Abstract
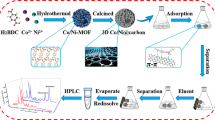
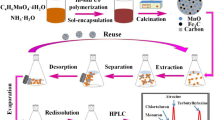
A unique waxberry-like magnetic hierarchical porous carbon hybrid was synthesized from a nickel based metal–organic framework (Ni-MOF) which, on calcination, produces hierarchical Ni/NiO nanocrystals covered with graphitic carbon (GrC). The material was applied to magnetic solid phase extraction (MSPE) of trace levels of four fluoroquinolones (FQs) from environmental water samples. It is shown to exhibit superior extraction capability for four FQs, because the novel 3D morphology provides an enhanced surface area along with transport channels, while Ni and graphitic carbon as potential adsorption sites are ideal components. The material with inherent magnetism is reusable and displays superb recycling stability for the adsorption and desorption (by using alkaline methanol) of FQs after 6 cycles. The FQs were quantified by HPLC with UV detection, and the limits of detection (at an S/N ratio of 3) range between 7.9 and 57 ng·L−1. Recoveries from spiked environmental water samples are between 88.8 and 103.7%.

A magnetic hierarchical porous carbon hybrid was prepared from a nickel-organic framework and applied to solid phase extraction of trace levels fluoroquinolones from environmental water samples.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Marouzi S, Sharifi Rad A, Beigoli S, Teimoori Baghaee P, Assaran Darban R, Chamani J (2017) Study on effect of lomefloxacin on human holo-transferrin in the presence of essential and nonessential amino acids: Spectroscopic and molecular modeling approaches. Int J Biol Macromol 97:688–699. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.01.047
Kamble R, Sharma S, Mehta P (2017) Norfloxacin mixed solvency based solid dispersions: In-vitro and In-vivo investigation. J Taibah Univ Sci. doi:10.1016/j.jtusci.2016.11.003
Jiang WT, Chang PH, Wang YS, Tsai Y, Jean JS, Li Z, Krukowski K (2013) Removal of ciprofloxacin from water by birnessite. J Hazard Mater 250:362–369. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.02.015
Ahn Y, Linder SW, Veach BT, Steve Yan S, Haydee Fernandez A, Pineiro SA, Cerniglia CE (2012) In vitro enrofloxacin binding in human fecal slurries. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol: RTP 62(1):74–84. doi:10.1016/j.yrtph.2011.11.013
Fengxian C, Reti H (2017) Analysis of positions and substituents on genotoxicity of fluoroquinolones with quantitative structure-activity relationship and 3D Pharmacophore model. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 136:111–118. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.10.036
Liu X, Liu Y, Xu J-R, Ren K-J, Meng X-Z (2016) Tracking aquaculture-derived fluoroquinolones in a mangrove wetland, South China. Environ Pollut 219:916–923. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2016.09.011
Golet EM, Alder AC, Hartmann A, Ternes TA, Giger W (2001) Trace determination of fluoroquinolone antibacterial agents in urban wastewater by solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. Anal Chem 73(15):3632–3638. doi:10.1021/ac0015265
Poliwoda A, Krzyzak M, Wieczorek PP (2010) Supported liquid membrane extraction with single hollow fiber for the analysis of fluoroquinolones from environmental surface water samples. J Chromatogr A 1217(22):3590–3597. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2010.03.051
Sun X, He J, Cai G, Lin A, Zheng W, Liu X, Chen L, He X, Zhang Y (2010) Room temperature ionic liquid-mediated molecularly imprinted polymer monolith for the selective recognition of quinolones in pork samples. J Sep Sci 33:3786–3793. doi:10.1002/jssc.201000337
Marazuela MD, Bogialli S (2009) A review of novel strategies of sample preparation for the determination of antibacterial residues in foodstuffs using liquid chromatography-based analytical methods. Anal Chim Acta 645(1–2):5–17. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2009.04.031
