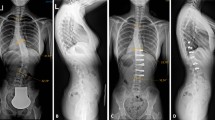
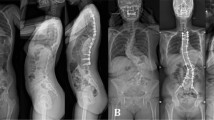
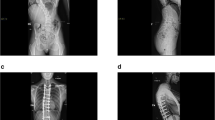
Abstract
Purpose
To assess the lumbar muscle conditions on the incidence of proximal junctional kyphosis (PJK) after long-level correction and instrumentation surgery for degenerative lumbar scoliosis (DLS) patients with a minimum 2-year follow-up.
Methods
Eighty-four DLS patients undergoing long instrumented fusion surgery (≥ 5 vertebrae) were retrospectively studied. According to the occurrence of PJK at the final follow-up, patients were divided into the PJK group and the Non-PJK group. Patient characteristics, surgical variables and radiographic parameters were analyzed statistically. The lumbar muscularity (cross-sectional area of muscle–disc ratio × 100) and fatty degeneration (signal intensity of muscle–subcutaneous fat ratio × 100) were evaluated on magnetic resonance imaging .
Results
The prevalence of PJK was 20.24%. Gender, age at surgery, body mass index, uppermost instrumented vertebrae level, fusions extending to the sacrum, and levels fused were not significantly different between the groups. Lower bone mineral density, smaller functional cross-sectional area (FCSA) of paraspinal extensor muscles (PSE), higher lean muscle–fat index and total muscle–fat index of PSE, greater preoperative thoracolumbar kyphosis (TLK), smaller preoperative sacral slope (SS), larger preoperative sagittal vertical axis were identified in PJK group. Logistic regression analysis showed that osteoporosis, preoperative TLK > 15°, SS > 24°, FCSA of PSE > 138.75, and total muscle–fat index of PSE > 4.08 were independently associated with PJK. The final follow-up VAS score for back pain was higher, and SRS-22 subcategories of pain, function, self-image, and total score were significantly lower in the PJK group.
Conclusion
Osteoporosis, lower lumbar muscularity and higher fatty degeneration, preoperative greater TLK and smaller SS were found to be strongly associated with the presence of PJK in DLS.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cheng T, Gerdhem P (2018) Outcome of surgery for degenerative lumbar scoliosis: an observational study using the Swedish spine register. Eur Spine J 27:622–629. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-017-5248-7
Hong JY, Suh SW, Modi HN, Hur CY, Song HR, Park JH (2010) The prevalence and radiological findings in 1347 elderly patients with scoliosis. J Bone Jt Surg Br 92:980–983. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620x.92b7.23331
Kebaish KM, Neubauer PR, Voros GD, Khoshnevisan MA, Skolasky RL (2011) Scoliosis in adults aged forty years and older: prevalence and relationship to age, race, and gender. Spine 36:731–736. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181e9f120
Perennou D, Marcelli C, Herisson C, Simon L (1994) Adult lumbar scoliosis. Epidemiologic aspects in a low-back pain population. Spine 19:123–128
Robin GC, Span Y, Steinberg R, Makin M, Menczel J (1982) Scoliosis in the elderly: a follow-up study. Spine 7:355–359
Schwab F, Dubey A, Pagala M, Gamez L, Farcy JP (2003) Adult scoliosis: a health assessment analysis by SF-36. Spine 28:602–606. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.brs.0000049924.94414.bb
Urrutia J, Diaz-Ledezma C, Espinosa J, Berven SH (2011) Lumbar scoliosis in postmenopausal women: prevalence and relationship with bone density, age, and body mass index. Spine 36:737–740. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181db7456
Xu L, Sun X, Huang S, Zhu Z, Qiao J, Zhu F, Mao S, Ding Y, Qiu Y (2013) Degenerative lumbar scoliosis in Chinese Han population: prevalence and relationship to age, gender, bone mineral density, and body mass index. Eur Spine J 22:1326–1331. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-013-2678-8
Faraj SS, Holewijn RM, van Hooff ML, de Kleuver M, Pellise F, Haanstra TM (2016) De novo degenerative lumbar scoliosis: a systematic review of prognostic factors for curve progression. Eur Spine J 25:2347–2358. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-016-4619-9
Ha KY, Jang WH, Kim YH, Park DC (2016) Clinical relevance of the SRS-Schwab classification for degenerative lumbar scoliosis. Spine 41:E282–288. https://doi.org/10.1097/brs.0000000000001229
Koerner JD, Reitman CA, Arnold PM, Rihn J (2015) Degenerative lumbar scoliosis. JBJS Rev 3:1–10. https://doi.org/10.2106/jbjs.rvw.n.00061
Cho KJ, Kim YT, Shin SH, Suk SI (2014) Surgical treatment of adult degenerative scoliosis. Asian Spine J 8:371–381. https://doi.org/10.4184/asj.2014.8.3.371
