Abstract
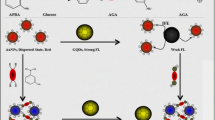
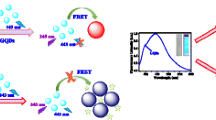
We report on a nanoparticle-based fluorescent sensing scheme for urea. It is based on the finding that graphene quantum dots (GQDs) display pH-sensitive green fluorescence if photoexcited at 460 nm. Fluorescence is gradually quenched due to an increase in the local pH value as a result of the hydrolysis of urea as catalyzed by urease. The effect was used to quantify urea in the 0.1–100 mM concentration range, with a limit of detection of 0.01 mM. The method was successfully applied to the determination of urea in human serum samples. The method is simple, effective, and therefore holds promise as a platform for sensing urea in blood.

The pH-sensitive fluorescence of graphene quantum dots was used in a detection scheme for urea that exploits the increase in pH as a result of urease-catalyzed hydrolysis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Prats-Alfonso E, Abad L, Casañ-Pastor N, Gonzalo-Ruiz J, Baldrich E (2013) Iridium oxide pH sensor for biomedical applications. Case urea-urease in real urine samples. Biosens Bioelectron 39:163–169
Ali SMU, Ibupotoa ZH, Salmanb S, Nura O, Willandera M, Danielsson B (2011) Selective determination of urea using urease immobilized on ZnO nanowires. Sensor Actuators B Chem 160:637–643
Soldatkin OO, Kucherenko IS, Marchenko SV, Ozansoy Kasap B, Akata B, Soldatkin AP, Dzyadevych SV (2014) Application of enzyme/zeolite sensor for urea analysis in serum. Mater Sci Eng C 42:155–160
Kuralay F, Özyörük H, Yıldız A (2006) Amperometric enzyme electrode for urea determination using immobilized urease in poly(vinylferrocenium) film. Sensors Actuators B 114:500–506
Miyauchi T, Miyachi Y, Takahashi M, Ishikawa N, Mori H (2010) Determination of urea in serum based on the combination of an enzymatic reaction with immobilized urease and Ion chromatographic analysis. ANAL SCI 26:847–851
Srivastava RK, Srivastava S, Narayanan TN, Mahlotra BD, Vajtai R, Ajayan PM, Srivastava A (2012) Functionalized multilayered graphene platform for urea sensor. ASC NANO 6:168–175
Siqueira JR Jr, Molinnus D, Beging S, Schöning MJ (2014) Incorporating a hybrid urease-carbon nanotubes sensitive nanofilm on capacitive field-effect sensors for urea detection. Anal Chem 86:5370–5375
Rajesh PN, Mishra SK, Laskar MJ, Srivastava AK (2014) Microstructural and potential dependence studies of urease-immobilized gold nanoparticles-polypyrrole composite film for urea detection. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 172:1055–1069
Ali A, Ansari AA, Kaushik A, Solanki PR, Barik A, Pandey MK, Malhotra BD (2009) Nanostructured zinc oxide film for urea sensor. Mat Lett 63:2473–2475
Shi H, Chen X, Li L, Tan L, Ren X, Rena J, Meng X (2014) One-pot and one-step synthesis of bioactive urease/ZnFe2O4 nanocomposites and their application in detection of urea. Dalton Trans 43:9016–9021
Srivastava S, Solanki PR, Kaushik A, Ali MA, Srivastavab A, Malhotra BD (2011) A self assembled monolayer based microfluidic sensor for urea detection. Nanoscale 3:2971–2977
Shalini J, Sankaran KJ, Lee CY, Tai NH, Lin IN (2014) An amperometric urea bisosensor based on covalent immobilization of urease on N2 in corporated diamond nanowire electrode. Biosens Bioelectron 56:64–70
Saiapina OY, Pyeshkova VM, Soldatkin OO, Melnik VG, Kur BA, Walcarius A, Dzyadevych SV, Jaffrezic-Renault N (2011) Conductometric enzyme biosensors based on natural zeolite clinoptilolite for urea determination. Mater Sci Eng C 31:1490–1497
Ruedas-Rama MJ, Hall EAH (2010) Analytical nanosphere sensors using quantum dot-enzyme conjugates for urea and creatinine. Anal Chem 82:9043–9049
Nikoleli GP, Nikolelis DP, Methenitis C (2010) Construction of a simple optical sensor based on air stable lipid film with incorporated urease for the rapid detection of urea in milk. Anal Chim Acta 675:58–63
Pandey PC, Singh G (2001) Tetraphenylborate doped polyaniline based novel pH sensor and solid-state urea biosensor. Talanta 55:773–782
Marchenko SV, Kucherenko IS, Hereshko AN, Panasiuk IV, Soldatkin OO, El’skaya AV, Soldatkin AP (2015) Application of potentiometric biosensor based on recombinant urease for urea determination in blood serum and hemodialyzate. Sensors Actuators B 207:981–986
Tiwari A, Aryal S, Pilla S, Gong S (2009) An amperometric urea biosensor based on covalently immobilized urease on an electrode made of hyperbranched polyester functionalized gold nanoparticles. Talanta 78:1401–1407