Nasiri J, Naghavi MR, Motamedi E, Alizadeh H, Moghadam MRF, Nabizadeh M, Mashouf A (2017) Carbonaceous sorbents alongside an optimized magnetic solid phase extraction (MSPE) towards enrichment of crude Paclitaxel extracts from callus cultures of Taxus baccata. J Chromatogr B 1043:96–106. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2016.10.029
Fan S, Zhu J, Ren L, Wang M, Bi W, Li H, Huang X, Chen DD (2017) Co-solvent enhanced adsorption with magnetic velvet-like carbon nitride for high efficiency solid phase extraction. Anal Chim Acta 960:63–71. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2017.01.020
Hekmatara H, Seifi M, Forooraghi K (2013) Microwave absorption property of aligned MWCNT/Fe3O4. J Magn Magn Mater 346:186–191. doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2013.06.032
Ma J, Jiang L, Wu G, Xia Y, Lu W, Li J, Chen L (2016) Determination of six sulfonylurea herbicides in environmental water samples by magnetic solid-phase extraction using multi-walled carbon nanotubes as adsorbents coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1466:12–20. doi:10.1016/j.chroma
Cao J, Zhang X, He X, Chen L, Zhang Y (2013) Facile synthesis of a Ni(II)-immobilized core–shell magnetic nanocomposite as an efficient affinity adsorbent for the depletion of abundant proteins from bovine blood. J Mater Chem B 1:3619–3718. doi:10.1039/c3tb20573h
Zhang Y, Zhang M, Yang J, Ding L, Zheng J, Xu J, Xiong S (2016) Formation of Fe3O4@SiO2@C/Ni hybrids with enhanced catalytic activity and histidine-rich protein separation. Nanoscale 8:15978–15988. doi:10.1039/C6NR05078F
Tang B, Song W-C, Yang E-C, Zhao X-J (2017) MOF-derived Ni-based nanocomposites as robust catalysts for chemoselective hydrogenation of functionalized nitro compounds. RSC Adv 7(3):1531–1539. doi:10.1039/c6ra26699a
Xu X, Nosheen F, Wang X (2016) Ni-decorated molybdenum carbide hollow structure derived from carbon-coated metal–organic framework for electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution reaction. Chem Mater 28(17):6313–6320. doi:10.1021/acs.chemmater.6b02586
Ma J, Yao Z, Hou L, Lu W, Yang Q, Li J, Chen L (2016) Metal organic frameworks (MOFs) for magnetic solid-phase extraction of pyrazole/pyrrole pesticides in environmental water samples followed by HPLC-DAD determination. Talanta 161:686–692. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2016.09.035
Zhou Q, Lei M, Li J, Liu Y, Zhao K, Zhao D (2017) Magnetic solid phase extraction of N- and S-containing polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons at ppb levels by using a zerovalent ironnanoscale material modified with a metal organic framework of type Fe@MOF-5, and their determination by HPLC. Microchim Acta 184:1029–1036. doi:10.1007/s00604-017-2094-6
Chen X, Ding N, Zang H, Yeung H, Zhao R-S, Cheng C, Liu J, Chan TWD (2013) Fe3O4@MOF core–shell magnetic microspheres for magnetic solid-phase extraction of polychlorinated biphenyls from environmental water samples. J Chromatogr A 1304:241–245. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2013.06.053
Wu Q, Cheng S, Wang C, Li X, Li Z, Hao C (2016) Magnetic porous carbon derived from a zinc-cobaltmetal-organic framework: a adsorbent for magnetic solid phase extraction of flunitrazepam. Microchim Acta 183:3009–3017. doi:10.1007/s00604-016-1948-7
Zou F, Chen YM, Liu K, Yu Z, Liang W, Bhaway SM, Gao M, Zhu Y (2016) Metal organic frameworks derived hierarchical hollow NiO/Ni/graphene composites for lithium and sodium storage. ACS Nano 10(1):377–386. doi:10.1021/acsnano.5b05041
Carrasco JA, Romero J, Abellan G, Hernandez-Saz J, Molina SI, Marti-Gastaldo C, Coronado E (2016) Small-pore driven high capacitance in a hierarchical carbon via carbonization of Ni-MOF-74 at low temperatures. Chem Commun 52(58):9141–9144. doi:10.1039/c6cc02252a