Buell TJ, Chen CJ, Quinn JC, Buchholz AL, Mazur MD, Mullin JP, Nguyen JH, Taylor DG, Bess S, Line BG, Ames CP, Schwab FJ, Lafage V, Shaffrey CI, Smith JS (2018) Alignment risk factors for proximal junctional kyphosis and the effect of lower thoracic junctional tethers for adult spinal deformity. World Neurosurg. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2018.08.242
Kim DK, Kim JY, Kim DY, Rhim SC, Yoon SH (2017) Risk factors of proximal junctional kyphosis after multilevel fusion surgery: more than 2 years follow-up data. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 60:174–180. https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2016.0707.014
Zhao J, Yang M, Yang Y, Yin X, Yang C, Li L, Li M (2018) Proximal junctional kyphosis in adult spinal deformity: a novel predictive index. Eur Spine J 27:2303–2311. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-018-5514-3
Kim HJ, Iyer S (2016) Proximal junctional kyphosis. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 24:318–326. https://doi.org/10.5435/jaaos-d-14-00393
Maruo K, Ha Y, Inoue S, Samuel S, Okada E, Hu SS, Deviren V, Burch S, William S, Ames CP, Mummaneni PV, Chou D, Berven SH (2013) Predictive factors for proximal junctional kyphosis in long fusions to the sacrum in adult spinal deformity. Spine 38:E1469–1476. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e3182a51d43
Ohba T, Ebata S, Oba H, Koyama K, Haro H (2018) Correlation between postoperative distribution of lordosis and reciprocal progression of thoracic kyphosis and occurrence of proximal junctional kyphosis following surgery for adult spinal deformity. Clin Spine Surg 31:E466–e472. https://doi.org/10.1097/bsd.0000000000000702
Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, Cho SK, Pahys JM, Zebala LP, Dorward IG, Cho W, Baldus C, Hill BW, Kang MM (2013) Proximal junctional kyphosis in primary adult deformity surgery: evaluation of 20 degrees as a critical angle. Neurosurgery 72:899–906. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0b013e31828bacd8
Kim HJ, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, Park MS, Song KS, Piyaskulkaew C, Chuntarapas T (2014) Patients with proximal junctional kyphosis requiring revision surgery have higher postoperative lumbar lordosis and larger sagittal balance corrections. Spine 39:E576–E580. https://doi.org/10.1097/brs.0000000000000246
Hyun SJ, Kim YJ, Rhim SC (2016) Patients with proximal junctional kyphosis after stopping at thoracolumbar junction have lower muscularity, fatty degeneration at the thoracolumbar area. Spine J 16:1095–1101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spinee.2016.05.008
Yagi M, King AB, Boachie-Adjei O (2012) Incidence, risk factors, and natural course of proximal junctional kyphosis: surgical outcomes review of adult idiopathic scoliosis. Minimum 5 years of follow-up. Spine 37:1479–1489. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e31824e4888
Fortin M, Lazary A, Varga PP, Battie MC (2017) Association between paraspinal muscle morphology, clinical symptoms and functional status in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis. Eur Spine J. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-017-5228-y
Silva FE, Lenke LG (2010) Adult degenerative scoliosis: evaluation and management. Neurosurg Focus 28:E1. https://doi.org/10.3171/2010.1.focus09271
Schwab F, Ungar B, Blondel B, Buchowski J, Coe J, Deinlein D, DeWald C, Mehdian H, Shaffrey C, Tribus C, Lafage V (2012) Scoliosis research society-Schwab adult spinal deformity classification: a validation study. Spine 37:1077–1082. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e31823e15e2
Cho KJ, Suk SI, Park SR, Kim JH, Choi SW, Yoon YH, Won MH (2009) Arthrodesis to L5 versus S1 in long instrumentation and fusion for degenerative lumbar scoliosis. Eur Spine J 18:531–537. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-009-0883-2
Iizuka Y, Iizuka H, Mieda T, Tajika T, Yamamoto A, Takagishi K (2016) Epidemiology and associated radiographic spinopelvic parameters of symptomatic degenerative lumbar scoliosis: are radiographic spinopelvic parameters associated with the presence of symptoms or decreased quality of life in degenerative lumbar scoliosis? Eur Spine J 25:2514–2519. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-015-4256-8
Wang H, Ma L, Yang D, Wang T, Yang S, Wang Y, Wang Q, Zhang F, Ding W (2016) Incidence and risk factors for the progression of proximal junctional kyphosis in degenerative lumbar scoliosis following long instrumented posterior spinal fusion. Medicine 95:e4443–e4443. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000004443
