Abstract
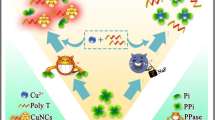
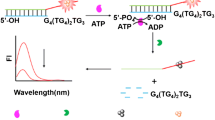
A fluorometric method is described for the determination of the activity of the enzyme T4 polynucleotide kinase phosphatase (T4 PNKP). A short 3′-terminus phosphorylated DNA strand is hybridized with a long DNA strand to produce a partially double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) substrate. On addition of T4 PNKP, the substrate is dephosphorylated to generate the long dsDNA, and then the long dsDNA acted as a template for synthesizing copper nanoclusters (CuNCs). The dsDNA-templated CuNCs display fluorescence with excitation/emission peak wavelengths of 340/570 nm. The fluorescence is DNA sequence-dependent. A DNA substrate was designed to enhance fluorescence and to reduce the background in order to improve the sensitivity of the assay. The assay has an analytical range that extends from 0.07 U mL−1 to 15 U mL−1 and a detection limit of 0.06 U mL−1.

The sequence-dependent fluorescence of DNA-templated copper nanoclusters, which are in-situ synthesized through the reduction of CuSO4 by ascorbate (Vc) in the presence of dsDNA template, is utilized to obtain the method for sensitive detection of T4 PNKP activity with near-zero background.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allinson SL (2010) DNA end-processing enzyme polynucleotide kinase as a potential target in the treatment of cancer. Future Oncol 6:1031–1042
Hu L, Lu C-H, Willner I (2015) Switchable catalytic DNA catenanes. Nano Lett 15:2099–2103
Karimi-Busheri F, Lee J, Tomkinson AE, Weinfeld M (1998) Repair of DNA strand gaps and nicks containing 3′-phosphate and 5′-hydroxyl termini by purified mammalian enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res 26:4395–4400
Wang LK, Shuman S (2001) Domain structure and mutational analysis of T4 polynucleotide kinase. J Biol Chem 276:26868–26874
Zhuang J, Lai W, Xu M, Zhou Q, Tang D (2015) Plasmonic AuNP/g-C3N4 nanohybrid-based photoelectro chemical sensing platform for ultrasensitive monitoring of polynucleotide kinase activity accompanying DNAzyme-catalyzed precipitation amplification. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:8330–8338
Liu S, Liu T, Wang L (2015) Label-free, isothermal and ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of DNA and DNA 3′-phosphatase using a cascade enzymatic cleavage strategy. Chem Commun 51:176–179
Jiang C, Yan C, Jiang J, Yu R (2013) Colorimetric assay for T4 polynucleotide kinase activity based on the horseradish peroxidase-mimicking DNAzyme combined with λ exonuclease cleavage. Anal Chim Acta 766:88–93
Jiang HX, Kong DM, Shen HX (2014) Amplified detection of DNA ligase and polynucleotide kinase/phosphatase on the basis of enrichment of catalytic G-quadruplex DNAzyme by rolling circle amplification. Biosens Bioelectron 55:133–138
Du J, Xu Q, Lu X, Zhang C (2014) A label-free bioluminescent sensor for real-time monitoring polynucleotide kinase activity. Anal Chem 86:8481–8488
Zhao H, Liu Q, Liu M, Jin Y, Li B (2017) Label-free fluorescent assay of T4 polynucleotide kinase phosphatase activity based on G-quadruplexe-thioflavin T complex. Talanta 165:653–658
Zhou L, Shen X, Sun N, Wang K, Zhang Y, Pei R (2015) Label-free fluorescence light-up detection of T4 polynucleotide kinase activity using the split-to-intact G-quadruplex strategy by ligation-triggered and toehold-mediated strand displacement release. Analyst 140:5450–5453
Hou T, Wang X, Liu X, Lu T, Liu S, Li F (2014) Amplified detection of T4 polynucleotide kinase activity by the coupled λ exonuclease cleavage reaction and catalytic assembly of bimolecular beacons. Anal Chem 86:884–890
Lin L, Liu Y, Zhao X, Li J (2011) Sensitive and rapid screening of T4 polynucleotide kinase activity and inhibition based on coupled exonuclease reaction and graphene oxide platform. Anal Chem 83:8396–8402
Ma C, Jin S, Wang J, Wang K, Liu H, Wu K (2016) A fluorescence-based assay for T4 polynucleotide kinase/phosphatase activity based on a terminal transferase-aided photoinduced electron transfer strategy. Anal Methods 8:1989–1994
Cen Y, Yang Y, Yu RQ, Chen TT, Chu X (2016) A cobalt oxyhydroxide nanoflake-based nanoprobe for the sensitive fluorescence detection of T4 polynucleotide kinase activity and inhibition. Nanoscale 8:8202–8209