Mukoyoshi M, Kobayashi H, Kusada K, Hayashi M, Yamada T, Maesato M, Taylor JM, Kubota Y, Kato K, Takata M, Yamamoto T, Matsumura S, Kitagawa H (2015) Hybrid materials of Ni NP@MOF prepared by a simple synthetic method. Chem Commun 51(62):12463–12466. doi:10.1039/c5cc04663g
Lee G, Lee C, Yoon CM, Kim M, Jang J (2017) High-performance three-dimensional mesoporous graphene electrode for supercapacitors using lyophilization and plasma reduction. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(6):5222–5230. doi:10.1021/acsami.6b13050
Wagil M, Kumirska J, Stolte S, Puckowski A, Maszkowska J, Stepnowski P, Bialk-Bielinska A (2014) Development of sensitive and reliable LC-MS/MS methods for the determination of three fluoroquinolones in water and fish tissue samples and preliminary environmental risk assessment of their presence in two rivers in northern Poland. Sci Total Environ 493:1006–1013. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.06.082
Tang Y, Guo H, Xiao L, Yu S, Gao N, Wang Y (2013) Synthesis of reduced graphene oxide/magnetite composites and investigation of their adsorption performance of fluoroquinolone antibiotics. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 424:74–80. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2013.02.030
Zhou Q, Zhu L, Xia X, Tang H (2016) The water – resistant zeolite imidazolate framework 67 is a viable solid phase sorbent for fluoroquinolones while efficiently excluding macromolecules. Microchim Acta 183(6):1839–1846. doi:10.1007/s00604-016-1814-7
Wu X, Huang M, Zhou T, Mao J (2016) Recognizing removal of norfloxacin by novel magnetic molecular imprinted chitosan/γ-Fe2O3 composites: Selective adsorption mechanisms, practical application and regeneration. Sep Purif Technol 165:92–100. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.20 16.03.04
Andrea S, Michela S, Federica M, Elettra M, Dhanalakshmi V, Daniele D, Antonella P (2016) Preparation of silica-supported carbon by Kraft lignin pyrolysis, and its use in solid-phase extraction of fluoroquinolone from environmental waters. Microchim Acta 183:2241–2249. doi:10.1007/s00604-016-1859-7
Wang R, Yuan Y, Yang X, Han Y, Yan H (2015) Polymethacrylate microparticles covalently functionalized with an ionic liquid for solid-phase extraction of fluoroquinolone antibiotics. Microchim Acta 182:2201–2208. doi:10.1007/s00604-015-1544-2
Parirokh L, Noor M, Mohammad R, Khalil A, Seyed M (2017) Colorimetric aptamer based assay for the determination of fluoroquinolones by triggering the reduction-catalyzing activity of gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 184:2039–2045. doi:10.1007/s00604-017-2213-4
Acknowledgements
This project was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (NSFC51672116), Science and technology foundation of ocean and fisheries of Liaoning province (201408, 201406), General project of scientific research of the education department of Liaoning province (L2015206), Liaoning scientific instruments service sharing information platform ability construction funds (201507A003), Liaoning provincial department of education innovation team projects (LT2015012) and the foundation of 211 project for innovative talent training, Liaoning university. The authors also thank their colleagues and other students who participated in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 730 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Wang, Y., Zhang, Z. et al. Waxberry-like magnetic porous carbon composites prepared from a nickel-organic framework for solid-phase extraction of fluoroquinolones. Microchim Acta 184, 4107–4115 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2438-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2438-2