Ogon I, Takebayashi T, Takashima H, Morita T, Yoshimoto M, Terashima Y, Yamashita T (2017) Magnetic resonance spectroscopic analysis of multifidus muscles lipid content and association with spinopelvic malalignment in chronic low back pain. Br J Radiol 90:20160753. https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr.20160753
Jun HS, Kim JH, Ahn JH, Chang IB, Song JH, Kim TH, Park MS, Chan Kim Y, Kim SW, Oh JK, Yoon DH (2016) The effect of lumbar spinal muscle on spinal sagittal alignment: evaluating muscle quantity and quality. Neurosurgery 79:847–855. https://doi.org/10.1227/neu.0000000000001269
Pourtaheri S, Issa K, Lord E, Ajiboye R, Drysch A, Hwang K, Faloon M, Sinha K, Emami A (2016) Paraspinal muscle atrophy after lumbar spine surgery. Orthopedics 39:e209–214. https://doi.org/10.3928/01477447-20160129-07
Kim YJ, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, Rhim S, Kim YW (2007) Is the T9, T11, or L1 the more reliable proximal level after adult lumbar or lumbosacral instrumented fusion to L5 or S1? Spine 32:2653–2661. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e31815a5a9d
Hu P, Yu M, Sun Z, Li W, Jiang L, Wei F, Liu X, Chen Z, Liu Z (2016) Analysis of global sagittal postural patterns in asymptomatic chinese adults. Asian Spine J 10:282–288. https://doi.org/10.4184/asj.2016.10.2.282
Xu L, Qin X, Zhang W, Qiao J, Liu Z, Zhu Z, Qiu Y, Qian BP (2015) Estimation of the ideal lumbar lordosis to be restored from spinal fusion surgery: a predictive formula for chinese population. Spine 40:1001–1005. https://doi.org/10.1097/brs.0000000000000871
Zhang HC, Zhang ZF, Wang ZH, Cheng JY, Wu YC, Fan YM, Wang TH, Wang Z (2017) Optimal pelvic incidence minus lumbar lordosis mismatch after long posterior instrumentation and fusion for adult degenerative scoliosis. Orthopa Surg 9:304–310. https://doi.org/10.1111/os.12343
Annis P, Lawrence BD, Spiker WR, Zhang Y, Chen W, Daubs MD, Brodke DS (2014) Predictive factors for acute proximal junctional failure after adult deformity surgery with upper instrumented vertebrae in the thoracolumbar spine. Evid Based Spine Care J 5:160–162. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0034-1386755
Nicholls FH, Bae J, Theologis AA, Eksi MS, Ames CP, Berven SH, Burch S, Tay BK, Deviren V (2017) Factors associated with the development of and revision for proximal junctional kyphosis in 440 consecutive adult spinal deformity patients. Spine 42:1693–1698. https://doi.org/10.1097/brs.0000000000002209
Mendoza-Lattes S, Ries Z, Gao Y, Weinstein SL (2011) Proximal junctional kyphosis in adult reconstructive spine surgery results from incomplete restoration of the lumbar lordosis relative to the magnitude of the thoracic kyphosis. Iowa Orthop J 31:199–206
Wang T, Zhao Y, Liang Y, Zhang H, Wang Z, Wang Y (2018) Risk factor analysis of proximal junctional kyphosis after posterior osteotomy in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. J Neurosurg Spine 29:75–80. https://doi.org/10.3171/2017.11.spine17228
Kim HJ, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, Park MS, Ahmad A, Song KS, Piyaskulkaew C, Hershman S, Fogelson J, Mesfin A (2013) Proximal junctional kyphosis results in inferior SRS pain subscores in adult deformity patients. Spine 38:896–901. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e3182815b42
Hassanzadeh H, Gupta S, Jain A, El Dafrawy MH, Skolasky RL, Kebaish KM (2013) Type of anchor at the proximal fusion level has a significant effect on the incidence of proximal junctional kyphosis and outcome in adults after long posterior spinal fusion. Spine Deform 1:299–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jspd.2013.05.008
Hart RA, Prendergast MA, Roberts WG, Nesbit GM, Barnwell SL (2008) Proximal junctional acute collapse cranial to multi-level lumbar fusion: a cost analysis of prophylactic vertebral augmentation. Spine J 8:875–881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spinee.2008.01.015
Cammarata M, Aubin C-É, Wang X, Mac-Thiong J-M (2014) Biomechanical risk factors for proximal junctional kyphosis: a detailed numerical analysis of surgical instrumentation variables. Spine 39:E500–E507. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0000000000000222
Battista C, Wild C, Kreul S, Albert M (2018) Prevention of proximal junctional kyphosis and failure using sublaminar bands in a hybrid construct in pediatric kyphosis deformity. Int J Spine Surg 12:644–649. https://doi.org/10.14444/5080
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, L., Zeng, Y., Chen, Z. et al. Degenerative lumbar scoliosis patients with proximal junctional kyphosis have lower muscularity, fatty degeneration at the lumbar area. Eur Spine J 30, 1133–1143 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-020-06394-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-020-06394-8