Abstract
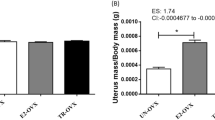
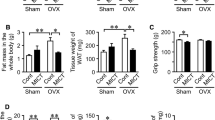
Estrogen deficiency intensifies sarcopenia by activation of inflammatory and oxidative pathways. Aerobic exercise training and antioxidant/inflammatory supplements might reverse such outcomes or decline the degenerative pathway. Thus, we investigated the impact of aerobic training and crocin (CRO) consumption on skeletal muscle MuRf-1 and plasma antioxidant and inflammatory statues in ovariectomized (OVX) rat models fed on a high-fat diet (HFD). 72 female Wistar rats (200 ± 20 gr) were randomly divided into 9 groups: (1) non-OVX + standard chow (nOVX + SC), (2) nOVX + HFD, (3) high-intensity continuous training (HICT) + OVX + HFD + CRO, (4) HICT + OVX + HFD, (5) moderate-intensity continuous training (MICT) + OVX + HFD + CRO, (6) MICT + OVX + HFD, (7) OVX + HFD + CRO, (8) OVX + SC, and (9) OVX + HFD. The OVX rats underwent surgery for menopause model induction. Immediately after the ovariectomy, rats were fed either by HFD or SC. Seven weeks later, exercise training (HICT/MICT; 8-week, 5-session, 12–30 m/min or 12–21 m/min) and CRO consumption (60 mg/kg) intervention per sessions were performed. The plasma levels of SOD, GSH, and TNF-α and muscle levels of MuRf-1 were assessed using the ELISA method. A two-tailed t-test and one-way ANOVA were applied for data analysis. There was not a significant difference in the protein levels of MuRF1 as the CRO caused an increase in the TNF-α levels as compared to the control. HICT significantly decreased SOD levels as compared to the control, CRO, and MICT. There was no significant difference in GSH levels between intervention arms. Exercise training and CRO supplementations did not make any significant changes in muscle mass regulation factors in the OVX rat model.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Abd El-Kader SM, Al-Jiffri OH (2019) Impact of aerobic versus resisted exercise training on systemic inflammation biomarkers and quality of life among obese post-menopausal women. Afr Health Sci 19(4):2881–2891
Boskabady MH, Farkhondeh T (2016) Antiinflammatory, antioxidant, and immunomodulatory effects of Crocus sativus L. and its main constituents. Phytother Res 30(7):1072–1094
Bupha-Intr T, Wattanapermpool J (2004) Cardioprotective effects of exercise training on myofilament calcium activation in ovariectomized rats. J Appl Physiol 96(5):1755–1760
Cao P-C et al (2014) Preventive effect of crocin on osteoporosis in an ovariectomized rat model. Evid Based Complementary Altern Med 2014
Costamagna D et al (2015) Role of inflammation in muscle homeostasis and myogenesis. Mediators Inflamm 2015
Davis SR et al (2012) Understanding weight gain at menopause. Climacteric 15(5):419–429
Droge W (2002) Free radicals in the physiological control of cell function. Physiol Rev 82(1):47–95
Emamian Rostami M, Fathi R, Nasiri K (2021) The impacts of an eight-week moderate aerobic exercise training on some gene expression involved in cholesterol metabolism in ovariectomized rats. Sport Sci Health 17(2):383–392
Fathi R et al (2020) Exercise protects against ethanol-induced damage in rat heart and liver through the inhibition of apoptosis and activation of Nrf2/Keap-1/HO-1 pathway. Life Sci 256:117958
Foster-Schubert KE et al (2012) Effect of diet and exercise, alone or combined, on weight and body composition in overweight-to-obese postmenopausal women. Obesity 20(8):1628–1638
Friedenreich CM et al (2016) Effects of exercise on markers of oxidative stress: an ancillary analysis of the Alberta Physical Activity and Breast Cancer Prevention Trial. BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med 2(1):e000171
Ghorbanzadeh V et al (2016) Protective effect of crocin and voluntary exercise against oxidative stress in the heart of high-fat diet-induced type 2 diabetic rats. Physiol Int 103(4):459–468
Hazman Ö, Aksoy L, Büyükben A (2016) Effects of crocin on experimental obesity and type-2 diabetes. Turk J Med Sci 46(5):1593–1602
Huang C-Y et al (2016) Antiapoptotic effect of exercise training on ovariectomized rat hearts. J Appl Physiol 121(2):457–465
Hussain MA et al (2021) Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of crocin ameliorate doxorubicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2021
Hyatt H et al (2019) Mitochondrial dysfunction induces muscle atrophy during prolonged inactivity: a review of the causes and effects. Arch Biochem Biophys 662:49–60
Jitmana R et al (2019) Role of cardiac mast cells in exercise training-mediated cardiac remodeling in angiotensin II-infused ovariectomized rats. Life Sci 219:209–218
Kander MC, Cui Y, Liu Z (2017) Gender difference in oxidative stress: a new look at the mechanisms for cardiovascular diseases. J Cell Mol Med 21(5):1024–1032
Karolkiewicz J et al (2009) Response of oxidative stress markers and antioxidant parameters to an 8-week aerobic physical activity program in healthy, postmenopausal women. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 49(1):e67–e71
Khalafi M, Malandish A, Rosenkranz SK (2021) The impact of exercise training on inflammatory markers in postmenopausal women: a systemic review and meta-analysis. Exp Gerontol 111398
Kim HJ, Lee WJ (2017) Low-intensity aerobic exercise training: inhibition of skeletal muscle atrophy in high-fat-diet-induced ovariectomized rats. J Exerc Nutr Biochem 21(3):19
Krishnaswamy V, Alugoju P, Periyasamy L (2020) Effect of short-term oral supplementation of crocin on age-related oxidative stress, cholinergic, and mitochondrial dysfunction in rat cerebral cortex. Life Sci 263:118545
Ku B-J et al (2021) Effect of regular taekwondo self-defense training on oxidative stress and inflammation markers in postmenopausal women in Healthcare. Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute.
