Abstract
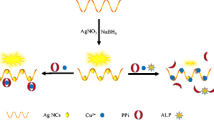
The authors describe a method for the determination of the activity of alkaline phosphatase (ALP) that utilizes dsDNA-templated copper nanoparticles (CuNPs) coupled to enzymatic amplification via λ exonuclease. A hybrid of a DNA modified with a phosphate moiety at the 5′-end (P-DNA) and a P-DNA complementary sequence (cP-DNA) is employed as the dsDNA substrate for ALP. In the absence of ALP, the dsDNA is cleaved by the λ exonuclease, which hinders the formation of CuNPs which display fluorescence with excitation/emission peaks at 340/565 nm. However, ALP-mediated hydrolysis of the 5′-phosphoryl end impedes the cleavage of dsDNA by the λ exonuclease, and this promotes the formation of fluorescent dsDNA-templated CuNPs via ascorbate-mediated reduction. Under the optimized experimental conditions, this method exhibits a high specificity to ALP and has a 0.1 U⋅L−1 limit of detection. The strategy also provides the basis for a screening platform for inhibitors of ALP.

Schematic presentation of a fluorescence assay for the detection of alkaline phosphatase based on dsDNA-templated copper nanoparticles and exonuclease based amplification.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coleman JE (1992) Structure and mechanism of alkaline phosphatase. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 21:441–483. doi:10.1146/annurev.bb.21.060192.002301
Mukaiyama K, Kamimura M, Uchiyama S, Ikegami S, Nakamura Y, Kato H (2015) Elevation of serum alkaline phosphatase (ALP) level in postmenopausal women is caused by high bone turnover. Aging Clin Exp Res 27:413–418. doi:10.1007/s40520-014-0296-x
Fishman WH (1987) Clinical and biological significance of an isozyme tumor marker-PLAP. Clin Biochem 20:387–392. doi:10.1016/0009-9120(87)90003-8
Kinoshita Y, Arai M, Ito N, Takashi Y, Makita N, Nangaku M, Shinoda Y, Fukumoto S (2016) High serum ALP level is associated with increased risk of denosumab-related hypocalcemia in patients with bone metastases from solid tumors. Endocr J 63:479–484. doi:10.1507/endocrj.EJ16-0003
Shi D, Sun Y, Lin L, Shi C, Wang G, Zhang X (2016) Naked-eye sensitive detection of alkaline phosphatase (ALP) and pyrophosphate (PPi) based on a horseradish peroxidase catalytic colorimetric system with Cu(ii). Analyst 141:5549–5554. doi:10.1039/c6an01124a
Molina-Delgado MÁ, Aguilar-Caballos MP, Gómez-Hens A (2016) Simultaneous photometric microplate assay for free and total thiamine using gold nanoparticles and alkaline phosphatase. Microchim Acta 183:1385–1390. doi:10.1007/s00604-016-1767-x
Deng J, Jiang Q, Wang Y, Yang L, Yu P, Mao L (2013) Real-time colorimetric assay of inorganic pyrophosphatase activity based on reversibly competitive coordination of Cu2+ between cysteine and pyrophosphate ion. Anal Chem 85:9409–9415. doi:10.1021/ac402524e
Li C, Zhen S, Wang J, Li Y, Huang C (2013) A gold nanoparticles-based colorimetric assay for alkaline phosphatase detection with tunable dynamic range. Biosens Bioelectron 43:366–371. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2012.12.015
Yang J, Zheng L, Wang Y, Li W, Zhang J, Gu J, Fu Y (2016) Guanine-rich DNA-based peroxidase mimetics for colorimetric assays of alkaline phosphatase. Biosens Bioelectron 77:549–556. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2015.10.003
Shen C, Li X, Rasooly A, Guo L, Zhang K, Yang M (2016) A single electrochemical biosensor for detecting the activity and inhibition of both protein kinase and alkaline phosphatase based on phosphate ions induced deposition of redox precipitates. Biosens Bioelectron 85:220–225. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2016.05.025
