Abstract
The presence of joints and other types of discontinuities has a significant effect on the mechanical behavior of rock, thereby fundamentally influencing the stability of rock excavations. The main challenge associated with the experimental research on jointed rock lies in the difficulty of sample preparation to represent the influence of discontinuities on the mechanical behavior of the rock material. In this study, 3D printing is used as a tool to examine the mechanical behavior of rock with discontinuities. Synthetic specimens are prepared from sand powder and tested in the laboratory to examine the validity of sand powder for simulating soft rock. Further 3D printed specimens with different joint geometries (dip angle, aperture, and trace length) are tested, and the effects of joint parameters on the specimens’ mechanical behaviors and failure patterns are investigated and quantitatively analyzed with a relative importance analysis. As expected, the results show that the dip angle has the strongest effect on the uniaxial compressive strength and failure patterns, and the dominant failure mechanism tends to switch from tensile to shear failure with increasing dip angle. The influence of aperture and trace length on the mechanical behavior is also determined and linked to the dip angle. The test results are validated and further analyzed with numerical simulation and analytical methods. The results of this study demonstrate the applicability of sand powder 3D printing as a suitable method for the simulation of soft rock mechanical behavior. The methodology presented in this study could be further extended to other applications in rock mechanics.
Highlights
-
Synthetic specimens are prepared from sand powder and tested in the laboratory to examine the validity of sand powder for simulating soft rock.
-
The effects of joint parameters on the specimens’ mechanical behaviors and failure patterns are investigated and quantitatively analyzed with a relative importance analysis.
-
The dip angle has the strongest effect on the uniaxial compressive strength and failure patterns, and the dominant failure mechanism tends to switch from tensile to shear failure with increasing dip angle.
-
The influence of aperture and trace length on the mechanical behavior is also determined and linked to the dip angle.






















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Ajamzadeh MR, Sarfarazi V, Haeri H, Dehghani H (2018) The effect of micro parameters of PFC software on the model calibration. Smart Struct Syst 22(6):643–662
Aliabadian Z, Sharafisafa M, Tahmasebinia F, Shen LM (2021) Experimental and numerical investigations on crack development in 3D printed rock-like specimens with pre-existing flaws. Eng Fract Mech 241:107396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2020.107396
Aliha MRM, Ayatollahi MR, Smith DJ, Pavier MJ (2010) Geometry and size effects on fracture trajectory in a limestone rock under mixed mode loading. Eng Fract Mech 77(11):2200–2212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2010.03.009
Ardila N, Zambrano-Narvaez G, Chalaturnyk RJ (2019) Wettability measurements on 3d printed sandstone analogues and its implications for fluid transport phenomena. Transp Porous Med 129(2):521–539. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-018-1176-1
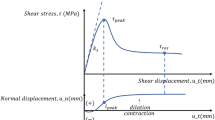
Ban LR, Du WS, Jin TW, Qi CZ, Li XZ (2021) A roughness parameter considering joint material properties and peak shear strength model for rock joints. Int J Min Sci Technol 31(3):413–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2021.03.007
Bobet A, Einstein HH (1998) Fracture coalescence in rock-type materials under uniaxial and biaxial compression. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 35(7):863–888. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0148-9062(98)00005-9
Bourke M, Viles H, Nicoli J, Lyew-Ayee P, Ghent R, Holmlund J (2008) Innovative applications of laser scanning and rapid prototype printing to rock breakdown experiments. Earth Surf Process Landforms 33(10):1614–1621. https://doi.org/10.1002/esp.1631
Cacciari PP, Futai MM (2022) A practical method for estimating the volumetric intensity of non-persistent discontinuities on rock exposures. Rock Mech Rock Eng 55(10):6063–6078. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-022-02966-w
Cao RH, Cao P, Lin H, Pu CZ, Ou K (2016) Mechanical behavior of brittle rock-like specimens with pre-existing fissures under uniaxial loading: experimental studies and particle mechanics approach. Rock Mech Rock Eng 49(3):763–783. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-015-0779-x
Carpinteri A, Lacidogna G, Niccolini G (2006) Critical behaviour in concrete structures and damage localization by acoustic emission. Key Eng Mater 312(2006):305–310. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.312.305
