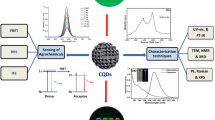
Abstract
Thioglycolic acid-functionalized ZnSe quantum dots (QDs) as a colorimetric nanoprobe were prepared and applied to the determination of cobalt(II) and iron(III). Test strips were obtained by a dipping-drying process. On exposure to Co(II), they undergo a color change from white to brown, and on exposure to Fe(III) from white to pink. The limits of detection (LOD) are 2.6 mg L−1 for Co(II) and 2.2 mg L−1 for Fe(III). Test strips introduce a low-cost, portable, rapid and convenient tool for determination of Co(II) and Fe(III). In addition, two other analytical methods have been studied for detection of Co(II) and Fe(III) at low concentration. The first is UV-vis spectrometry which has a LOD as low as 0.14 mg L−1 for Co(II) (at 412 nm) and 0.12 mg L−1 for Fe(III) (at 400 nm). The second is dynamic light scattering (DLS) with a LOD of 3.0 μg L−1 for Co(II) and 2.5 μg L−1 for Fe(III).

Thioglycolic acid-functionalized ZnSe quantum dots (TGA-ZnSe QDs) show high sensitivity and low detection limits for Co2+ and Fe3+.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gore AH, Gunjal DB, Kokate MR, Sudarsan V, Anbhule PV, Patil SR, Kolekar GB (2012) Highly selective and sensitive recognition of cobalt (II) ions directly in aqueous solution using carboxyl-functionalized CdS QDs as a naked eye colorimetric probe: applications to environmental analysis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4:5217–5226
Wang GX, Chen Y, Konstantinov K et al (2002) Nanosize cobalt oxides as anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. J Alloys Compd 340:5–10
Sato J, Omori T, Oikawa K, Ohnuma I, Kainuma R, Ishida K (2006) Cobalt-base high-temperature alloys. Science 312:90–91
Paulsen JA, Ring AP, Lo CCH, Snyder JE, Jiles DC (2005) Manganese-substituted cobalt ferrite magnetostrictive materials for magnetic stress sensor applications. J Appl Phys 97:044502
Lu XB, Darensbourg DJ (2012) Cobalt catalysts for the coupling of CO2 and epoxides to provide polycarbonates and cyclic carbonates. Chem Soc Rev 41:1462–1484
Meseguer S, Tena MA, Gargori C, Badenes JA, Llusar M, Monrós G (2007) Structure and colour of cobalt ceramic pigments from phosphates. Ceram Int 33:843–849
Okamoto S, Eltis LD (2011) The biological occurrence and trafficking of cobalt. Metallomics 3:963–970
Maity D, Raj A, Karthigeyan D (2013) Reaction-based probes for co(II) and cu(I) with dual output modes: fluorescence live cell imaging. RSC Adv 3:16788
Li CY, Zhang XB, Jin Z (2006) A fluorescent chemosensor for cobalt ions based on a multi-substituted phenol-ruthenium(II) tris(bipyridine) complex. Anal Chim Acta 580:143–148
Liu Z, Wang W, Xu H (2015) A “naked eye” and ratiometric chemosensor for cobalt(II) based on coumarin platform in aqueous solution. Inorg Chem Commun 62:19–23
Lee SY, Kim SY, Kim JA (2016) A dual chemosensor: colorimetric detection of Co2+ and fluorometric detection of Zn2+. J Lumin 179:602–609
Ryu KY, Lee SY, Park DY, Kim SY, Kim C (2017) A novel colorimetric chemosensor for detection of Co2+ and S2− in an aqueous environment. Sensors Actuators B Chem 242:792–800
Chen C, Zhang X, Gao P, Hu M (2018) A water stable europium coordination polymer as fluorescent sensor for detecting Fe3+, CrO4 2−, and Cr2O7 2− ions. J Solid State Chem 258:86–92
Zhou M, Guo J, Yang C (2018) Ratiometric fluorescence sensor for Fe3+ ions detection based on quantum dot-doped hydrogel optical fiber. Sensors Actuators B Chem 264:52–58
Chen X, Zhao Q, Zou W, Qu Q, Wang F (2017) A colorimetric Fe3+ sensor based on an anionic poly(3,4-propylenedioxythiophene) derivative. Sensors Actuators B Chem 244:891–896
Gupta VK, Mergu N, Kumawat LK (2016) A new multifunctional rhodamine-derived probe for colorimetric sensing of cu(II) and Al(III) and fluorometric sensing of Fe(III) in aqueous media. Sensors Actuators B Chem 223:101–113
Wei TB, Cheng XB, Li H, Zheng F, Lin Q, Yao H, Zhang YM (2016) Novel functionalized pillar[5]arene: synthesis, assembly and application in sequential fluorescent sensing for Fe3+ and F− in aqueous media. RSC Adv 6:20987–20993
Soylak M, Aydin A (2011) Determination of some heavy metals in food and environmental samples by flame atomic absorption spectrometry after coprecipitation. Food Chem Toxicol 49:1242–1248
Chamsaz M, Eftekhari M, Tafreshi S, Yekkebashi A, Eftekhari A (2014) Speciation and determination of iron using dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction based on solidification of organic drop followed by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Int J Environ Anal Chem 94:348–355
Rao KS, Balaji T, Rao TP et al (2002) Determination of iron, cobalt, nickel, manganese, zinc, copper, cadmium and lead in human hair by inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry. Spectrochim Acta B 57:1333–1338