Rajesh, Bisht V, Takashima W, Kaneto K (2005) An amperometric urea biosensor based on covalent immobilization of urease onto an electrochemically prepared copolymer poly (N-3-aminopropyl pyrrole-co-pyrrole) film. Biomaterials 26:3683–3690
Suye S, Miura J, Ohue M (1999) A fluorometric determination of urea with urease. Anal Lett 32:1543–1551
Huang CP, Li YK, Chen TM (2007) A highly sensitive system for urea detection by using CdSe/ZnS core-shell quantum dots. Biosens Bioelectron 22:1835–1838
Li LL, Ji J, Fei R, Wang CZ, Lu Q, Zhang JR, Jiang LP, Zhu JJ (2012) A facile microwave avenue to electrochemiluminescent two-color graphene quantum dots. Adv Funct Mater 22:2971–2979
Li LL, Wu GH, Yang GH, Peng J, Zhao JW, Zhu JJ (2013) Focusing on luminescent graphene quantum dots: current status and future perspectives. Nanoscale 5:4015–4039
Peng J, Gao W, Gupta BK, Liu Z, Romero-Aburto R, Ge LH, Song L, Alemany LB, Zhan XB, Gao GH, Vithayathil SA, Kaipparettu BA, Marti AA, Hayashi T, Zhu JJ, Ajayan PM (2012) Graphene quantum dots derived from carbon fibers. Nano Lett 12:844–849
Lu Z, Chen X, Wang Y, Zheng X, Li CM (2015) Aptamer based fluorescence recovery assay for aflatoxin B1 using a quencher system composed of quantum dots and graphene oxide. Microchim Acta 182:571–578
Li L, Li L, Wang C, Liu K, Zhu R, Qiang H, Lin Y (2015) Synthesis of nitrogen-doped and amino acid-functionalized graphene quantum dots from glycine, and their application to the fluorometric determination of ferric ion. Microchim Acta 182:763–770
Duan N, Wu S, Dai S, Miao T, Chen J, Wang Z (2014) Simultaneous detection of pathogenic bacteria using an aptamer based biosensor and dual fluorescence resonance energy transfer from quantum dots to carbon nanoparticles. DOI 10.1007/s00604-014-1406-3
Shen PF, Xia YS (2014) Synthesis-modification integration: one-step fabrication of boronic acid functionalized carbon dots for fluorescent blood sugar sensing. Anal Chem 86:5323–5329
Shao TL, Wang GD, An XT, Zhuo SJ, Xia YS, Zhu CQ (2014) A reformative oxidation strategy using high concentration nitric acid for enhancing the emission performance of graphene quantum dots. RSC Adv 4:47977–47981
Koncki R, Mohr GJ, Wolfbeis OS (1995) Enzyme biosensor for urea based on a novel pH bulk optode membrane. Biosens Bioelectron 10(8):653–659
Dong YQ, Lin JP, Chen YM, Fu FF, Chi YW, Chen GN (2014) Graphene quantum dots, graphene oxide, carbon quantum dots and graphite nanocrystals in coals. Nanoscale 6:7410–7415
Ye RQ, Xiang CS, Lin J, Peng ZW, Huang KW, Yan Z, Cook NP, Samuel ELG, Hwang CC, Ruan GD, Ceriotti G, Raji AO, Martí AA, Tour JM (2013) Coal as an abundant source of graphene quantum dots. Nat Commun 4:2943–2948
Shen JH, Zhu YH, Yang XL, Li CZ (2012) Graphene quantum dots: emergent nanolights for bioimaging, sensors, catalysis and photovoltaic devices. Chem Commun 48:3686–3699
Baker SN, Baker GA (2010) Luminescent carbon nanodots: emergent nanolights. Angew Chem Int Ed 49:6726–6744
Li HT, Kang ZH, Liu Y, Lee ST (2012) Carbon nanodots: synthesis, properties and applications. J Mater Chem 22:24230–24253
Bourlinos AB, Stassinopoulos A, Anglos D, Zboril R, Karakassides M, Giannelis EP (2008) Surface functionalized carbogenic quantum dots. Small 4:455–458
Liu S, Tian JQ, Wang L, Luo YL, Zhai JF, Sun XP (2011) Preparation of photoluminescent carbon nitride dots from CCl4 and 1, 2-ethylenediamine: a heat-treatment-based strategy. J Mater Chem 21(32):11726–11729
Pan D, Zhang J, Li Z, Wu M (2010) Hydrothermal route for cutting graphene sheets into blue-luminescent graphene quantum dots. Adv Mater 22:734–738
Shen J, Zhu Y, Chen C, Yang X, Li C (2011) Facile preparation and upconversion luminescence of graphene quantum dots. Chem Commun 47:2580–2582
Kochmann S, Hirsch T, Wolfbeis OS (2012) The pH dependence of the total fluorescence of graphite oxide. J Fluoresc 22:849–855
Tian DH, Qian ZS, Xia YS, Zhu CQ (2012) Gold nanocluster-based fluorescent probes for near-infrared and turn-on sensing of glutathione in living cells. Langmuir 28:3945–3951
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 21375003, 21175003, C. Z.; 21303003, S. Z.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 329 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shao, T., Zhang, P., Tang, L. et al. Highly sensitive enzymatic determination of urea based on the pH-dependence of the fluorescence of graphene quantum dots. Microchim Acta 182, 1431–1437 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1469-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1469-9