Lebon J et al (2014) Additive effects of isoflavones and exercise training on inflammatory cytokines and body composition in overweight and obese postmenopausal women: a randomized controlled trial. Menopause 21(8):869–875
Li X et al (2020) Combined intervention of 17β-estradiol and treadmill training ameliorates energy metabolism in skeletal muscle of female ovariectomized mice. Climacteric 23(2):192–200
Lin Y-Y et al (2019) Antiapoptotic and mitochondrial biogenetic effects of exercise training on ovariectomized hypertensive rat hearts. J Appl Physiol 126(6):1661–1672
Lovejoy J et al (2008) Increased visceral fat and decreased energy expenditure during the menopausal transition. Int J Obes 32(6):949–958
Ludgero-Correia A Jr et al (2012) Effects of high-fat diet on plasma lipids, adiposity, and inflammatory markers in ovariectomized C57BL/6 mice. Nutrition 28(3):316–323
Macêdo Santiago LÂ et al (2018) Effects of resistance training on immunoinflammatory response, TNF-alpha gene expression, and body composition in elderly women. J Aging Res 2018
Manolopoulos K, Karpe F, Frayn K (2010) Gluteofemoral body fat as a determinant of metabolic health. Int J Obes 34(6):949–959
Massafra C et al (2002) Gender-related differences in erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase activity in healthy subjects. Clin Endocrinol 57(5):663–667
Mohamed-Ali V et al (1997) Subcutaneous adipose tissue releases interleukin-6, but not tumor necrosis factor-α, in vivo. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 82(12):4196–4200
Monteiro-Junior RS et al (2018) Effect of exercise on inflammatory profile of older persons: systematic review and meta-analyses. J Phys Act Health 15(1):64–71
Narumi M et al (2018) Oxidative stress in the visceral fat is elevated in postmenopausal women with gynecologic cancer. J Womens Health (larchmt) 27(1):99–106
Nikawa T, Ulla A, Sakakibara I (2021) Polyphenols and their effects on muscle atrophy and muscle health. Molecules 26(16):4887
Papavagelis C et al (2018) Dietary patterns, Mediterranean diet and obesity in postmenopausal women. Maturitas 110:79–85
Poehlman ET, Toth MJ, Gardner AW (1995) Changes in energy balance and body composition at menopause: a controlled longitudinal study. Ann Intern Med 123(9):673–675
Sardeli AV et al (2018) Effect of resistance training on inflammatory markers of older adults: a meta-analysis. Exp Gerontol 111:188–196
Seo DY et al (2012) Aged garlic extract enhances exercise-mediated improvement of metabolic parameters in high fat diet-induced obese rats. Nurs Res Pract 6(6):513–519
Seo DY, Hwang BG (2020) Effects of exercise training on the biochemical pathways associated with sarcopenia. Phys Act Nutr 24(3):32
Steckling FM et al (2019) High-intensity interval training improves inflammatory and adipokine profiles in postmenopausal women with metabolic syndrome. Arch Physiol Biochem 125(1):85–91
Tayebi SM et al (2019) Plasma retinol-binding protein-4 and tumor necrosis factor-α are reduced in postmenopausal women after combination of different intensities of circuit resistance training and Zataria supplementation. Sport Sci Health 15(3):551–558
Thomas DR (2007) Loss of skeletal muscle mass in aging: examining the relationship of starvation, sarcopenia and cachexia. Clin Nutr 26(4):389–399
van Gemert WA et al (2015) Quality of life after diet or exercise-induced weight loss in overweight to obese postmenopausal women: the SHAPE-2 randomised controlled trial. PLoS ONE 10(6):e0127520
Vincent J, Inassi J (2020) Comparison of oxidative stress between premenopausal and postmenopausal women. Natl J Physiol Pharm Pharmacol 10(05)
Wahrenberg H, Wennlund A, Hoffstedt J (2002) Increased adipose tissue secretion of interleukin-6, but not of leptin, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 or tumour necrosis factor alpha, in Graves’ Hyperthyroidism. Eur J Endocrinol 146(5):607–611
Wang Y et al (2018) Superoxide dismutases: dual roles in controlling ROS damage and regulating ROS signaling. J Cell Biol 217(6):1915–1928
Woods JA, Vieira VJ, Keylock KT (2009) Exercise, inflammation, and innate immunity. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am 29(2):381–393
Zacarías-Flores M et al (2018) Relationship between oxidative stress and muscle mass loss in early postmenopause: an exploratory study. Endocrinología, Diabetes y Nutrición (English ed.) 65(6):328–334
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design, material preparation, and data analysis. Sh Kh wrote the first draft of the manuscript, and H R and E T reviewed the manuscript. All authors approved the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was not supported by any funding.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The article does not contain any studies involving human participants performed by any of the authors. All applicable institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were approved by the ethical committee of the Science and Research Branch, Mazandaran University (IR.UMZ.REC.1400.026). All experimental procedures were performed on the animals according to the guidelines of the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals by the National Institutes of Health (USA).
Informed consent
For this type of study, informed consent is not required.
Consent for publication
For this type of study, consent for publication is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kheradmand, S., Rajabi, H. & Talebi-Garakani, E. The impact of aerobic exercise training and crocin consumption on MuRf-1 level in skeletal muscle in high-fat fed ovariectomized rat models. Comp Clin Pathol 32, 941–948 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-023-03505-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-023-03505-x