Fukuda M, Hayashibe Y, Sayama Y (1995) Determination of nickel, cobalt, copper, thorium and uranium in high-purity zinc metal by ICP-MS with on-line matrix separation. Anal Sci 11:13–16
Sakamoto-arnold CM, Johnson KS (1987) Determination of picomolar levels of cobalt in seawater by flow injection analysis with chemiluminescence detection. Anal Chem 59:1789–1794
Maity D, Govindaraju T (2011) Highly selective colorimetric chemosensor for Co2+. Inorg Chem 50:11282–11284
Liu X, Yang Y, Li Q, Wang Z, Xing X, Wang Y (2018) Portably colorimetric paper sensor based on ZnS quantum dots for semi-quantitative detection of Co2+ through the measurement of grey level. Sensors Actuators B Chem 260:1068–1075
Kao MH, Wan CF, Wu AT (2017) A selective colorimetric chemosensor for Fe3+. Luminescence 32:1561–1566
Park GJ, Na YJ, Jo HY, Lee SA, Kim C (2014) A colorimetric organic chemo-sensor for Co2+ in a fully aqueous environment. Dalton T 43:6618–6622
Liu H, Zhao H, Tong Z (2017) A colorimetric, ratiometric, and fluorescent cobalt(II) chemosensor based on mixed organic ligands. Sensors Actuators B Chem 239:511–514
Na YJ, Choi YW, You GR, Kim C (2016) A novel selective colorimetric chemosensor for cobalt ions in a near perfect aqueous solution. Sensors Actuators B Chem 223:234–240
Singhal D, Singh AK, Upadhyay A (2014) Highly selective potentiometric and colorimetric determinations of cobalt (II) ion using thiazole based ligands. Mater Sci Eng C 45:216–224
Wang X, Zheng W, Lin H (2010) A new fluorescent chemosensor detecting Co2+ and K+ in DMF buffered solution. J Fluoresc 20:557–561
Wang X, Zheng W, Lin H, Liu G, Chen Y, Fang J (2009) A new selective phenanthroline-based fluorescent chemosensor for Co2+. Tetrahedron Lett 50:1536–1538
Kim Y, Johnson RC, Hupp JT (2001) Gold nanoparticle-based sensing of “spectroscopically silent” heavy metal ions. Nano Lett 1:165–167
Liu X, Dai Q, Austin L, Coutts J, Knowles G, Zou J, Chen H, Huo Q (2008) A one-step homogeneous immunoassay for cancer biomarker detection using gold nanoparticle probes coupled with dynamic light scattering. J Am Chem Soc 130:2780–2782
Raschke G, Kowarik S, Franzl T, Sönnichsen C, Klar TA, Feldmann J, Nichtl A, Kürzinger K (2003) Biomolecular recognition based on single gold nanoparticle light scattering. Nano Lett 3:935–938
Du BA, Li ZP, Liu CH (2006) One-step homogeneous detection of DNA hybridization with gold nanoparticle probes by using a linear light-scattering technique. Angew Chem 118:8190–8193
Ipe BI, Shukla A, Lu H, Zou B, Rehage H, Niemeyer CM (2006) Dynamic light-scattering analysis of the electrostatic interaction of hexahistidine-tagged cytochrome P450 enzyme with semiconductor quantum dots. ChemPhysChem 7:1112–1118
Deng DW, Yu JS, Pan Y (2006) Water-soluble CdSe and CdSe/CdS nanocrystals: a greener synthetic route. J Colloid Interface Sci 299:225–232
Shu C, Huang B, Chen X, Wang Y, Li X, Ding L, Zhong W (2013) Facile synthesis and characterization of water soluble ZnSe/ZnS quantum dots for cellar imaging. Spectrochim Acta A 104:143–149
Ding Y, Sun H, Liu D, Liu F, Wang D, Jiang Q (2013) Water-soluble, high-quality ZnSe@ZnS core/shell structure nanocrystals. J Chinese Adv Mater Soc 1:56–64
Mahapatra N, Panja S, Mandal A, Halder M (2014) A single source-precursor route for the one-pot synthesis of highly luminescent CdS quantum dots as ultra-sensitive and selective photoluminescence sensor for Co2+ and Ni2+ ions. J Mater Chem C 2:7373
Mahapatra N, Panja S, Mandal A et al (2017) A study of structural, morphological and optical properties of nanostructured ZnSe/ZnS multilayer thin films. J Alloys Compd 726:707–711
Vikraman AE, Jose AR, Jacob M et al (2015) Thioglycolic acid capped CdS quantum dots as a fluorescent probe for the nanomolar determination of dopamine. Anal Methods 7:6791–6798
Xie R, Li L, Li Y, Liu L, Xiao D, Zhu J (2011) Fe:ZnSe semiconductor nanocrystals: synthesis, surface capping, and optical properties. J Alloys Compd 509:3314–3318
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Yunnan University’s Research Innovation Fund for Graduate Students (YDY17106) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.61761047 and No. 41876055).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 5.09 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xing, X., Yang, Y., Zou, T. et al. Thioglycolic acid-capped ZnSe quantum dots as nanoprobe for cobalt(II) and iron(III) via measurement of grey level, UV-vis spectra and dynamic light scattering. Microchim Acta 186, 444 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3561-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3561-z