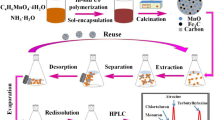
Abstract
A three-dimensional magnetic hollow porous raspberry-like hierarchical Co/Ni@carbon microspheres (3D Co/Ni@carbon) were synthesized by using a bimetal-organic framework (Co/Ni-MOF) as a precursor and subsequent calcination under nitrogen. The 3D Co/Ni@carbon is a novel solid phase extractant that displays outstanding extraction capability and separation efficiency for the pyrethroid pesticides ethofenprox and bifenthrin. This is ascribed to the beneficial effects of facile analyte transport (due to the presence of free pores), the abundant number of adsorption sites (which warrant efficient extraction), and the excellent structural stability of the material. The 3D Co/Ni@carbon was applied to dispersive magnetic solid-phase extraction (d-MSPE), and the two pyrethroids were quantified by HPLC (UV detection wavelength: 220 nm). The method has a high preconcentration factor (937–1012) and give recoveries that range between 85.6–106.9%, with RSDs (for n = 5) of <6% in case of real samples.

The hierarchical porous Co/Ni@carbon microsphere as adsorbent was fabricated, and it showed high extraction efficiency for two pyrethroids.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bagheri H, Yamini Y, Safari M, Asiabi H, Karimi M, Heydari A (2016) Simultaneous determination of pyrethroids residues in fruit and vegetable samples via supercritical fluid extraction coupled with magnetic solid phase extraction followed by HPLC-UV. J Supercrit Fluids 107:571–580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.supflu.2015.07.017
Zhang Y, Wang X, Lin C, Fang G, Wang S (2012) A novel SPME Fiber chemically linked with 1-Vinyl-3-hexadecylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate ionic liquid coupled with GC for the simultaneous determination of Pyrethroids in vegetables. Chromatographia 75(13–14):789–797. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-012-2244-2
Yu X, Yang H (2017) Pyrethroid residue determination in organic and conventional vegetables using liquid-solid extraction coupled with magnetic solid phase extraction based on polystyrene-coated magnetic nanoparticles. Food Chem 217:303–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.08.115
Hou X, Zheng X, Zhang C, Ma X, Ling Q, Zhao L (2014) Ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction based on the solidification of a floating organic droplet followed by gas chromatography for the determination of eight pyrethroid pesticides in tea samples. J Chromatogr B 969:123–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2014.08.010
Rashidi Nodeh H, Sereshti H, Gaikani H, Kamboh MA, Afsharsaveh Z (2017) Magnetic graphene coated inorganic-organic hybrid nanocomposite for enhanced preconcentration of selected pesticides in tomato and grape. J Chromatogr A 1509:26–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2017.06.032
Hu L, Zhang P, Shan W, Wang X, Li S, Zhou W, Gao H (2015) In situ metathesis reaction combined with liquid-phase microextraction based on the solidification of sedimentary ionic liquids for the determination of pyrethroid insecticides in water samples. Talanta 144:98–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2015.05.077
Ibarra IS, Miranda JM, Rodriguez JA, Nebot C, Cepeda A (2014) Magnetic solid phase extraction followed by high-performance liquid chromatography for the determination of sulphonamides in milk samples. Food Chem 157:511–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.02.069
Mariño-Repizo L, Kero F, Vandell V, Senior A, Isabel Sanz-Ferramola M, Cerutti S, Raba J (2015) A novel solid phase extraction – ultra high performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry method for the quantification of ochratoxin a in red wines. Food Chem 172:663–668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.09.094
Das R, Pachfule P, Banerjee R, Poddar P (2012) Metal and metal oxidenanoparticle synthesis from metal organic frameworks (MOFs): finding the border of metal and metal oxides. Nanoscale 4(2):591–599. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1nr10944h
Song Y, Li X, Sun L, Wang L (2015) Metal/metal oxide nanostructures derived from metal–organic frameworks. RSC Adv 5(10):7267–7279. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra12273a
Sun J-K, Xu Q (2014) From metal–organic framework to carbon: toward controlled hierarchical pore structures via a double-template approach. Chem Commun 50(88):13502–13505. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4cc06212d
Chaikittisilp W, Ariga K, Yamauchi Y (2013) A new family of carbon materials: synthesis of MOF-derived nanoporous carbons and their promising applications. J Mater Chem A 1(1):14–19. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2ta00278g