Zhang L, Hou T, Li H, Li F (2015) A highly sensitive homogeneous electrochemical assay for alkaline phosphatase activity based on single molecular beacon-initiated T7 exonuclease-mediated signal amplification. Analyst 140:4030–4036. doi:10.1039/c5an00516g
Shen B, Li J, Cheng W, Yan Y, Tang R, Li Y (2015) Electrochemical aptasensor for highly sensitive determination of cocaine using a supramolecular aptamer and rolling circle amplification. Microchim Acta 182:361–367. doi:10.1007/s00604-014-1333-3
Dong J, Li Y, Zhang M, Yan T, Qian W (2014) Ultrasensitive surface-enhanced Raman scattering detection of alkaline phosphatase. Anal Methods 6:9168–9172. doi:10.1039/C4AY01885K
Du J, Xiong L, Ma C, Liu H, Wang J, Wang K (2016) Label-free DNA hairpin probe for real-time monitoring of alkaline phosphatase activity. Anal Methods 8:5095–5100. doi:10.1039/C6AY00989A
Kong R, Fu T, Sun NN, Qu FL, Zhang SF, Zhang XB (2013) Pyrophosphate-regulated Zn2+-dependent DNAzyme activity: an amplified fluorescence sensing strategy for alkaline phosphatase. Biosens Bioelectron 50:351–355. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2013.06.064
Li Y, Li YN, Liu Z, Su X (2014) Sensitive fluorometric detection of alkaline phosphatase using a water-soluble conjugated polymer. RSC Adv 4:42825–42830. doi:10.1039/C4RA05844E
Liu S, Pang S, Na W, Su X (2014) Near-infrared fluorescence probe for the determination of alkaline phosphatase. Biosens Bioelectron 55:249–254. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2013.12.023
Liu XG, Xing XJ, Li B, Guo YM, Zhang YZ, Yang Y, Zhang LF (2016) Fluorescent assay for alkaline phosphatase activity based on graphene oxide integrating with λ exonuclease. Biosens Bioelectron 81:460–464. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2016.03.030
Park KS, Lee CY, Park HG (2014) A sensitive dual colorimetric and fluorescence system for assaying the activity of alkaline phosphatase that relies on pyrophosphate inhibition of the peroxidase activity of copper ions. Analyst 139:4691–4695. doi:10.1039/c4an00778f
Tang C, Qian Z, Huang Y, Xu J, Ao H, Zhao M, Zhou J, Chen J, Feng H (2016) A fluorometric assay for alkaline phosphatase activity based on β-cyclodextrin-modified carbon quantum dots through host-guest recognition. Biosens Bioelectron 83:274–280. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2016.04.047
Wang Y, Chen J, Jiao H, Chen Y, Li W, Zhang Q, Yu C (2013) Polymer templated perylene-probe noncovalent self-assembly: a new strategy for label-free ultrasensitive fluorescence turn-on biosensing. Chem Eur J 19:12846–12852. doi:10.1002/chem.201203998
Wang FY, Li YX, Li WY, Zhang QF, Chen J (2014) A facile method for detection of alkaline phosphatase activity based on the turn-on fluorescence of resorufin. Anal Methods 6:6105–6109. doi:10.1039/C4AY00634H
Xiang MH, Liu JW, Li N, Tang H, Yu RQ, Jiang JH (2016) A fluorescent graphitic carbon nitride nanosheet biosensor for highly sensitive, label-free detection of alkaline phosphatase. Nano 8:4727–4732. doi:10.1039/c5nr08278a
Wolfbeis OS, Koller E (1985) Photometric and fluorimetric assay of alkaline phosphatase with new coumarin-derived substrates. Microchim Acta 85:389–395. doi:10.1007/BF01201534
Zhu WP, Zhao ZW, Li Z, Jiang JH, Shen GL, Yu RQ (2013) A graphene oxide platform for the assay of DNA 3- phosphatases and their inhibitors based on hairpin primer and polymerase elongation. J Mater Chem B 1:361–367. doi:10.1039/C2TB00109H
Kang W, Ding Y, Zhou H, Liao Q, Yang X, Yang Y, Jiang J, Yang M (2015) Monitoring the activity and inhibition of alkaline phosphatase via quenching and restoration of the fluorescence of carbon dots. Microchim Acta 182:1161–1167. doi:10.1007/s00604-014-1439-7
