Abstract
Purpose
The altered anatomic positions of important structures adjacent to the vertebrae in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS) patients have been comprehensively investigated by previous radiographic studies. However, no study has evaluated the altered position of left subclavian artery (SA) in these patients. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the altered position of left subclavian artery in AIS patients with a double thoracic curve pattern.
Methods
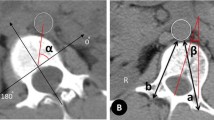
Nineteen Lenke type 2 AIS patients and thirteen normal teenagers were included in this study. Axial computed tomography images at T2 and T3 levels were obtained in all these subjects to evaluate the subclavian artery-vertebral angle (SAVA, defined as 0° when the artery was located directly lateral to the left and 180° when directly lateral to the right) and subclavian artery-vertebral distance (SAVD, the shortest distance between the artery and vertebral body). The percentage of left subclavian arteries at potential risk of injury from excessively long pedicle screws was calculated.
Results
The SAVA was significantly larger in AIS patients than that in normal teenagers at both T2 and T3 levels (P < 0.05) while the SAVD was significantly smaller in AIS patients compared with normal teenagers at both T2 and T3 levels (P < 0.05). The left SA was at potential risk of injury from excessively long left pedicle screws in 6 (31.6 %) AIS patients at T2 level and in 10 (52.6 %) patients at T3 level. The patients with risk of left SA injury had larger proximal thoracic (PT) and larger AVT of PT curve when compared with those without. No left SA was at potential risk of injury from excessively long left pedicle screws in normal teenagers.
Conclusions
The left SA is located much closer to the vertebrae in the proximal thoracic curve of Lenke type 2 AIS patients when compared with normal teenagers. The spine surgeons should be aware of such altered position of left SA and choose appropriate pedicle length to avoid anterior cortical penetration in Lenke type 2 AIS patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Catan H, Buluc L, Anik Y, Ayyildiz E, Sarlak AY (2007) Pedicle morphology of the thoracic spine in preadolescent idiopathic scoliosis: magnetic resonance supported analysis. Eur Spine J 16:1203–1208
Jiang J, Mao S, Zhao Q, Liu Z, Qian B, Zhu F, Qiu Y (2012) Different proximal thoracic curve patterns have different relative positions of esophagus to spine in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a computed tomography study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 37:193–199
Krismer M, Bauer R, Sterzinger W (1992) Scoliosis correction by Cotrel–Dubousset instrumentation. The effect of derotation and three dimensional correction. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 17:S263–S269
Kuklo TR, Lehman RA Jr, Lenke LG (2005) Structures at risk following anterior instrumented spinal fusion for thoracic adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Spinal Disord Tech 18(Suppl):S58–S64
Kuklo TR, Potter BK, Schroeder TM, O’Brien MF (2006) Comparison of manual and digital measurements in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 31:1240–1246
Liljenqvist UR, Allkemper T, Hackenberg L, Link TM, Steinbeck J, Halm HF (2002) Analysis of vertebral morphology in idiopathic scoliosis with use of magnetic resonance imaging and multiplanar reconstruction. J Bone Joint Surg Am 84-A:359–368
Liljenqvist UR, Halm HF, Link TM (1997) Pedicle screw instrumentation of the thoracic spine in idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 22:2239–2245
Milbrandt TA, Sucato DJ (2007) The position of the aorta relative to the spine in patients with left thoracic scoliosis: a comparison with normal patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 32:E348–E353
Qian B, Jiang J, Zhu F, Zhu Z, Liu Z, Qiu Y (2013) How is the trachea at risk of injury from pedicle screw insertion in proximal thoracic curve of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patients? Eur Spine J 22:338–344
Qiu Y, He YX, Wang B, Zhu F, Wang WJ (2007) The anatomical relationship between the aorta and the thoracic vertebral bodies and its importance in the placement of the screw in thoracoscopic correction of scoliosis. Eur Spine J 16:1367–1372
Sarlak AY, Buluç L, Sarisoy HT, Memişoğlu K, Tosun B (2008) Placement of pedicle screws in thoracic idiopathic scoliosis: a magnetic resonance imaging analysis of screw placement relative to structures at risk. Eur Spine J 17:657–662
Sarwahi V, Suggs W, Wollowick AL, Kulkarni PM, Lo Y, Amaral TD, Thornhill B (2014) Pedicle screws adjacent to the great vessels or viscera: a study of 2132 pedicle screws in pediatric spine deformity. J Spinal Disord Tech 27:64–69
Sucato DJ, Duchene C (2003) The position of the aorta relative to the spine: a comparison of patients with and without idiopathic scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 85-A:1461–1469
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the support from Maternal and Child Health Project of Health Department of Jiangsu Province (F201353).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, J., Qian, Bp., Qiu, Y. et al. The potential risk of left subclavian artery injury from excessively long thoracic pedicle screws placed in the proximal thoracic regions of Lenke type 2 adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patients and normal teenagers: an anatomical study. Eur Spine J 25, 3282–3287 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-016-4569-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-016-4569-2