Chen Y, Xu J, Peng S, Jiao F, Chen C, Xiao Z (2021) Experimental study on the acoustic emission and fracture propagation characteristics of sandstone with variable angle joints. Eng Geol 292:106247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2021.106247
China Academy of Building Research (2015) Code for design of concrete structures (GB50010-2010). China Building Industry Press, Beijing
Cong Y, Kong L, Zheng YR, Erdi A, Wang ZQ (2015) Experimental study on shear strength of concrete. Concr China 5:40–45
Du K, Sun Y, Yang S, Lv S, Wang S (2021) Differences of mechanical parameters and rockburst tendency indices between coal and non-coal rocks and modified rockburst tendency classification criteria for non-coal rocks. Appl Sci 11(6):2641. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11062641
Dyskin AV, Sahouryeh E, Jewell RJ, Joer H, Ustinov KB (2003) Influence of shape and locations of initial 3-D cracks on their growth in uniaxial compression. Eng Fract Mech 70(15):2115–2136. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-7944(02)00240-0
Fan WC, Yang H, Jiang XL, Cao P (2021) Experimental and numerical investigation on crack mechanism of folded flawed rock-like material under uniaxial compression. Engineering Geology 291(4),106210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2021.106210
Fedrizzi RM, de Ceia MAR, Missagia RM, Santos VH, Neto IL (2018) Artificial carbonate rocks: synthesis and petrophysical characterization. J Petrol Sci Eng 163:303–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2017.12.089
Fereshtenejad S, Song JJ (2016) Fundamental study on applicability of powder-based 3D printer for physical modeling in rock mechanics. Rock Mech Rock Eng 49(6):2065–2074. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-015-0904-x
Fereshtenejad S, Song JJ (2021) Applicability of powder-based 3D printing technology in shear behavior analysis of rock mass containing non-persistent joints. J Struct Geol 143:104251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsg.2020.104251
Fields GS (2003) Accounting for income inequality and its change: A new method, with application to the distribution of earnings in the United States. Worker well-being and public policy. Bingley, Emerald Group Publishing Limited, pp 1–38
Gell EM, Walley SM, Braithwaite CH (2019) Review of the validity of the use of artificial specimens for characterizing the mechanical properties of rocks. Rock Mech Rock Eng 59(36):2949–2961. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-01787-8
Gomez JS, Chalaturnyk RJ, Zambrano-Narvaez G (2019) Experimental investigation of the mechanical behavior and permeability of 3D printed sandstone analogues under triaxial conditions. Transp Porous Media 129(2):541–557. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-018-1177-0
Haeri H, Khaloo A, Marji MF (2015) Experimental and numerical analysis of Brazilian discs with multiple parallel cracks. Arab J Geosci 8(8):5897–5908. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1598-1
Kong X, Wang E, He X, Li Z, Li D, Liu Q (2017) Multifractal characteristics and acoustic emission of coal with joints under uniaxial loading. Fractals 25(05):1750045. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218348X17500451
Konietzky H, Heftenberger A, Feige M (2009) Life-time prediction for rocks under static compressive and tensile loads: a new simulation approach. Acta Geotech 4(2009):73–78. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-009-0085-4
Krasikova D, LeBreton JM, Tonidandel S (2011) Estimating the relative importance of variables in multiple regression models. International review of industrial and organizational psychology. Wiley, Indianapolis, pp 119–141
Lee CS, Kim SG, Kim HJ, Ahn SH (2007) Measurement of anisotropic compressive strength of rapid prototyping parts. J Mater Process Technol 187:627–630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2006.11.095
Li DY, Han ZY, Sun XL, Zhou T, Li XB (2019) Dynamic mechanical properties and fracturing behavior of marble specimens containing single and double flaws in SHPB tests. Rock Mech Rock Eng 52(6):1623–1643. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-018-1652-5
Liu JJ, Yang M, Wang D, Zhang JH (2018) Different bedding loaded coal mechanics properties and acoustic emission. Environ Earth Sci 77(8):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7504-5
Liu S, Li X, Li Z, Chen P, Yang X, Liu Y (2019) Energy distribution and fractal characterization of acoustic emission during coal deformation and fracturing. Measurement 136:122–131
Lockner DA, Madden TR (1991) A multiple-crack model of brittle fracture: 1. Non-time-dependent simulations. J Geophys Res 96(B12):19623–19642. https://doi.org/10.1029/91JB01642
