, Suh K, Kim Y, Yoon M, Park H, Dybtsev DN, Kim K (2012) Porous carbon materials with a controllable surface area synthesized from metal–organic frameworks. Chem Commun 48:7447–7449. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CC33439A
Huang L, Liu X, Yu R (2018) An efficient Co/C microwave absorber with tunable co nanoparticles derived from a ZnCo bimetallic zeolitic imidazolate framework. Part Part Syst Charact 35:1800107. https://doi.org/10.1002/ppsc.201800107
Wang M, Gao M, Zhang K, Wang L, Wang W, Fu Q, Xia Z, Gao D (2019) Magnetic covalent organic frameworks with core-shell structure as sorbents for solid phase extraction of fluoroquinolones, and their quantitation by HPLC. Microchim Acta 186:827. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3757-2
Li N, Chen J, Shi Y-P (2015) Magnetic graphene solid-phase extraction for the determination of carbamate pesticides in tomatoes coupled with high performance liquid chromatography. Talanta 141:212–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2015.04.018
Gao L, Chen L, Li X (2015) Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers based on carbon nanotubes for extraction of carbamates. Microchim Acta 182:781–787. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-014-1388-1
Wang Y, Ma R, Xiao R, Wu Q, Wang C, Wang Z (2017) Preparation of a magnetic porous carbon with hierarchical structures from waste biomass for the extraction of some carbamates. J Sep Sci 40:2451–2458. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201601439
Wu Q, Zhao G, Feng C, Wang C, Wang Z (2011) Preparation of a graphene-based magnetic nanocomposite for the extraction of carbamate pesticides from environmental water samples. J Chromatogr A 1218:7936–7942. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2011.09.027
Issa AA, Al-Saad KA, Luyt AS (2018) Magnetic solid phase extraction for chromatographic separation of carbamates. J Am Ceram Soc 101. https://doi.org/10.1111/jace.15360
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21861035) and the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 2018D01C083).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 3940 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, M., Wang, J., Wang, K. et al. Magnetic porous carbon derived from Zn/Co metal–organic framework as an adsorbent for extraction and determination of carbamates. Microchim Acta 187, 507 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04426-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04426-0