Abstract
Purpose
The treatment of irreducible or severely displaced metacarpal and phalangeal bone fractures is still much debated. The recent development of the bioabsorbable magnesium K-wire is thought to allow effective treatment upon insertion via intramedullary fixation by minimizing articular cartilage injuries without discomfort until pin removal and drawbacks, such as pin track infection and metal plate removal. Therefore, this study investigated and reported the effects of intramedullary fixation with the bioabsorbable magnesium K-wire in unstable metacarpal and phalangeal bone fractures.
Methods
This study included 19 patients admitted to our clinic for metacarpal or phalangeal bone fractures from May 2019 to July 2021. As a result, 20 cases were examined among these 19 patients.
Results
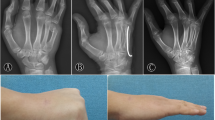
Bone union was observed in all 20 cases, with a mean bone union time of 10.5 (SD 3.4) weeks. Reduction loss was observed in six cases, all showing dorsal angulation with a mean angle of 6.6° (SD 3.5°) at 4.6 weeks as compared with that noted in the unaffected side. The gas cavity upon H2 gas formation was first observed approximately 2 weeks postoperatively. The mean DASH score was 33.5 for instrumental activity and 9.5 for work/task performance. No patient complained of notable discomfort after surgery.
Conclusion
Intramedullary fixation with the bioabsorbable magnesium K-wire may be used for unstable metacarpal and phalanx bone fractures. This wire is expected to be a particularly favorable indication for shaft fractures, although care should be taken due to the possibility of complications related to rigidity and deformity.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beck CM, Horesh E, Taub PJ (2019) Intramedullary screw fixation of metacarpal fractures results in excellent functional outcomes: a literature review. Plast Reconstr Surg 143:1111–1118. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000005478
Boulton CL, Salzler M, Mudgal CS (2010) Intramedullary cannulated headless screw fixation of a comminuted subcaptial metacarpal fracture: case report. J Hand Surg Am 35:1260–1263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhsa.2010.04.032
Bozic KJ, Perez LE, Wilson DR, Fitzgibbons PR, Jupiter JB (2001) Mechanical testing of bioresorbable implants for use in metacarpal fracture fixation. J Hand Surg Am 26:755–761. https://doi.org/10.1053/jhsu.2001.24145
Burns AE, Varin J (1998) Poly-l-lactic acid rod fixation results in foot surgery. J Foot Ankle Surg 37:37–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1067-2516(98)80009-4
Cha SM, Shin HD, Kim YK (2019) Comparison of low-profile locking plate fixation versus antegrade intermedullary nailing for unstable metacarpal shaft fractures—a prospective comparative study. Injury 50:2252–2258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2019.10.018
del Piñal F, Moraleda E, Rúas JS, de Piero GH, Cerezal L (2015) Minimally invasive fixation of fractures of the phalanges and metacarpals with intramedullary cannulated headless compression screws. J Hand Surg Am 40:692–700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhsa.2014.11.023
Friedrich JB, Vedder NB (2010) An evidence-based approach to metacarpal fractures. Plast Reconstr Surg 126:2205–2209. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181f830ad
Gudmundsen TE, Borgen L (2009) Fractures of the fifth metacarpal. Acta Radiol 50:296–300. https://doi.org/10.1080/02841850802709201
Huang C, Li J, Zhu J, Li P, Xie G, Gong Y (2004) A comparative study on two different absorbable intramedullary nails in treating metacarpal and phalanx fractures. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi 18:360–363
Hughes TB (2006) Bioabsorbable implants in the treatment of hand fractures: an update. Clin Orthop Relat Res 445:169–174. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.blo.0000205884.81328.cc
Kim Y-K, Kim S-G (2002) Treatment of mandible fractures using bioabsorbable plates. Plast Reconstr Surg 110:323. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-200207000-00006
Kuhlmann J, Bartsch I, Willbold E et al (2013) Fast escape of hydrogen from gas cavities around corroding magnesium implants. Acta Biomater 9:8714–8721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2012.10.008
Lazarus P, Hidalgo Diaz JJ, Xaxier F, Gouzou S, Facca S, Fiverneaux P (2020) Transverse and oblique fractures of the diaphysis of the fifth metacarpal : surgical outcomes for antegrade intramedullary pinning versus combined antegrade and retrograde intramedullary pinning. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 30:425–433. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-019-02587-0
Lee J-W, Han H-S, Han K-J et al (2016) Long-term clinical study and multiscale analysis of in vivo biodegradation mechanism of Mg alloy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113:716–721. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1518238113
Lee SG, Jupiter JB (2000) Phalangeal and metacarpal fractures of the hand. Hand Clin 16:323–332
Nakashian MN, Pointer L, Owens BD, Wolf JM (2012) Incidence of metacarpal fractures in the US population. HAND (NY) 7:426–430. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11552-012-9442-0
Peiji W, Qirong D, Jianzhong Q, Huayi W, Kailong Z, Nan Y (2012) Intramedullary fixation in digital replantation using bioabsorbable poly-dl-lactic acid rods. J Hand Surg Am 37:2547–2552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhsa.2012.09.022
Poinern GEJ, Brundavanam S, Fawcett D (2012) Biomedical magnesium alloys: a review of material properties, surface modifications and potential as a biodegradable orthopaedic implant. Am J Biomed Eng 2:218–240. https://doi.org/10.5923/j.ajbe.20120206.02
Stahl S, Schwartz O (2001) Complications of K-wire fixation of fractures and dislocations in the hand and wrist. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 121:527–530. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004020100279
Stern PJ (2000) Management of fractures of the hand over the last 25 years. J Hand Surg Am 25:817–823. https://doi.org/10.1053/jhsu.2000.4214
Urbanschitz L, Dreu M, Wagner J, Kaufmann R, Jeserschek JM, Borbas P (2020) Cartilage and extensor tendon defects after headless compression screw fixation of phalangeal and metacarpal fractures. J Hand Surg Eur 45:601–607. https://doi.org/10.1177/1753193420919060
Waizy H, Diekmann J, Weizbauer A et al (2014) In vivo study of a biodegradable orthopedic screw (MgYREZr-alloy) in a rabbit model for up to 12 months. J Biomater Appl 28:667–675. https://doi.org/10.1177/0885328212472215
Warrender WJ, Ruchelsman DE, Livesey MG, Mudgal CS, Rivlin M (2020) Low rate of complications following intramedullary headless compression screw fixation of metacarpal fractures. HAND (NY) 15:798–804. https://doi.org/10.1177/1558944719836214
Funding
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CHL conceptualized the study and its methodology. BJL prepared the study’s original draft, reviewed, and edited the manuscript. YHL contributed to the reviewing and editing of the manuscript, curated, and validated the data used for the study. SW also contributed to data curation, reviewing, and editing. All authors reviewed and edited the manuscript and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Ethical approval
Ethical approval to report these cases was obtained from the Institutional Review Board of Daejeon Sun Hospital (DSH-인-22–04). The study conforms to the Declaration of Helsinki.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient(s) for their anonymized information to be published in this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, BJ., Lee, CH., Lee, YH. et al. Intramedullary fixation of metacarpal and phalangeal bone fractures with bioabsorbable Mg K-wire in 20 cases. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 33, 2911–2920 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-023-03503-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-023-03503-3