Lotidis MA, Nomikos PP, Sofianos AI (2019) Numerical study of the fracturing process in marble and plaster hollow plate specimens subjected to uniaxial compression. Rock Mech Rock Eng 52:4361–4386. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-01884-8
Ma SW, Han L, Chen C (2021) Laboratory study of deformational characteristics and acoustic emission properties of coal with different strengths under uniaxial compression. Minerals 11(10):1070. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11101070
Patel S, Martin CD (2020) Impact of the initial crack volume on the intact behavior of a bonded particle model. Comput Geotech 127:103764. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2020.103764
Perera M, Sampath K (2020) Modelling of free and adsorbed CO2-induced mechanical property alterations in coal. Int J Coal Geol 217:103348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2019.103348
Perras MA, Daniel V (2019) Compressive and tensile behavior of 3D-printed and natural sandstones. Transp Porous Media 129(2):559–581. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-018-1153-8
Potyondy DO, Cundall PA (2004) A bonded-particle model for rock. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 41(8):1329–1364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2004.09.011
Potyondy DO (2012) A flat-jointed bonded-particle material for hard rock. In: Proceedings of the 46th US rock mechanics/geomechanics symposium. OnePetro, Chicago ARMA-2012–501
Poulsen BA, Adhikary DP (2013) A numerical study of the scale effect in coal strength. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 63:62–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2013.06.006
Primkulov B, Chalaturnyk J, Chalaturnyk R, Zambrano NG (2017) 3D printed sandstone strength: curing of furfuryl alcohol resin-based sandstones. 3D Print Addit Manuf 4(3):149–156. https://doi.org/10.1089/3dp.2017.0032
Rankin TM, Giovinco NA, Cucher DJ, Watts G, Hurwitz B, Armstrong DG (2014) Three-dimensional printing surgical instruments: are we there yet? J Surg Res 189(2):193–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2014.02.020
Ríos-Bayona F, Johansson F, Mas-Ivars D (2021) Prediction of peak shear strength of natural, unfilled rock joints accounting for matedness based on measured aperture. Rock Mech Rock Eng 54(3):1533–1550. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-020-02340-8
Sagong M, Bobet A (2002) Coalescence of multiple flaws in a rock-model material in uniaxial compression. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 39(2):229–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1365-1609(02)00027-8
Sainoki A, Mitri HS, Chinnasane D, Schwartzkopff AK (2019) Quantitative energy-based evaluation of the intensity of mining-induced seismic activity in a fractured rock mass. Rock Mech Rock Eng 52(11):4651–4667. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-01861-1
Sanei M, Faramarzi L, Fahimifar A, Goli S, Rahmati A (2015) Shear strength of discontinuities in sedimentary rock masses based on direct shear tests. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 75(2015):119–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2014.11.009
Sarfarazi V, Haeri H (2016) A review of experimental and numerical investigations about crack propagation. Comput Concr 18(2):235–266. https://doi.org/10.12989/cac.2016.18.2.235
Sharafisafa M, Shen LM, Xu QF (2018) Characterisation of mechanical behaviour of 3D printed rock-like material with digital image correlation. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 112:122–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2018.10.012
Sharafisafa M, Aliabadian Z, Tahmasebinia F, Shen LM (2021) A comparative study on the crack development in rock-like specimens containing unfilled and filled flaws. Eng Fract Mech 241:107405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2020.107405
Shen B, Stephansson O, Einstein HH, Ghahreman B (1995) Coalescence of fractures under shear stresses in experiments. J Geophys Res 100(B4):5975–5990. https://doi.org/10.1029/95JB00040
Shorrocks AF (2013) Decomposition procedures for distributional analysis: a unified framework based on the Shapley value. J Econ Inequal 11(1):99–126. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10888-011-9214-z
Sondergeld CH, Estey LH (1981) Acoustic emission study of microfracturing during the cyclic loading of Westerly granite. J Geophys Res 86(B4):2915–2924. https://doi.org/10.1029/JB086iB04p02915
Song SL, Liu XS, Tan YL, Fan DY, Ma Q, Wang HL (2020) Study on failure modes and energy evolution of coal-rock combination under cyclic loading. Shock Vib 2020:5731721. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/5731721
Squelch A (2018) 3D printing rocks for geo-educational, technical, and hobbyist pursuits. Geosphere 14(1):360–366. https://doi.org/10.1130/GES01364.1
StataCorp L (2019) Stata glossary and index. Stata press, Texas
