Abstract
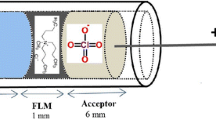
This study presents a method for the selective determination of Hg(II) using electromembrane extraction (EME), followed by square wave anodic stripping voltammetry (SWASV), using a gold nanoparticle-modified glassy carbon electrode, (AuNP/GCE). By applying an electrical potential of typically 60 V for 12 min through a thin supported liquid membrane (1-octanol), Hg(II) ions are extracted from a donor phase (i.e., the sample solution) to an acidic acceptor solution (15 μL) placed in the lumen of a hollow fiber. The influences of experimental parameters during EME were optimized using face-centered central composite design. The calibration plot, established at a working voltage of 0.55 V (vs. Ag/AgCl), extends from 0.2 to 10 μg.L−1 of Hg(II). The limit of detection, at a signal to noise ratio of 3, is 0.01 μg.L−1 and the relative standard deviations (for 5 replicate determinations at 3 concentration levels) are between 7.5 and 8.7 %. The method was successfully applied to the determination of Hg(II) in spiked real water samples to give recoveries ranging from 89 to 97 %. The results were validated by cold vapor atomic absorption spectroscopy.

Hg(II) ions were extracted from a donor phase into an acidic acceptor phase (15 μL) placed in the lumen of a hollow fiber using electromembrane extraction. The acceptor phase was then analyzed using anodic stripping voltammetry.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rofouei MK, Sabouri A, Ahmadalinezhad A, Ferdowsi H (2011) Solid phase extraction of ultra traces mercury (II) using octadecyl silica membrane disks modified by 1, 3-bis (2-ethoxyphenyl) triazene (EPT) ligand and determination by cold vapor atomic absorption spectrometry. J Hazard Mater 192(3):1358–1363
Allibone J, Fatemian E, Walker PJ (1999) Determination of mercury in potable water by ICP-MS using gold as a stabilising agent. J Anal At Spectrom 14(2):235–239
Abu-Shawish HM (2009) A mercury (II) selective sensor based on N, N′-bis (salicylaldehyde)-phenylenediamine as neutral carrier for potentiometric analysis in water samples. J Hazard Mater 167(1):602–608
Jagner D, Josefson M, Årén K (1982) Flow potentiometric stripping analysis for mercury (II). Anal Chim Acta 141:147–156
Wen J, Cassidy RM (1996) Anodic and cathodic pulse amperometric detection of metal ions separated by capillary electrophoresis. Anal Chem 68(6):1047–1053
Sipos L, Nürnberg H, Valenta P, Branica M (1980) The reliable determination of mercury traces in sea water by subtractive differential pulse voltammetry at the twin gold electrode. Anal Chim Acta 115:25–42
Meyer S, Scholz F, Trittler R (1996) Determination of inorganic ionic mercury down to 5× 10–14 mol l − 1 by differential-pulse anodic stripping voltammetry. Fresenius J Anal Chem 356(3–4):247–252
Salaün P, van den Berg CM (2006) Voltammetric detection of mercury and copper in seawater using a gold microwire electrode. Anal Chem 78(14):5052–5060
Razmi H, Musevi SJ, Mohammad-Rezaei R (2015) Solid phase extraction of mercury (II) using soluble eggshell membrane protein doped with reduced graphene oxide, and its quantitation by anodic stripping voltammetry. Microchimica Acta:1–8
Zhou N, Chen H, Li J, Chen L (2013) Highly sensitive and selective voltammetric detection of mercury (II) using an ITO electrode modified with 5-methyl-2-thiouracil, graphene oxide and gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 180(5–6):493–499
Pinilla J, Hernandez L, Conesa A (1996) Determination of mercury by open circuit adsorption stripping voltammetry on a platinum disk electrode. Anal Chim Acta 319(1):25–30
Bonfil Y, Brand M, Kirowa-Eisner E (2000) Trace determination of mercury by anodic stripping voltammetry at the rotating gold electrode. Anal Chim Acta 424(1):65–76
Viltchinskaia E, Zeigman L, Garcia D, Santos P (1997) Simultaneous determination of mercury and arsenic by anodic stripping voltammetry. Electroanalysis 9(8):633–640
Daniele S, Bragato C, Baldo MA, Wang J, Lu J (2000) The use of a remote stripping sensor for the determination of copper and mercury in the lagoon of Venice. Analyst 125(4):731–735
Garnier C, Lesven L, Billon G, Magnier A, Mikkelsen Ø, Pižeta I (2006) Voltammetric procedure for trace metal analysis in polluted natural waters using homemade bare gold-disk microelectrodes. Anal Bioanal Chem 386(2):313–323