Ye L, Chai G, Wen Z (2017) Zn-MOF-74 derived N-doped mesoporous carbon as pH-universal Electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction reaction. Adv Funct Mater 27(14):1606190. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201606190
Zhang S, Li D, Chen S, Yang X, Zhao X, Zhao Q, Komarneni S, Yang D (2017) Highly stable supercapacitors with MOF-derived Co9S8/carbon electrodes for high rate electrochemical energy storage. J Mater Chem A 5(24):12453–12461. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ta03070c
Xiao L, Xu R, Yuan Q, Wang F (2017) Highly sensitive electrochemical sensor for chloramphenicol based on MOF derived exfoliated porous carbon. Talanta 167:39–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.01.078
Pan Y, Zhao Y, Mu S, Wang Y, Jiang C, Liu Q, Fang Q, Xue M, Qiu S (2017) Cation exchanged MOF-derived nitrogen-doped porous carbons for CO2 capture and supercapacitor electrode materials. J Mater Chem A 5(20):9544–9552. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ta00162b
Wang Z, Lu Y, Yan Y, Larissa TYP, Zhang X, Wuu D, Zhang H, Yang Y, Wang X (2016) Core-shell carbon materials derived from metal-organic frameworks as an efficient oxygen bifunctional electrocatalyst. Nano Energy 30:368–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2016.10.017
Liu X, Ai L, Jiang J (2015) Interconnected porous hollow CuS microspheres derived from metal-organic frameworks for efficient adsorption and electrochemical biosensing. Powder Technol 283:539–548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2015.06.016
Shi X-H, Ban J-J, Zhang L, Sun Z-P, Jia D-Z, Xu G-C (2017) Preparation and exceptional adsorption performance of porous MgO derived from a metal–organic framework. RSC Adv 7(26):16189–16195. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra00526a
Hao L, Wang C, Wu Q, Li Z, Zang X, Wang Z (2014) Metal–organic framework derived magnetic Nanoporous carbon: novel adsorbent for magnetic solid-phase extraction. Anal Chem 86(24):12199–12205. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac5031896
Liu X, Wang C, Wu Q, Wang Z (2015) Magnetic porous carbon-based solid-phase extraction of carbamates prior to HPLC analysis. Microchim Acta 183(1):415–421. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1664-8
Wang Y, Tong Y, Xu X, Zhang L (2018) Metal-organic framework-derived three-dimensional porous graphitic octahedron carbon cages-encapsulated copper nanoparticles hybrids as highly efficient enrichment material for simultaneous determination of four fluoroquinolones. J Chromatogr A 1533:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2017.12.021
Huang X, Qiu N, Yuan D, Lin Q (2010) Preparation of a mixed stir bar for sorptive extraction based on monolithic material for the extraction of quinolones from wastewater. J Chromatogr A 1217(16):2667–2673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2009.09.072
Li M, Wang J, Jiao C, Wang C, Wu Q, Wang Z (2016) Magnetic porous carbon derived from a Zn/co bimetallic metal-organic framework as an adsorbent for the extraction of chlorophenols from water and honey tea samples. J Sep Sci 39(10):1884–1891. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201600097
Bhadra BN, Ahmed I, Kim S, Jhung SH (2017) Adsorptive removal of ibuprofen and diclofenac from water using metal-organic framework-derived porous carbon. Chem Eng J 314:50–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.12.127
Ahmed I, Bhadra BN, Lee HJ, Jhung SH (2018) Metal-organic framework-derived carbons: Preparation from ZIF-8 and application in the adsorptive removal of sulfamethoxazole from water. Catal Today 301:90–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2017.02.011
Ma R, Hao L, Wang J, Wang C, Wu Q, Wang Z (2016) Magnetic porous carbon derived from a metal-organic framework as a magnetic solid-phase extraction adsorbent for the extraction of sex hormones from water and human urine. J Sep Sci 39(18):3571–3577. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201600347
Liu X, Feng T, Wang C, Hao L, Wang C, Wu Q, Wang Z (2016) A metal–organic framework-derived nanoporous carbon/iron composite for enrichment of endocrine disrupting compounds from fruit juices and milk samples. Anal Methods 8(17):3528–3535. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ay00191b
He X, Yang W, Li S, Liu Y, Hu B, Wang T, Hou X (2018) An amino-functionalized magnetic framework composite of type Fe3O4-NH2@MIL-101(Cr) for extraction of pyrethroids coupled with GC-ECD. Mikrochimica acta 185 (2):125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2672-2
Jiao Y, Pei J, Chen D, Yan C, Hu Y, Zhang Q, Chen G (2017) Mixed-metallic MOF based electrode materials for high performance hybrid supercapacitors. J Mater Chem A 5(3):1094–1102. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ta09805c
