Abstract
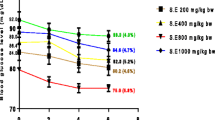
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a growing health concern worldwide. Many traditional treatments have been recommended in the alternative system of medicine for treatment of DM. Pistacia atlantica and Amygdalus scoparia have a long history as a medicinal plant since the ancient times. The present study evaluated the differential effects of N-hexane extraction of these plants on the blood glucose concentration and the pathology of the pancreas in diabetic mice. DM was induced in 40 out of 50 adult female mice, using intraperitoneal injection of 60 mg/kg BW streptozotocin. The diabetic mice were assigned into four groups, three of which were treated with extract of garlic and P. atlantica, A. scoparia, and glibenclamide (200 mg/kg) for 15 days and the mice of the fourth group, as the untreated group, received ordinary diet. Ten nondiabetic mice remained as the normal control group. The results of this study indicate that these plants were able to reduce blood glucose significantly compared with the control diabetic group (P < 0.05). The P. atlantica extract was found to be more effective than A. scoparia extract. Histopathologically, streptozotocin (STZ) resulted in severe necrotic changes in the pancreatic islets, especially in the central area of the islets. Tissue sections of the pancreas in the treated mice demonstrated improved regeneration of B cells and increased size of pancreatic islets. The present study indicated a significant anti-hyperglycemic effect of P. atlantica, A. scoparia, and supported their traditional usage in the treatment of DM.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abo KA, Fred-Jaiyesimi AA, Jaiyesimi AEA (2008) Ethnobotanical studies of medicinal plants used in the management of diabetes mellitus in South Western Nigeria. J Ethnopharmacol 115:67–71
Dallak M, Al-Khateeb M, Al-Hashem F, Bashir N, Abbas M, Elessa R et al (2009) In vivo, acute, normo-hypoglycemic, antihyperglycemic, insulinotropic actions of orally administered ethanol extract of Citrullus colocynthis (L.) schrab pulp. Am J Biochem Biotech 5:118–125
Dedoussis GVZ, Kaliora AC, Psarras S, Chiou A, Mylona A, Papadapoulos NG, Andrikopoulos NK (2004) Antiatherogenic effect of Pistacia lentiscus via GSH restoration and down regulation of CD36 mRNA expression. Atherosclerosis 174:293–303
Eddouks M, Lemhadri A, Michel JB (2004) Caraway and caper: potential anti-hyperglycaemic plants in diabetic rats. J Ethnopharmacol 94:143–148
Eidia A, Eidib M, Esmaeilia E (2006) Antidiabetic effect of garlic (Allium sativum L.) in normal and streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Phytomedicine 13:624–629
Farhoosh R, Tavakoli J (2008) Physicochemical properties of the kernel oil from Amygdalus scoparia growing wild in Iran. J Food Lipids 15(4):433–443
Ghalem BR, Mohamed B (2009) Essential oil from gum of Pistacia atlantica Desf.: screening of antimicrobial activity. African. J Pharm Pharmacol 3(3):087–091
Giner-Larza EM, Manez S, Giner-Pons RM, Recio MC, Rios JL (2000) On the anti-inflammatory and anti-phospholipase A2 activity of extracts from lanostane-rich species. J Ethnopharmacol 73:61–69
Hamdan II, Afifi FU (2004) Studies on the in vitro and in vivo hypoglycemic activities of some medicinal plants used in treatment of diabetes in Jordanian traditional medicine. J Ethnopharmacol 93:117–121
Hashemnia M, Oryan A, Hamidi AR, Mohammadalipour A (2012) Blood glucose levels and pathology of organs in alloxan-induced diabetic rats treated with hydro-ethanol extracts of Allium sativum and Capparis spinosa. Afr J Pharma Pharmacol 6(21):1559–1564
Jelodar GA, Maleki M, Motadayen SS (2005) Effect of fenugreek, onion and garlic on blood glucose and histopathology of pancreas of alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Indian J Med Sci 52:54–69
Merzouk H, Madani S, Chabane D (2000) Time course of changes in serum glucose, insulin, lipids and tissue lipase activities in macrosomic offspring of rats with streptozotocin- induced diabetes. Clin Sci 98:21–30
Mohini P, Subhash P, Manohar P, Abhijit T, Vijay N (2012) Effect of thespesone-vanadium complex in alloxan induced diabetic rats. Afr J Pharm Pharmacol 6:692–697
Mukherjee PK, Maiti K, Mukherjee K, Houghton PJ (2006) Leads from Indian medicinal plants with hypoglycemic potentials. J Ethnopharmacol 106:1–28
Oryan A, Hashemnia M, Hamidi AR, Mohammadalipour A (2014) Effects of hydro-ethanol extract of Citrullus colocynthis on blood glucose levels and pathology of organs in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Asian Pac J Trop Dis 4(2):125–130
Pari L, Umamaheswari J (2000) Antihyperglycaemic activity of Musa sapientum flowers: effect on lipid peroxidation in alloxan diabetic rats. Phytother Res 14:1–3
Rajalakshmi M, Eliza J, Priya CE, Nirmala A, Daisy P (2009) Anti-diabetic properties of Tinospora cordifolia stem extracts on streptozotocin- induced diabetic rats. Afr J Pharm Pharmacol 3:171–180
Saffarzadeh A, Vincze L, Csapo J (1999) Determination of the chemical composition of acorn (Quercus branti), Pistacia atlantica and Pistacia khinjuk seed as non-conventional feedstuffs. Acta Agric Kaposvar 3(3):59–69
Tang LQ, Wei W, Chen LM, Liu S (2006) Effects of berberine on diabetes induced by alloxan and a high-fat/high-cholesterol diet in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 108:109–115
Thomson M, Al-Amin ZM, Al-Qattan KK, Shaban LH, Ali M (2007) Anti-diabetic and hypolipidaemic properties of garlic (Allium sativum) in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Int J Diabetes Metabolism 15:108–115
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hashemnia, M., Nikousefat, Z. & Yazdani-Rostam, M. Antidiabetic effect of Pistacia atlantica and Amygdalus scoparia in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Comp Clin Pathol 24, 1301–1306 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-015-2068-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-015-2068-1