Ordeig O, Banks CE, del Campo J, Muñoz FX, Compton RG (2006) Trace detection of mercury (II) using gold ultra-microelectrode arrays. Electroanalysis 18(6):573–578
Gao X, Wei W, Yang L, Yin T, Wang Y (2005) Simultaneous determination of lead, copper, and mercury free from macromolecule contaminants by square wave stripping voltammetry. Anal Lett 38(14):2327–2343
Kjelsen IJØ, Gjelstad A, Rasmussen KE, Pedersen-Bjergaard S (2008) Low-voltage electromembrane extraction of basic drugs from biological samples. J Chromatogr A 1180(1):1–9
Gjelstad A, Rasmussen KE, Pedersen-Bjergaard S (2009) Electromembrane extraction of basic drugs from untreated human plasma and whole blood under physiological pH conditions. Anal Bioanal Chem 393(3):921–928
Kiplagat IK, Doan TKO, Kubáň P, Boček P (2011) Trace determination of perchlorate using electromembrane extraction and capillary electrophoresis with capacitively coupled contactless conductivity detection. Electrophoresis 32(21):3008–3015
Basheer C, Tan SH, Lee HK (2008) Extraction of lead ions by electromembrane isolation. J Chromatogr A 1213(1):14–18
Kubáň P, Strieglerová L, Gebauer P, Boček P (2011) Electromembrane extraction of heavy metal cations followed by capillary electrophoresis with capacitively coupled contactless conductivity detection. Electrophoresis 32(9):1025–1032
Safari M, Nojavan S, Davarani SSH, Morteza-Najarian A (2013) Speciation of chromium in environmental samples by dual electromembrane extraction system followed by high performance liquid chromatography. Anal Chim Acta 789:58–64
Gao F, El-Deab MS, Okajima T, Ohsaka T (2005) Electrochemical preparation of a Au crystal with peculiar morphology and unique growth orientation and its catalysis for oxygen reduction. J Electrochem Soc 152(6):A1226–A1232
El-Deab MS, Sotomura T, Ohsaka T (2005) Size and crystallographic orientation controls of gold nanoparticles electrodeposited on GC electrodes. J Electrochem Soc 152(1):C1–C6
Hezard T, Fajerwerg K, Evrard D, Collière V, Behra P, Gros P (2012) Influence of the gold nanoparticles electrodeposition method on Hg (II) trace electrochemical detection. Electrochim Acta 73:15–22
Basheer C, Lee J, Pedersen-Bjergaard S, Rasmussen KE, Lee HK (2010) Simultaneous extraction of acidic and basic drugs at neutral sample pH: a novel electro-mediated microextraction approach. J Chromatogr A 1217(43):6661–6667
Balchen M, Gjelstad A, Rasmussen KE, Pedersen-Bjergaard S (2007) Electrokinetic migration of acidic drugs across a supported liquid membrane. J Chromatogr A 1152(1):220–225
Seidi S, Yamini Y, Rezazadeh M, Esrafili A (2012) Low-voltage electrically-enhanced microextraction as a novel technique for simultaneous extraction of acidic and basic drugs from biological fluids. J Chromatogr A 1243:6–13
Guideline IHT (2005) Validation of analytical procedures: text and methodology. Q2 (R1) 1
Hezard T, Fajerwerg K, Evrard D, Collière V, Behra P, Gros P (2012) Gold nanoparticles electrodeposited on glassy carbon using cyclic voltammetry: application to Hg (II) trace analysis. J Electroanal Chem 664:46–52
Lin Y, Peng Y, Di J (2015) Electrochemical detection of Hg (II) ions based on nanoporous gold nanoparticles modified indium tin oxide electrode. Sensors Actuators B Chem 220:1086–1090
Alves GM, Magalhães JM, Salaün P, Van den Berg CM, Soares HM (2011) Simultaneous electrochemical determination of arsenic, copper, lead and mercury in unpolluted fresh waters using a vibrating gold microwire electrode. Anal Chim Acta 703(1):1–7
Jovanovski V, Hrastnik N, Hočevar S (2015) Copper film electrode for anodic stripping voltammetric determination of trace mercury and lead. Electrochem Commun 57:1–4
Perone S, Kretlow WJ (1965) Anodic stripping voltammetry of mercury (II) at the graphite electrode. Anal Chem 37(8):968–970
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to express their gratitude to the University of Zanjan Research Council for support of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(DOCX 514 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamyabi, M.A., Aghaei, A. Electromembrane extraction and anodic stripping voltammetric determination of mercury(II) using a glassy carbon electrode modified with gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 183, 2411–2419 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1884-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1884-6