Das S, Kim H, Kim K (2009) Metathesis in single crystal: complete and reversible exchange of metal ions constituting the frameworks of metal−organic frameworks. J Am Chem Soc 131(11):3814–3815. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja808995d
Lammert M, Gli SN (2017) Tuning the stability of bimetallic Ce(iv)/Zr(iv)-based MOFs with UiO-66 and MOF-808 structures. Dalton Trans 46(8):2425–2429. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7DT00259A
Hu J, Yu H, Dai W, Yan X, Hu X, Huang H (2014) Enhanced adsorptive removal of hazardous anionic dye “Congo red” by a Ni/cu mixed-component metal–organic porous material. RSC Adv 4(66):35124–35130. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra05772d
Zhou Z, Mei L, Ma C, Xu F, Xiao J, Xia Q, Li Z (2016) A novel bimetallic MIL-101(Cr, mg) with high CO2 adsorption capacity and CO2/N2 selectivity. Chem Eng Sci 147:109–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2016.03.035
Smith SJ, Ladewig BP, Hill AJ, Lau CH, Hill MR (2015) Post-synthetic Ti exchanged UiO-66 metal-organic frameworks that deliver exceptional gas permeability in mixed matrix membranes. Sci Rep 5:7823. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep07823
Chen Y-Z, Wang C, Wu Z-Y, Xiong Y, Xu Q, Yu S-H, Jiang H-L (2015) From bimetallic metal-organic framework to porous carbon: high surface area and multicomponent active dopants for excellent Electrocatalysis. Adv Mater 27(34):5010–5016. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201502315
Song Y, Qiang T, Ye M, Ma Q, Fang Z (2015) Metal organic framework derived magnetically separable 3-dimensional hierarchical Ni@C nanocomposites: synthesis and adsorption properties. Appl Surf Sci 359:834–840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.10.215
Wu X, Huang M, Zhou T, Mao J (2016) Recognizing removal of norfloxacin by novel magnetic molecular imprinted chitosan/γ-Fe2O3 composites: selective adsorption mechanisms, practical application and regeneration. Sep Purif Technol 165:92–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2016.03.041
Zhang S, Yang Q, Yang X, Wang W, Li Z, Zhang L, Wang C, Wang Z (2017) A zeolitic imidazolate framework based nanoporous carbon as a novel fiber coating for solid-phase microextraction of pyrethroid pesticides. Talanta 166:46–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.01.042
Wu Q, Li Z, Wang C, Wu C, Wang W, Wang Z (2011) Dispersive solid-phase extraction clean-up combined with dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for the determination of neonicotinoid insecticides in vegetable samples by high-performance liquid chromatography. Food Anal Methods 4(4):559–566. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-011-9200-x
Jiang C, Sun Y, Yu X, Gao Y, Zhang L, Wang Y, Zhang H, Song D (2013) Liquid–solid extraction coupled with magnetic solid-phase extraction for determination of pyrethroid residues in vegetable samples by ultra fast liquid chromatography. Talanta 114:167–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2013.04.004
Fan C, Liang Y, Dong H, Ding G, Zhang W, Tang G, Yang J, Kong D, Wang D, Cao Y (2017) In-situ ionic liquid dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction using a new anion-exchange reagent combined Fe 3 O 4 magnetic nanoparticles for determination of pyrethroid pesticides in water samples. Anal Chim Acta 975:20–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2017.04.036
Zhou Q, Gao Y, Bai H, Xie G (2010) Preconcentration sensitive determination of pyrethroid insecticides in environmental water samples with solid phase extraction with SiO2 microspheres cartridge prior to high performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1217(31):5021–5025. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2010.05.060
Yang X, Zhang P, Li X, Hu L, Gao H, Zhang S, Zhou W, Lu R (2016) Effervescence-assisted β-cyclodextrin/attapulgite composite for the in-syringe dispersive solid-phase extraction of pyrethroids in environmental water samples. Talanta 153:353–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2016.03.007
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (Nos. NSFC 51672116 and 21707061), Science and Technology Foundation of Ocean and Fisheries of Liaoning Province (201408, 201406) and the Liaoning Scientific Instruments Service Sharing Information Platform Ability Construction (201507A003). The authors also thank their colleagues and other students who participated in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 832 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Wu, X. & Zhang, L. Three-dimensional hollow porous raspberry-like hierarchical Co/Ni@carbon microspheres for magnetic solid-phase extraction of pyrethroids. Microchim Acta 185, 437 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2973-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2973-5