Zhao MM, Guo YJ, Wang LX, Luo F, Lin CY, Lin ZY, Chen GN (2016) A sensitive fluorescence biosensor for alkaline phosphatase activity based on the Cu(II)-dependent DNAzyme. Anal Chim Acta 948:98–103. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2016.10.033
Qian ZS, Chai LJ, Huang YY, Tang C, Shen JJ, Chen JR, Feng H (2015) A real-time fluorescent assay for the detection of alkaline phosphatase activity based on carbon quantum dots. Biosens Bioelectron 68:675–680. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2015.01.068
Schrenkhammer P, Rosnizeck IC, Duerkop A, Wolfbeis OS, Schäferling M (2008) Time-resolved fluorescence-based assay for the determination of alkaline phosphatase activity and application to the screening of its inhibitors. J Biomol Screen 13(1):9–16. doi:10.1177/1087057107312031
Guo YM, Cao FP, Lei XL, Mang LH, Cheng SJ, Song JT (2016) Fluorescent copper nanoparticles: recent advances in synthesis and applications for sensing metal ions. Nanoscale 8:4852–4863. doi:10.1039/c6nr00145a
Chen J, Liu J, Fang Z, Zeng L (2012) Random dsDNA-templated formation of copper nanoparticles as novel fluorescence probes for label-free lead ions detection. Chem Commun 48:1057–1059. doi:10.1039/c2cc16668b
Chen J, Ji X, Tinnefeld P, He Z (2016) Multifunctional dumbbell-shaped DNA-templated selective formation of fluorescent silver nanoclusters or copper nanoparticles for sensitive detection of biomolecules. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:1786–1794. doi:10.1021/acsami.5b09678
Lai QQ, Liu MD, Gu CC, Nie HG, Xu XJ, Li Z, Yang Z, Huang SM (2016) A novel label-free fluorescence strategy for methyltransferase activity assay based on dsDNAtemplated copper nanoparticles coupled with an endonuclease-assisted signal transduction system. Analyst 141:1383–1389. doi:10.1039/c5an02123e
Park KW, Batule BS, Kang KS, Park KS, Park HG (2016) Rapid and ultrasensitive detection of microRNA by target-assisted isothermal exponential amplification coupled with poly (thymine)-templated fluorescent copper nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 27:425502–425509. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/27/42/425502
Yang L, Wang Y, Li B, Jin Y (2017) High-throughput identification of telomere-binding ligands based on the fluorescence regulation of DNA-copper nanoparticles. Biosens Bioelectron 87:915–917. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2016.09.055
Zhang L, Zhao J, Duan M, Zhang H, Jiang J, Yu R (2013) Inhibition of dsDNA-templated copper nanoparticles by pyrophosphate as a label-free fluorescent strategy for alkaline phosphatase assay. Anal Chem 85:3797–3801. doi:10.1021/ac4001942
Li J, Si L, Bao J, Wang Z, Dai Z (2017) Fluorescence regulation of poly(thymine)-templated copper nanoparticles via an enzyme-triggered reaction toward sensitive and selective detection of alkaline phosphatase. Anal Chem. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.6b05112
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21205142, 31370104), The Research Innovation Program for Graduates of Central South University (2016zzts580).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 2667 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Ma, C., Wang, J. et al. A turn-on fluorescent method for determination of the activity of alkaline phosphatase based on dsDNA-templated copper nanoparticles and exonuclease based amplification. Microchim Acta 184, 2483–2488 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2256-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2256-6