Wang L, Zhang Q, Tang B, Zhang C (2017) Single-molecule detection of polynucleotide kinase based on phosphorylation-directed recovery of fluorescence quenched by au nanoparticles. Anal Chem 89:7255–7261
Xu M, Li B (2015) Label-free fluorescence strategy for sensitive detection of exonuclease activity using SYBR green I as probe. Spectrochim Acta A 151:22–26
Hu H, Zhang J, Ding Y, Zhang X, Xu K, Hou X, Wu P (2017) Modulation of the singlet oxygen generation from the double strand DNA-SYBR green I complex mediated by T-melamine-T mismatch for visual detection of melamine. Anal Chem 89:5101–5106
Li X, Xu X, Song J, Xue Q, Li C, Jiang W (2017) Sensitive detection of T4 polynucleotide kinase activity based on multifunctional magnetic probes and polymerization nicking reactions mediated hyperbranched rolling circle amplification. Biosens Bioelectron 91:631–636
Zhu W, Zhao Z, Li Z, Jiang J, Shen G, Yu R (2013) A graphene oxide platform for the assay of DNA 3′-phosphatases and their inhibitors based on hairpin primer and polymerase elongation. J Mater Chem B 1:361–367
Liao H, Liu G, Liu Y, Li R, Fu W, Hu L (2017) Aggregation-induced accelerating peroxidase-like activity of gold nanoclusters and their applications for colorimetric Pb2+ detection. Chem Commun 53:10160–10163
Huang L, Zhang W, Chen K, Zhu W, Liu X, Wang R, Zhang X, Hu N, Suo Y, Wang J (2017) Facet-selective response of trigger molecule to CeO2{110} for up-regulating oxidase-like activity. Chem Eng J 330:746–752
Huang L, Chen K, Zhang W, Zhu W, Zhu X, Liu X, Wang J, Wang R, Hu N, Suo Y, Wang J (2018) ssDNA-tailorable oxidase-mimicking activity of spinel MnCo2O4 for sensitive biomolecular detection in food sample. Sensors Actuators B Chem 269:79–87
Yuan Z, Chen YC, Li HW, Chang HT (2014) Fluorescent silver nanoclusters stabilized by DNA scaffolds. Chem Commun 50:9800–9815
Huang J, Lin L, Sun D, Chen H, Yang D, Li Q (2015) Bio-inspired synthesis of metal nanomaterials and applications. Chem Soc Rev 44:6330–6374
Hu X, Liu T, Zhuang Y, Wang W, Li Y, Fan W, Huang Y (2016) Recent advances in the analytical applications of copper nanoclusters. Trends Anal Chem 77:66–75
Xu F, Shi H, He X, Wang K, He D, Guo Q, Qing Z, Yan L, Ye X, Li D, Tang J (2014) Concatemeric dsDNA-templated copper nanoparticles strategy with improved sensitivity and stability based on rolling circle replication and its application in microRNA detection. Anal Chem 86:6976–6982
Ge J, Zhang L, Dong ZZ, Cai QY, Li ZH (2016) Sensitive and label-free T4 polynucleotide kinase/phosphatase detection based on poly(thymine)-templated copper nanoparticles coupled with nicking enzyme-assisted signal amplification. Anal Methods 8:2831–2836
Zhang L, Zhao J, Zhang H, Jiang J, Yu R (2013) Double strand DNA-templated copper nanoparticle as a novel fluorescence indicator for label-free detection of polynucleotide kinase activity. Biosens Bioelectron 44:6–9
Qing Z, He X, He D, Wang K, Xu F (2013) Poly(thymine)-templated selective formation of fluorescent copper nanoparticles. Angew Chem Int Ed 52:9719–9722
Song Q, Shi Y, He D, Xu S, Ouyang J (2015) Sequence−dependent dsDNA−templated formation of fluorescent copper nanoparticles. Chem Eur J 21:2417–2422
Wei W, Lu Y, Chen W, Chen S (2011) One-pot synthesis, photoluminescence, and electrocatalytic properties of subnanometer-sized copper clusters. J Am Chem Soc 133:2060–2063
Liu G, Shao Y, Peng J, Dai W, Liu L, Xu S, Wu F, Wu X (2013) Highly thymine-dependent formation of fluorescent copper nanoparticles template by ssDNA. Nanotechnology 24:345502–345508
Qing T, Qing Z, Mao Z, He X, Xu F, Wen L, He D, Shi H, Wang K (2014) dsDNA-templated fluorescent copper nanoparticles: poly(AT-TA)-dependent formation. RSC Adv 4:61092–61095
Zhou F, Meng R, Liu Q, Jin Y, Li B (2016) Photoinduced electron transfer-based fluorescence quenching combined with rolling circle amplification for sensitive detection of microRNA. ChemistrySelect 1:6422–6428
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 21775099 and 21475083).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 662 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Liu, Q., Jin, Y. et al. Determination of the activity of T4 polynucleotide kinase phosphatase by exploiting the sequence-dependent fluorescence of DNA-templated copper nanoclusters. Microchim Acta 186, 3 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3102-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3102-1