Suzuki A, Watanabe N, Li K, Horne RN (2017) Fracture network created by 3-D printer and its validation using CT images. Water Resour Res 53(7):6330–6339. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017WR021032
Tahmasebinia F, Zhang CG, Canbulat I, Vardar O, Saydam S (2018) Computing the damage and fracture energy in a coal mass based on joint density. Int J Min Sci Technol 28(5):813–817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2018.08.013
Tian W, Han NV (2017) Mechanical properties of rock specimens containing pre-existing flaws with 3 D printed materials. Strain 53(6):e12240. https://doi.org/10.1111/str.12240
Tonidandel S, LeBreton JM (2011) Relative importance analysis: a useful supplement to regression analysis. J Bus Psychol 26(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10869-010-9204-3
Tymrak BM, Kreiger M, Pearce JM (2014) Mechanical properties of components fabricated with open-source 3-D printers under realistic environmental conditions. Mater Des 58:242–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2014.02.038
Vallejos JA, Salinas JM, Delonca A, MasIvars D (2017) Calibration and verification of two bonded-particle models for simulation of intact rock behavior. Int J Geomech 17(4):06016030. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GM.1943-5622.0000773
Vaziri MR, Tavakoli H, Bahaaddini M (2022) 2D numerical study of the mechanical behaviour of non-persistent jointed rock masses under uniaxial and biaxial compression tests. Geomech Eng 28(2):117–133. https://doi.org/10.12989/gae.2022.28.2.117
Vogler D, Walsh SDC, Dombrovski E (2017) A comparison of tensile failure in 3D-printed and natural sandstone. Eng Geol 226:221–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.06.011
Wang C, Song DZ, Zhang CL, Liu L, Zhou ZH, Huang XC (2019) Research on the classification model of coal’s bursting liability based on database with large samples. Arab J Geosci 12(13):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-4562-2
Wang HY, Wang GD, Zhang GJ, Du F, Ma J (2020) Acoustic emission response characteristics of anthracitic coal under uniaxial compression. Shock Vib 2020:8874164. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8874164
Wang C, Li Y, Li Y, Xu J, Zhang C (2021a) Acoustic Emission and fractal precursory characteristics of coals with different bursting liabilities in loading failure process. Shock Vib 2021:9930407. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/9930407
Wang HW, Song JQ, Wang ZL, Zhang Y, Zhang SZ, Jiang YD (2021b) Numerical investigation of relationship between bursting proneness and mechanical parameters of coal. Shock Vib 2021:9928168. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/9928168
Wong LNY, Einstein HH (2006) Fracturing behavior of prismatic specimens containing single flaws. In: Proceedings of the 41st US symposium rock mechanics. OnePetro, Golden rocks pp 06–899.
Wong LNY, Einstein HH (2009) Systematic evaluation of cracking behavior in specimens containing single flaws under uniaxial compression. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 46(2):239–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2008.03.006
Xu YH, Cai M (2017) Numerical study on the influence of cross-sectional shape on strength and deformation behaviors of rocks under uniaxial compression. Comput Geotech 84:129–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2016.11.017
Xu T, Ranjith PG, Wasantha PLP, Zhao J, Tang CA, Zhu WC (2013) Influence of the geometry of partially-spanning joints on mechanical properties of rock in uniaxial compression. Eng Geol 167:134–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2013.10.011
Yang H, Wen G, Hu Q, Li Y, Dai L (2018) Experimental investigation on influence factors of acoustic emission activity in coal failure process. Energies 11(6):1414. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11061414
Ye DZ, Ng YK, Lian YJ (2015) Culture and happiness. Soc Indic Res 123(2):519–547. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11205-014-0747-y
Yan Z, Dai F, Zhu JB, Xu Y (2021) Dynamic cracking behaviors and energy evolution of multi-flawed rocks under static pre-compression. Rock Mech Rock Eng 54(9):5117–5139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-021-02564-2
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52074166) and Shandong Province (ZR2021YQ38), and the Open Grant of State Key Laboratory of Mining Response and Disaster Prevention and Control in Deep Coal Mines (SKLMRDPC20KF02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Y., Jiang, L., Li, C. et al. Experimental Investigation into the Mechanical Behavior of Jointed Soft Rock Using Sand Powder 3D Printing. Rock Mech Rock Eng 56, 5383–5404 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-023-03346-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-023-03346-8